Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Synovial Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 30916045
- PMCID: PMC6448456
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.915451
Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Synovial Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
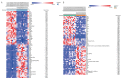
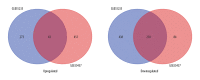
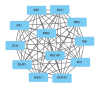
BACKGROUND Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has a high prevalence in the elderly population. The genes and pathways in the inflamed synovium in patients with RA are poorly understood. This study aimed to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) linked to the progression of synovial inflammation in RA using bioinformatics analysis. MATERIAL AND METHODS Gene expression profiles of datasets GSE55235 and GSE55457 were acquired from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. DEGs were identified using Morpheus software, and co-expressed DEGs were identified with Venn diagrams. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks were assembled with Cytoscape software and separated into subnetworks using the Molecular Complex Detection (MCODE) algorithm. The functions of the top module were assessed using the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID). The Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis were performed. RESULTS DEGs that were upregulated were significantly enhanced in protein binding, the cell cytosol, organization of the extracellular matrix (ECM), regulation of RNA transcription, and cell adhesion. DEGs that were downregulated were associated with control of the immune response, B-cell and T-cell receptor signaling pathway regulation. KEGG pathway analysis showed that upregulated DEGs enhanced pathways associated with the cell adherens junction, osteoclast differentiation, and hereditary cardiomyopathies. Downregulated DEGs were enriched in primary immunodeficiency, cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, and hematopoietic cell lineages. CONCLUSIONS The findings from this bioinformatics network analysis study identified molecular mechanisms and the key hub genes that may contribute to synovial inflammation in patients with RA.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of potential biomarkers for differential diagnosis between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis via integrative genome‑wide gene expression profiling analysis.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jan;19(1):30-40. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9677. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30483789 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis to identify key genes and pathways influencing synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Dec;18(6):5594-5602. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9575. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30365099 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of pivotal genes and pathways in the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis through integrated bioinformatic analysis.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Oct;22(4):3513-3524. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11406. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32945465
-
Identification of hub genes in placental dysfunction and recurrent pregnancy loss through transcriptome data mining: A meta-analysis.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2024 May;63(3):297-306. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2024.01.035. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2024. PMID: 38802191 Review.
-
Effects of dietary curcumin on gene expression: An analysis of transcriptomic data in mice.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Nov;263:155653. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155653. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39426142 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of inflammatory molecular mechanisms between osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis via gene microarrays.Mol Biol Res Commun. 2024;13(4):211-222. doi: 10.22099/mbrc.2024.49924.1963. Mol Biol Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 39315289 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of immune-related diagnostic markers in primary Sjögren's syndrome based on bioinformatics analysis.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Apr;10(8):487. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-1494. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35571446 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of potential hub genes in pulmonary thromboembolism.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jan;23(1):18. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10940. Epub 2021 Oct 30. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 34815770 Free PMC article.
-
Location, location, location: how the tissue microenvironment affects inflammation in RA.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021 Apr;17(4):195-212. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-00570-2. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33526927 Review.
-
Identification of Hub Genes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Bioinformatics Analysis.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 May 22;13:1793-1801. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S245165. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 32547141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grøn KL, Arkema EV, Glintborg B, et al. Risk of serious infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated in routine care with abatacept, rituximab and tocilizumab in Denmark and Sweden. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(3):320–27. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Liu C, Li L, et al. High levels of antibodies to citrullinated alpha-enolase peptide-1 (CEP-1) identify erosions and interstitial lung disease (ILD) in a Chinese rheumatoid arthritis cohort. Clin Immunol. 2019;200:10–15. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

