Regional and Cellular Mapping of Sortilin Immunoreactivity in Adult Human Brain
- PMID: 30914927
- PMCID: PMC6422922
- DOI: 10.3389/fnana.2019.00031
Regional and Cellular Mapping of Sortilin Immunoreactivity in Adult Human Brain
Abstract
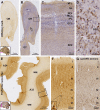
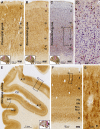
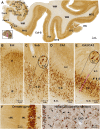
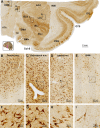
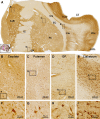
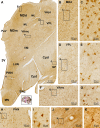
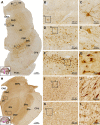
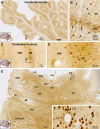
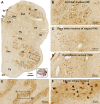
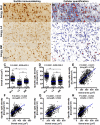
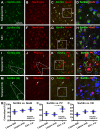
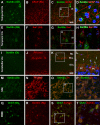
Sortilin is a member of the vacuolar protein sorting 10 protein (VPS10P) domain receptor family, which carries out signal transduction and protein transport in cells. Sortilin serves as the third, G-protein uncoupled, receptor of neurotensin that can modulate various brain functions. More recent data indicate an involvement of sortilin in mood disorders, dementia and Alzheimer-type neuropathology. However, data regarding the normal pattern of regional and cellular expression of sortilin in the human brain are not available to date. Using postmortem adult human brains free of neuropathology, the current study determined sortilin immunoreactivity (IR) across the entire brain. Sortilin IR was broadly present in the cerebrum and subcortical structures, localizing to neurons in the somatodendritic compartment, but not to glial cells. In the cerebrum, sortilin IR exhibited differential regional and laminar patterns, with pyramidal, multipolar and polymorphic neurons in cortical layers II-VI, hippocampal formation and amygdaloid complex more distinctly labeled relative to GABAergic interneurons. In the striatum and thalamus, numerous small-to-medium sized neurons showed light IR, with a small group of large sized neurons heavily labeled. In the midbrain and brainstem, sortilin IR was distinct in neurons at the relay centers of descending and ascending neuroanatomical pathways. Dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, cholinergic neurons in the basal nuclei of Meynert and noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus co-expressed strong sortilin IR in double immunofluorescence. In comparison, sortilin IR was weak in the olfactory bulb and cerebellar cortex, with the mitral and Purkinje cells barely visualized. A quantitative analysis was carried out in the lateral, basolateral, and basomedial nuclei of the amygdaloid complex, as well as cortical layers II-VI, which established a positive correlation between the somal size and the intensity of sortilin IR among labeled neurons. Together, the present study demonstrates a predominantly neuronal expression of sortilin in the human brain with substantial regional and cell-type variability. The enriched expression of sortilin in pyramidal, dopaminergic, noradrenergic and cholinergic neurons suggests that this protein may be particularly required for signal transduction, protein trafficking and metabolic homeostasis in populations of relatively large-sized projective neurons.
Keywords: Vps10p; dementia; neurodegenerative diseases; neuronal mapping; neuropeptides; protein trafficking.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distribution of NTS3 receptor/sortilin mRNA and protein in the rat central nervous system.J Comp Neurol. 2003 Jul 7;461(4):483-505. doi: 10.1002/cne.10708. J Comp Neurol. 2003. PMID: 12746864
-
A detailed mapping of the histamine H(3) receptor and its gene transcripts in rat brain.Neuroscience. 2002;114(1):173-93. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00135-5. Neuroscience. 2002. PMID: 12207964
-
Calcium-binding proteins in the human developing brain.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2002;165:III-IX, 1-92. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12236093 Review.
-
Sortilin Fragments Deposit at Senile Plaques in Human Cerebrum.Front Neuroanat. 2017 Jun 7;11:45. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00045. eCollection 2017. Front Neuroanat. 2017. PMID: 28638323 Free PMC article.
-
Post mortem studies in Parkinson's disease--is it possible to detect brain areas for specific symptoms?J Neural Transm Suppl. 1999;56:1-29. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6360-3_1. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1999. PMID: 10370901 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of the Excitatory Postsynaptic Scaffolding Protein, Shank3, in Human Brain: Effect of Age and Alzheimer's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Aug 24;13:717263. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.717263. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34504419 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Sortilin Proteopathy Relative to β-Amyloid and Tau in Aged and Alzheimer's Disease Human Brains.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 May 12;12:93. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.00093. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32477092 Free PMC article.
-
Intervention of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Other Neurotrophins in Adult Neurogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1331:95-115. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-74046-7_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34453295 Review.
-
RIP3/MLKL-mediated neuronal necroptosis induced by methamphetamine at 39°C.Neural Regen Res. 2020 May;15(5):865-874. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.268902. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31719251 Free PMC article.
-
Early Dendritic Dystrophy in Human Brains With Primary Age-Related Tauopathy.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Dec 7;12:596894. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.596894. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33364934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen J. L., Schrøder T. J., Christensen S., Strandbygård D., Pallesen L. T., García-Alai M. M., et al. (2014). Identification of the first small-molecule ligand of the neuronal receptor sortilin and structure determination of the receptor-ligand complex. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 70(Pt 2), 451–460. 10.1107/S1399004713030149 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

