Trkb-IP3 Pathway Mediating Neuroprotection in Rat Hippocampal Neuronal Cell Culture Following Induction of Kainic Acid
- PMID: 30914877
- PMCID: PMC6422567
- DOI: 10.21315/mjms2018.25.6.4
Trkb-IP3 Pathway Mediating Neuroprotection in Rat Hippocampal Neuronal Cell Culture Following Induction of Kainic Acid
Abstract
Background: Following brain injury, development of hippocampal sclerosis often led to the temporal lobe epilepsy which is sometimes resistant to common anti-epileptic drugs. Cellular and molecular changes underlying epileptogenesis in animal models were studied, however, the underlying mechanisms of kainic acid (KA) mediated neuronal damage in rat hippocampal neuron cell culture alone has not been elucidated yet.
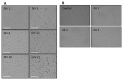
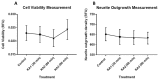
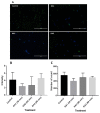
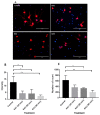
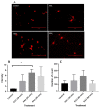
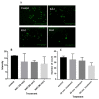
Methods: Embryonic day 18 (E-18) rat hippocampus neurons were cultured with poly-L-lysine coated glass coverslips. Following optimisation, KA (0.5 μM), a chemoconvulsant agent, was administered at three different time-points (30, 60 and 90 min) to induce seizure in rat hippocampal neuronal cell culture. We examined cell viability, neurite outgrowth density and immunoreactivity of the hippocampus neuron culture by measuring brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), γ-amino butyric acid A (GABAA) subunit α-1 (GABRA1), tyrosine receptor kinase B (TrkB), and inositol trisphosphate receptor (IP3R/IP3) levels.
Results: The results revealed significantly decreased and increased immunoreactivity changes in TrkB (a BDNF receptor) and IP3R, respectively, at 60 min time point.
Conclusion: The current findings suggest that TrkB and IP3 could have a neuroprotective role which could be a potential pharmacological target for anti-epilepsy drugs.
Keywords: GABAA receptor; IP3 & BDNF-TrkB receptor; epilepsy; kainic acid; rat hippocampal neuron culture.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BDNF, and full length and truncated TrkB expression in the hippocampus of the rat following kainic acid excitotoxic damage. Evidence of complex time-dependent and cell-specific responses.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998 Aug 31;59(2):154-64. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(98)00156-9. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998. PMID: 9729353
-
TrkB-Shc Signaling Protects against Hippocampal Injury Following Status Epilepticus.J Neurosci. 2019 Jun 5;39(23):4624-4630. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2939-18.2019. Epub 2019 Mar 29. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30926745 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine protects neurons from kainic acid-induced excitotoxicity by activating BDNF signaling.Neurochem Int. 2019 Oct;129:104493. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2019.104493. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Neurochem Int. 2019. PMID: 31220473
-
Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and the BDNF Receptor, TrkB.In: Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Olsen RW, Delgado-Escueta AV, editors. Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies [Internet]. 4th edition. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012. In: Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Olsen RW, Delgado-Escueta AV, editors. Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies [Internet]. 4th edition. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2012. PMID: 22787630 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Glutamate receptor antibodies in neurological diseases: anti-AMPA-GluR3 antibodies, anti-NMDA-NR1 antibodies, anti-NMDA-NR2A/B antibodies, anti-mGluR1 antibodies or anti-mGluR5 antibodies are present in subpopulations of patients with either: epilepsy, encephalitis, cerebellar ataxia, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and neuropsychiatric SLE, Sjogren's syndrome, schizophrenia, mania or stroke. These autoimmune anti-glutamate receptor antibodies can bind neurons in few brain regions, activate glutamate receptors, decrease glutamate receptor's expression, impair glutamate-induced signaling and function, activate blood brain barrier endothelial cells, kill neurons, damage the brain, induce behavioral/psychiatric/cognitive abnormalities and ataxia in animal models, and can be removed or silenced in some patients by immunotherapy.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014 Aug;121(8):1029-75. doi: 10.1007/s00702-014-1193-3. Epub 2014 Aug 1. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2014. PMID: 25081016 Review.
Cited by
-
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against CMS-induced depression-like behaviors in mice via regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 and TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathways.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020 May;41(5):612-619. doi: 10.1038/s41401-019-0317-6. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020. PMID: 31796867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soukupová M, Binaschi A, Falcicchia C, Zucchini S, Roncon P, Palma E, et al. Impairment of GABA release in the hippocampus at the time of the first spontaneous seizure in the pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Exp Neurol. 2014;257:39–49. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.04.014. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
