SALL4 induces radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the ATM/Chk2/p53 pathway
- PMID: 30907073
- PMCID: PMC6488116
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2056
SALL4 induces radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via the ATM/Chk2/p53 pathway
Abstract
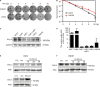
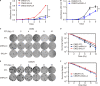
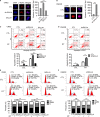
Radiotherapy is the mainstay and primary curative treatment modality in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), whose efficacy is limited by the development of intrinsic and acquired radioresistance. Thus, deciphering new molecular targets and pathways is essential for enhancing the radiosensitivity of NPC. SALL4 is a vital factor in the development and prognosis of various cancers, but its role in radioresistance remains elusive. This study aimed to explore the association of SALL4 expression with radioresistance of NPC. It was revealed that SALL4 expression was closely correlated with advanced T classification of NPC patients. Inhibition of SALL4 reduced proliferation and sensitized cells to radiation both in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, SALL4 silencing increased radiation-induced DNA damage, apoptosis, and G2/M arrest in CNE2 and CNE2R cells. Moreover, knockdown of SALL4 impaired the expression of p-ATM, p-Chk2, p-p53, and anti-apoptosis protein Bcl-2, while pro-apoptosis protein was upregulated. These findings indicate that SALL4 could induce radioresistance via ATM/Chk2/p53 pathway and its downstream proteins related to apoptosis. Targeting SALL4 might be a promising approach for the development of novel radiosensitizing therapeutic agents for radioresistant NPC patients.
Keywords: SALL4; apoptosis; cell cycle; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; radioresistance.
© 2019 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CHAF1B induces radioresistance by promoting DNA damage repair in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Mar;123:109748. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109748. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31869663
-
In Vivo and In Vitro Effects of ATM/ATR Signaling Pathway on Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Radiosensitivity of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2017 Aug;32(6):193-203. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2017.2212. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2017. PMID: 28820634
-
Long noncoding RNA LINC00173 induces radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via inhibiting CHK2/P53 pathway.Cancer Gene Ther. 2023 Sep;30(9):1249-1259. doi: 10.1038/s41417-023-00634-x. Epub 2023 May 31. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023. PMID: 37258811
-
Epigenetic disruption of cell signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Chin J Cancer. 2011 Apr;30(4):231-9. doi: 10.5732/cjc.011.10080. Chin J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21439244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs involved in chemo- and radioresistance of high-grade gliomas.Tumour Biol. 2013 Aug;34(4):1969-78. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0772-5. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23568705 Review.
Cited by
-
SALL4 promotes cancer stem-like cell phenotype and radioresistance in oral squamous cell carcinomas via methyltransferase-like 3-mediated m6A modification.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Feb 14;15(2):139. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06533-9. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38355684 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of lncRNA UCA1 enhances radiosensitivity in prostate cancer by suppressing EIF4G1 expression via sponging miR-331-3p.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Sep 11;20:449. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01538-8. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32943997 Free PMC article.
-
Riluzole Enhances the Response of Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells to Ionizing Radiation via ATM/P53 Signalling Pathway.J Cancer. 2020 Mar 4;11(11):3089-3098. doi: 10.7150/jca.41217. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32231713 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-Induced DNMT3B Promotes Radioresistance in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Methylation of p53 and p21.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020 Apr 21;17:306-319. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.04.007. eCollection 2020 Jun 26. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020. PMID: 32382655 Free PMC article.
-
EBV LMP1-C terminal binding affibody molecule downregulates MEK/ERK/p90RSK pathway and inhibits the proliferation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in mouse tumor xenograft models.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jan 4;12:1078504. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1078504. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36683690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115‐132. - PubMed
-
- Fu ZT, Guo XL, Zhang SW, et al. Incidence and mortality of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in China, 2014. Chinese journal of oncology. 2018;40:566‐571. - PubMed
-
- Lee AW, Poon YF, Foo W, et al. Retrospective analysis of 5037 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated during 1976‐1985: overall survival and patterns of failure. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;23(2):261‐270. - PubMed
-
- Sweetman D, Munsterberg A. The vertebrate spalt genes in development and disease. Dev Biol. 2006;293(2):285‐293. - PubMed
-
- Masuda S, Suzuki K, Izpisua Belmonte JC. Oncofetal gene SALL4 in aggressive hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

