Activation and counteraction of antiviral innate immunity by KSHV: an Update
- PMID: 30906617
- PMCID: PMC6426151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.07.009
Activation and counteraction of antiviral innate immunity by KSHV: an Update
Abstract
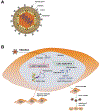
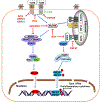
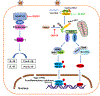
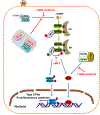
The innate immune responses triggering production of type I interferons and inflammatory cytokines constitute a nonspecific innate resistance that eliminates invading pathogens including viruses. The activation of innate immune signaling through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) is by sensing pathogen-associated molecular patterns derived from viruses. According to their distribution within cells, PRRs are classified into three types of receptors: membrane, cytoplasmic, and nuclear. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), a large DNA virus, replicates in the nucleus. Its genome is protected by capsid proteins during transport in the cytosol. Multiple PRRs are involved in KSHV recognition. To successfully establish latent infection, KSHV has evolved to manipulate different aspects of the host antiviral innate immune responses. This review presents recent advances in our understanding about the activation of the innate immune signaling in response to infection of KSHV. It also reviews the evasion strategies used by KSHV to subvert host innate immune detection for establishing a persistent infection.
Keywords: Evasion strategies; Innate immune response; KSHV; PRRs.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Pattern Recognition Receptors in KSHV Infection.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Mar 20;10(3):85. doi: 10.3390/cancers10030085. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29558453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral Inhibition of PRR-Mediated Innate Immune Response: Learning from KSHV Evasion Strategies.Mol Cells. 2016 Nov 30;39(11):777-782. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2016.0232. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Mol Cells. 2016. PMID: 27871174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and the innate immune system.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Oct;25(5):597-609. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.06.001. Epub 2014 Jun 21. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 25037686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guanylate-Binding Protein 1 Inhibits Nuclear Delivery of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Virions by Disrupting Formation of Actin Filament.J Virol. 2017 Jul 27;91(16):e00632-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00632-17. Print 2017 Aug 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28592529 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-step regulation of innate immune signaling by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.Virus Res. 2015 Nov 2;209:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 25796211 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Histamine and Related Signaling in Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Pathogenesis and Oncogenesis.Viruses. 2023 Apr 20;15(4):1011. doi: 10.3390/v15041011. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37112991 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of valganciclovir therapy on severe IRIS-Kaposi Sarcoma mortality: An open-label, parallel, randomized controlled trial.PLoS One. 2023 May 17;18(5):e0280209. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280209. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37195970 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
RNA Granules in Antiviral Innate Immunity: A Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Journey.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jan 5;12:794431. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.794431. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35069491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host RAB11FIP5 protein inhibits the release of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus particles by promoting lysosomal degradation of ORF45.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Dec 14;16(12):e1009099. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009099. eCollection 2020 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 33315947 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum-Shaping Atlastin Proteins Facilitate KSHV Replication.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 13;11:790243. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.790243. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35096644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS et al. (1994) Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Science 266:1865–1869 - PubMed
-
- Soulier J, Grollet L, Oksenhendler E et al. (1995) Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman’s disease. Blood 86:1276–1280 - PubMed
-
- Nador RG, Cesarman E, Chadburn A et al. (1996) Primary effusion lymphoma: a distinct clinicopathologic entity associated with the Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpes virus. Blood 88:645–656 - PubMed
-
- Neipel F, Fleckenstein B (1999) The role of HHV-8 in Kaposi’s sarcoma. Semin Cancer Biol 9:151–164 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

