Signaling control of antibody isotype switching
- PMID: 30904131
- PMCID: PMC7875453
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ai.2019.01.001
Signaling control of antibody isotype switching
Abstract
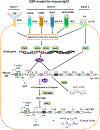
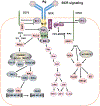
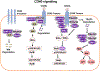
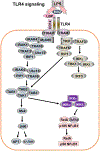
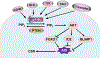
Class switch recombination (CSR) generates isotype-switched antibodies with distinct effector functions essential for mediating effective humoral immunity. CSR is catalyzed by activation-induced deaminase (AID) that initiates DNA lesions in the evolutionarily conserved switch (S) regions at the immunoglobulin heavy chain (Igh) locus. AID-initiated DNA lesions are subsequently converted into DNA double stranded breaks (DSBs) in the S regions of Igh locus, repaired by non-homologous end-joining to effect CSR in mammalian B lymphocytes. While molecular mechanisms of CSR are well characterized, it remains less well understood how upstream signaling pathways regulate AID expression and CSR. B lymphocytes express multiple receptors including the B cell antigen receptor (BCR) and co-receptors (e.g., CD40). These receptors may share common signaling pathways or may use distinct signaling elements to regulate CSR. Here, we discuss how signals emanating from different receptors positively or negatively regulate AID expression and CSR.
Keywords: Activation-induced deaminase; B cell antigen receptor; CD40; Class switch recombination; PI3K; PTEN; Signal transduction; Toll-like receptor.
© 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Zhangguo Chen and Jing H. Wang declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase-initiated off-target DNA breaks are detected and resolved during S phase.J Immunol. 2012 Sep 1;189(5):2374-82. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200414. Epub 2012 Jul 23. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22826323 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and regulation of class switch recombination by IgH transcriptional control elements.Adv Immunol. 2020;147:89-137. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2020.06.003. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Adv Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32981636
-
Orientation-specific joining of AID-initiated DNA breaks promotes antibody class switching.Nature. 2015 Sep 3;525(7567):134-139. doi: 10.1038/nature14970. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26308889 Free PMC article.
-
How the Signaling Crosstalk of B Cell Receptor (BCR) and Co-Receptors Regulates Antibody Class Switch Recombination: A New Perspective of Checkpoints of BCR Signaling.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 25;12:663443. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.663443. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33841447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of the immunoglobulin heavy chain class switch recombination mechanism.Adv Immunol. 2007;94:157-214. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(06)94006-1. Adv Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17560275 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis C virus modified sE2F442NYT as an antigen in candidate vaccine facilitates human immune cell activation.J Virol. 2024 Jan 23;98(1):e0180923. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01809-23. Epub 2023 Dec 12. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38084956 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of Neutralizing Antibodies and Their Potential in COVID-19.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Nov 23;9(12):1376. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9121376. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34960121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-neutralizing functions in anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies.Biomed J. 2024 Feb;47(1):100666. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.100666. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Biomed J. 2024. PMID: 37778697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Designing spatial and temporal control of vaccine responses.Nat Rev Mater. 2022;7(3):174-195. doi: 10.1038/s41578-021-00372-2. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Nat Rev Mater. 2022. PMID: 34603749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and experimental treatment of primary humoral immunodeficiencies.Clin Exp Immunol. 2024 Apr 23;216(2):120-131. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxae008. Clin Exp Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38306460 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu-Rish EY, Amrani Y, and Browning MJ (2013). Toll-like receptor 9 activation induces expression of membrane-bound B-cell activating factor (BAFF) on human B cells and leads to increased proliferation in response to both soluble and membrane-bound BAFF. Rheumatology (Oxford) 52, 1190. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, and Takeda K (2004). Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4, 499. - PubMed
-
- Allen RC, Armitage RJ, Conley ME, Rosenblatt H, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Bedell MA, Edelhoff S, Disteche CM, Simoneaux DK, and et al. (1993). CD40 ligand gene defects responsible for X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. Science 259, 990. - PubMed
-
- Andersen-Nissen E, Hawn TR, Smith KD, Nachman A, Lampano AE, Uematsu S, Akira S, and Aderem A (2007). Cutting edge: Tlr5−/− mice are more susceptible to Escherichia coli urinary tract infection. J Immunol 178, 4717. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

