Cross-Talk Signaling in Rice During Combined Drought and Bacterial Blight Stress
- PMID: 30894866
- PMCID: PMC6415615
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00193
Cross-Talk Signaling in Rice During Combined Drought and Bacterial Blight Stress
Abstract
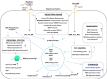
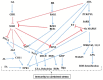
Due to climatic changes, rice crop is affected by moisture deficit stress and pathogens. Tissue water limitation besides reducing growth rates, also renders the crop susceptible to the infection by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) that causes bacterial leaf blight. Independently, both drought adaptation and Xoo resistance have been extensively studied. Though the cross-talk between drought and Xoo stress responses have been explored from individual stress studies, examining the combinatorial stress response is limited in rice. Recently published combined stress studies showed that under the combined stress, maintenance of carbon assimilation is hindered and such response is regulated by overlapping cellular mechanisms that are different from either of the individual stresses. Several receptors, MAP kinases, transcription factors, and ribosomal proteins, are predicted for playing a role in cellular homeostasis and protects cells from combined stress effects. Here we provide a critical analysis of these aspects using information from the recently published combined stress literature. This review is useful for researchers to comprehend combinatorial stress response of rice plants to drought and Xoo.
Keywords: QTL; Xanthomonas; combined stress; drought; protein synthesis; rice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic responses under combined bacterial blight and drought stress in rice reveal potential genes to improve multi-stress tolerance.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jul 18;22(1):349. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03725-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35850621 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of miR169o, an Overlapping MicroRNA in Response to Both Nitrogen Limitation and Bacterial Infection, Promotes Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Susceptibility to Bacterial Blight in Rice.Plant Cell Physiol. 2018 Jun 1;59(6):1234-1247. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcy060. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29566243
-
Time-resolved pathogenic gene expression analysis of the plant pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.BMC Genomics. 2016 May 10;17:345. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2657-7. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27165035 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance Genes and their Interactions with Bacterial Blight/Leaf Streak Pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)-an Updated Review.Rice (N Y). 2020 Jan 8;13(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12284-019-0358-y. Rice (N Y). 2020. PMID: 31915945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rice versus Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae: a unique pathosystem.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2013 May;16(2):188-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2013.02.008. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23466254 Review.
Cited by
-
Exogenous application of nanocarrier-mediated double-stranded RNA manipulates physiological traits and defence response against bacterial diseases.Mol Plant Pathol. 2024 Jan;25(1):e13417. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13417. Mol Plant Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38279851 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Rice Resistance to Bacterial Leaf Blight via Phytohormones.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 10;13(18):2541. doi: 10.3390/plants13182541. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic regions and candidate genes selected during the breeding of rice in Vietnam.Evol Appl. 2022 Jul 9;15(7):1141-1161. doi: 10.1111/eva.13433. eCollection 2022 Jul. Evol Appl. 2022. PMID: 35899250 Free PMC article.
-
Responses to Drought Stress Modulate the Susceptibility to Plasmopara viticola in Vitis vinifera Self-Rooted Cuttings.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jan 30;10(2):273. doi: 10.3390/plants10020273. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33573332 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal protein QM/RPL10 positively regulates defence and protein translation mechanisms during nonhost disease resistance.Mol Plant Pathol. 2020 Nov;21(11):1481-1494. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12991. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Mol Plant Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32964634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achard P., Gong F., Cheminant S., Alioua M., Hedden P., Genschik P. (2008). The cold-inducible CBF1 factor-dependent signaling pathway modulates the accumulation of the growth-repressing DELLA proteins via its effect on gibberellin metabolism. Plant Cell 20 2117–2129. 10.1105/tpc.108.058941 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aghamolki M. T. K., Yusop M. K., Oad F. C., Zakikhani H., Jaafar H. Z., Kharidah S., et al. (2014). Heat stress effects on yield parameters of selected rice cultivars at reproductive growth stages. J. Food Agric. Environ. 12 741–746.
-
- Albrecht C., Boutrot F., Segonzac C., Schwessinger B., Gimenez-Ibanez S., Chinchilla D. (2012). Brassinosteroids inhibit pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immune signaling independent of the receptor kinase BAK1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109 303–308. 10.1073/pnas.1109921108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

