Knockdown of Cytochrome P450 Genes Gh_D07G1197 and Gh_A13G2057 on Chromosomes D07 and A13 Reveals Their Putative Role in Enhancing Drought and Salt Stress Tolerance in Gossypium hirsutum
- PMID: 30889904
- PMCID: PMC6471685
- DOI: 10.3390/genes10030226
Knockdown of Cytochrome P450 Genes Gh_D07G1197 and Gh_A13G2057 on Chromosomes D07 and A13 Reveals Their Putative Role in Enhancing Drought and Salt Stress Tolerance in Gossypium hirsutum
Abstract
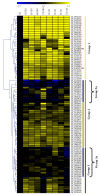
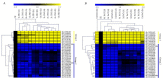
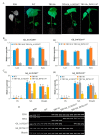
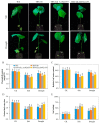
We identified 672, 374, and 379 CYPs proteins encoded by the CYPs genes in Gossypiumhirsutum, Gossypiumraimondii, and Gossypiumarboreum, respectively. The genes were found to be distributed in all 26 chromosomes of the tetraploid cotton, with chrA05, chrA12, and their homeolog chromosomes harboring the highest number of genes. The physiochemical properties of the proteins encoded by the CYP450 genes varied in terms of their protein lengths, molecular weight, isoelectric points (pI), and even grand hydropathy values (GRAVY). However, over 99% of the cotton proteins had GRAVY values below 0, which indicated that the majority of the proteins encoded by the CYP450 genes were hydrophilic in nature, a common property of proteins encoded by stress-responsive genes. Moreover, through the RNA interference (RNAi) technique, the expression levels of Gh_D07G1197 and Gh_A13G2057 were suppressed, and the silenced plants showed a higher concentration of hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) with a significant reduction in the concentration levels of glutathione (GSH), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and proline compared to the wild types under drought and salt stress conditions. Furthermore, the stress-responsive genes 1-Pyrroline⁻5-Carboxylate Synthetase (GhP5CS), superoxide dismutase (GhSOD), and myeloblastosis (GhMYB) were downregulated in VIGS plants, but showed upregulation in the leaf tissues of the wild types under drought and salt stress conditions. In addition, CYP450-silenced cotton plants exhibited a high level of oxidative injury due to high levels of oxidant enzymes, in addition to negative effects on CMS, ELWL, RLWC, and chlorophyll content The results provide the basic foundation for future exploration of the proteins encoded by the CYP450 genes in order to understand the physiological and biochemical mechanisms in enhancing drought and salt stress tolerance in plants.
Keywords: cytochrome P450 genes; drought and salt stress; oxidant and antioxidant enzymes; stress-responsive genes; virus-induced-gene-silencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Map-Based Functional Analysis of the GhNLP Genes Reveals Their Roles in Enhancing Tolerance to N-Deficiency in Cotton.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 8;20(19):4953. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194953. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31597268 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of Gh_A08G1120 (GH3.5) gene reveal their significant role in enhancing drought and salt stress tolerance in cotton.BMC Genet. 2019 Jul 23;20(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12863-019-0756-6. BMC Genet. 2019. PMID: 31337336 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of GhIQD31 and GhIQD32 increases drought and salt stress sensitivity in Gossypium hirsutum.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019 Nov;144:166-177. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.09.027. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31568959
-
Genome wide identification of the trihelix transcription factors and overexpression of Gh_A05G2067 (GT-2), a novel gene contributing to increased drought and salt stresses tolerance in cotton.Physiol Plant. 2019 Nov;167(3):447-464. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12920. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Physiol Plant. 2019. PMID: 30629305 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Genome Analysis of Cyclin Dependent Kinase (CDK) Gene Family in Cotton and Functional Evaluation of the Role of CDKF4 Gene in Drought and Salt Stress Tolerance in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 5;19(9):2625. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092625. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30189594 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cytochrome P450 Gene Families: Role in Plant Secondary Metabolites Production and Plant Defense.J Xenobiot. 2023 Jul 25;13(3):402-423. doi: 10.3390/jox13030026. J Xenobiot. 2023. PMID: 37606423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of CYP450 Family Members in Fritillaria cirrhosa D. Don and Profiling of Key CYP450s Related to Isosteroidal Alkaloid Biosynthesis.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 14;14(1):219. doi: 10.3390/genes14010219. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672960 Free PMC article.
-
Combined physiological and metabolomic analysis reveals the effects of different biostimulants on maize production and reproduction.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 23;13:1062603. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1062603. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36507449 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of tandem duplicated genes and their expression under salt stress in seashore paspalum.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 30;13:971999. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.971999. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36247543 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Defensive Characterization of PmCYP720B11v2 from Pinus massoniana.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 14;23(12):6640. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126640. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu J., Wang X.Y., Guo W.Z. The cytochrome P450 superfamily: Key players in plant development and defense. J. Integr. Agric. 2015;14:1673–1686. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(14)60980-1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

