The Role of Probiotics and Prebiotics in the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity
- PMID: 30875987
- PMCID: PMC6470608
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11030635
The Role of Probiotics and Prebiotics in the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity
Abstract
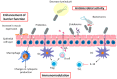
Obesity is a global pandemic complex to treat due to its multifactorial pathogenesis-an unhealthy lifestyle, neuronal and hormonal mechanisms, and genetic and epigenetic factors are involved. Scientific evidence supports the idea that obesity and metabolic consequences are strongly related to changes in both the function and composition of gut microbiota, which exert an essential role in modulating energy metabolism. Modifications of gut microbiota composition have been associated with variations in body weight and body mass index. Lifestyle modifications remain as primary therapy for obesity and related metabolic disorders. New therapeutic strategies to treat/prevent obesity have been proposed, based on pre- and/or probiotic modulation of gut microbiota to mimic that found in healthy non-obese subjects. Based on human and animal studies, this review aimed to discuss mechanisms through which gut microbiota could act as a key modifier of obesity and related metabolic complications. Evidence from animal studies and human clinical trials suggesting potential beneficial effects of prebiotic and various probiotic strains on those physical, biochemical, and metabolic parameters related to obesity is presented. As a conclusion, a deeper knowledge about pre-/probiotic mechanisms of action, in combination with adequately powered, randomized controlled follow-up studies, will facilitate the clinical application and development of personalized healthcare strategies.
Keywords: gut microbiota; nutrition; obesity; prebiotics; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Probiotics and prebiotics, targeting obesity with functional foods.Bratisl Lek Listy. 2021;122(9):647-652. doi: 10.4149/BLL_2021_104. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2021. PMID: 34463111 Review.
-
The impact of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on the biochemical, clinical, and immunological markers, as well as on the gut microbiota of obese hosts.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(2):337-355. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1733483. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32156153 Review.
-
Gut microbiota in obesity and related comorbidities in children and adolescents: the role of biotics in treatment.Minerva Pediatr (Torino). 2022 Dec;74(6):632-649. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5276.22.06964-6. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Minerva Pediatr (Torino). 2022. PMID: 35708037 Review.
-
Diet, Gut Microbiota, and Obesity: Links with Host Genetics and Epigenetics and Potential Applications.Adv Nutr. 2019 Jan 1;10(suppl_1):S17-S30. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy078. Adv Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30721960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota in obesity and metabolic disorders.Proc Nutr Soc. 2010 Aug;69(3):434-41. doi: 10.1017/S0029665110001813. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Proc Nutr Soc. 2010. PMID: 20540826
Cited by
-
Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Paraprobiotics as a Therapeutic Alternative for Intestinal Mucositis.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 17;11:544490. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.544490. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33042054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary patterns interfere with gut microbiota to combat obesity.Front Nutr. 2024 Jun 17;11:1387394. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1387394. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38953044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut dysbiosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic implications.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Nov 8;12:997018. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.997018. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36425787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Supplementation with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum IMC 510 Modifies Microbiota Composition and Prevents Body Weight Gain Induced by Cafeteria Diet in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 16;22(20):11171. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011171. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681831 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Weight Loss in Subjects with Overweight or Obesity: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2021 Oct 17;13(10):3627. doi: 10.3390/nu13103627. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34684633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2000. - PubMed
-
- Khayatzadeh-Mahani A., Ruckert A., Labonté R. Obesity prevention: Co-framing for intersectoral ‘buy-in’. Crit. Public Health. 2018;28:4–11. doi: 10.1080/09581596.2017.1282604. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

