Prospective comparative study of the effects of lidocaine on urodynamic and sensory parameters in bladder pain syndrome
- PMID: 30874834
- PMCID: PMC6647211
- DOI: 10.1007/s00192-019-03892-2
Prospective comparative study of the effects of lidocaine on urodynamic and sensory parameters in bladder pain syndrome
Abstract
Introduction and hypothesis: Intravesically administered lidocaine is used in patients with bladder pain syndrome (BPS) to test the hypothesis that symptoms have a peripheral versus central mechanism.
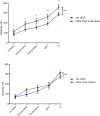
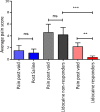
Methods: A cross-sectional study of 24 female patients with BPS was performed. The Central Sensitisation Inventory (CSI) and Kings Health Questionnaire (KHQ) were completed. Urodynamic assessment was undertaken. Women were asked to report their pain using a numeric rating scale at cystometric capacity and post void. Participants then received an intravesical instillation of either 20 ml of 2% alkalinised lidocaine (n = 16) or 20 ml of normal saline (n = 8). These solutions were allowed to remain in situ for 20 min and pain score repeated. Urodynamics was repeated.
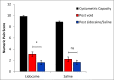
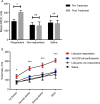
Results: There was a statistically significant volume increase following lidocaine treatment: maximal cystometric capacity (MCC) 192-261 ml post lidocaine (p = 0.005.) In contrast, there was no significant difference in the saline controls: MCC 190-183 ml (p = 0.879.) Individual analysis revealed five of 16 lidocaine participants did not respond to lidocaine. These five reported a significantly worse quality of life (QoL) than lidocaine responders and had a tendency towards central sensitivity syndromes.
Conclusion: Lidocaine significantly improved MCC in 11/16 participants in this study. These patients appear to have peripherally mediated disease. However, the failure of response to treatment in five participants, as well as their tendency towards central sensitivity syndromes, implies that in this subgroup, a peripheral drive from the bladder is not critical to their pain, suggesting central nervous system (CNS) pathology. This simple and safe test could be used to stratify patients for research or therapeutic trials.
Keywords: Bladder pain syndrome; Central sensitisation; Lidocaine; Peripheral pain modulation; Urodynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Comment in
-
Commentary to: Prospective comparative study on the effects of lidocaine on urodynamic and sensory parameters in bladder-pain syndrome.Int Urogynecol J. 2019 Aug;30(8):1303. doi: 10.1007/s00192-019-03922-z. Epub 2019 Apr 13. Int Urogynecol J. 2019. PMID: 30982084 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Beyond a Simple Anesthetic Effect: Lidocaine in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Interstitial Cystitis/bladder Pain Syndrome.Urology. 2015 May;85(5):1025-1033. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2015.01.021. Urology. 2015. PMID: 25917728 Review.
-
Successful downregulation of bladder sensory nerves with combination of heparin and alkalinized lidocaine in patients with interstitial cystitis.Urology. 2005 Jan;65(1):45-8. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2004.08.056. Urology. 2005. PMID: 15667861 Clinical Trial.
-
Intravesical alkalinized lidocaine (PSD597) offers sustained relief from symptoms of interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome.BJU Int. 2009 Apr;103(7):910-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08162.x. Epub 2008 Nov 13. BJU Int. 2009. PMID: 19021619 Clinical Trial.
-
Electromotive drug-administration: a pilot study for minimal-invasive treatment of therapy-resistant idiopathic detrusor overactivity.Neurourol Urodyn. 2009;28(3):209-13. doi: 10.1002/nau.20624. Neurourol Urodyn. 2009. PMID: 19205067
-
[Intravesical therapy of heparin and lidocaine for interstitial cystitis : a case report].Hinyokika Kiyo. 2011 Sep;57(9):513-6. Hinyokika Kiyo. 2011. PMID: 22075614 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
A randomised controlled trial of the effect of intra-articular lidocaine on pain scores in inflammatory arthritis.Pain. 2024 Nov 1;165(11):2578-2585. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003291. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Pain. 2024. PMID: 38888846 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Does large volume of distribution of lidocaine masks its systemic uptake from bladder?Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2023 Apr 15;11(2):121-135. eCollection 2023. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2023. PMID: 37168943 Free PMC article.
-
Broaden Horizons: The Advancement of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 23;23(23):14594. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314594. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36498919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Stellate Ganglion Block Combined with Lidocaine at Different Concentrations for Preemptive Analgesia on Postoperative Pain Relief and Adverse Reactions of Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Apr 11;2022:6027093. doi: 10.1155/2022/6027093. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Nov 24;2022:9804601. doi: 10.1155/2022/9804601. PMID: 35450203 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
Indwelling urinary catheter assembled with lidocaine-loaded polymeric strand for local sustained alleviation of bladder discomfort.Bioeng Transl Med. 2021 Mar 31;6(2):e10218. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10218. eCollection 2021 May. Bioeng Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34027100 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

