Recent Advances in Electrosynthesized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensing Platforms for Bioanalyte Detection
- PMID: 30857285
- PMCID: PMC6427210
- DOI: 10.3390/s19051204
Recent Advances in Electrosynthesized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensing Platforms for Bioanalyte Detection
Abstract
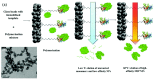
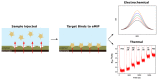
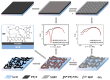
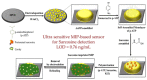
The accurate detection of biological materials has remained at the forefront of scientific research for decades. This includes the detection of molecules, proteins, and bacteria. Biomimetic sensors look to replicate the sensitive and selective mechanisms that are found in biological systems and incorporate these properties into functional sensing platforms. Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) are synthetic receptors that can form high affinity binding sites complementary to the specific analyte of interest. They utilise the shape, size, and functionality to produce sensitive and selective recognition of target analytes. One route of synthesizing MIPs is through electropolymerization, utilising predominantly constant potential methods or cyclic voltammetry. This methodology allows for the formation of a polymer directly onto the surface of a transducer. The thickness, morphology, and topography of the films can be manipulated specifically for each template. Recently, numerous reviews have been published in the production and sensing applications of MIPs; however, there are few reports on the use of electrosynthesized MIPs (eMIPs). The number of publications and citations utilising eMIPs is increasing each year, with a review produced on the topic in 2012. This review will primarily focus on advancements from 2012 in the use of eMIPs in sensing platforms for the detection of biologically relevant materials, including the development of increased polymer layer dimensions for whole bacteria detection and the use of mixed monomer compositions to increase selectivity toward analytes.
Keywords: bacteria; biomolecules; electropolymerization; electrosynthesis; molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs); proteins; sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Artificial Biomimetic Electrochemical Assemblies.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 15;12(1):44. doi: 10.3390/bios12010044. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35049673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances and future prospects in molecularly imprinted polymers-based electrochemical biosensors.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Feb 15;100:56-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.058. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 28863325 Review.
-
Molecularly imprinted polymers as recognition materials for electronic tongues.Biosens Bioelectron. 2015 Dec 15;74:856-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.054. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015. PMID: 26233642 Review.
-
Nanostructured molecularly imprinted polymers for protein chemosensing.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Apr 15;102:17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.10.045. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 29101784 Review.
-
[Recent advances in applications of fragment/dummy molecularly imprinted polymers].Se Pu. 2021 Feb;39(2):134-141. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.08008. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34227346 Free PMC article. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of ligand modified poly (N-Isopropyl acrylamide) hydrogel for etiological diagnosis of corneal infection.Exp Eye Res. 2022 Jan;214:108881. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108881. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Exp Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 34871569 Free PMC article.
-
Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Surface Imprinted Polymers Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Infectious Diseases.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Feb 13;20(4):996. doi: 10.3390/s20040996. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32069788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Bio-Inspired Intelligent Imprinted Polymers for Virus Determination.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 21;11(3):89. doi: 10.3390/bios11030089. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screen-Printed Electrode-Based Sensors for Food Spoilage Control: Bacteria and Biogenic Amines Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2020 Sep 30;10(10):139. doi: 10.3390/bios10100139. Biosensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33008005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Reliable Is the Electrochemical Readout of MIP Sensors?Sensors (Basel). 2020 May 8;20(9):2677. doi: 10.3390/s20092677. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32397160 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Canfarotta F., Rapini R., Piletsky S. Recent advances in electrochemical sensors based on chiral and nano-sized imprinted polymers. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018;7:146–152. doi: 10.1016/j.coelec.2017.11.018. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

