The MicroRNA Family Both in Normal Development and in Different Diseases: The miR-17-92 Cluster
- PMID: 30854399
- PMCID: PMC6378081
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9450240
The MicroRNA Family Both in Normal Development and in Different Diseases: The miR-17-92 Cluster
Abstract
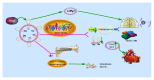
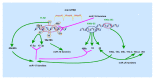
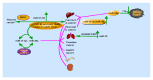
An increasing number of research studies over recent years have focused on the function of microRNA (miRNA) molecules which have unique characteristics in terms of structure and function. They represent a class of endogenous noncoding single-strand small molecules. An abundance of miRNA clusters has been found in the genomes of various organisms often located in a polycistron. The miR-17-92 family is among the most famous miRNAs and has been identified as an oncogene. The functions of this cluster, together with the seven individual molecules that it comprises, are most related to cancers, so it would not be surprising that they are considered to have involvement in the development of tumors. The miR-17-92 cluster is therefore expected not only to be a tumor marker, but also to perform an important role in the early diagnosis of those diseases and possibly also be a target for tumor biotherapy. The miR-17-92 cluster affects the development of disease by regulating many related cellular processes and multiple target genes. Interestingly, it also has important roles that cannot be ignored in disease of the nervous system and circulation and modulates the growth and development of bone. Therefore, it provides new opportunities for disease prevention, clinical diagnosis, prognosis, and targeted therapy. Here we review the role of the miR-17-92 cluster that has received little attention in relation to neurological diseases, cardiac diseases, and the development of bone and tumors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of miR-183 cluster in immunity.Cancer Lett. 2019 Feb 28;443:108-114. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.11.035. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 30529154 Review.
-
Application of the microRNA-302/367 cluster in cancer therapy.Cancer Sci. 2020 Apr;111(4):1065-1075. doi: 10.1111/cas.14317. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31957939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of miR-17-92 Cluster in Cardiovascular Development and Common Diseases.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9102909. doi: 10.1155/2017/9102909. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28164128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of miR-302/367 cluster in human physiology and pathophysiology.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020 Aug 5;52(8):791-800. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmaa065. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020. PMID: 32785592 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of conserved miRNAs in cynomolgus macaque genome using small RNA sequencing and homology searching.PeerJ. 2020 Jul 10;8:e9347. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9347. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32728489 Free PMC article.
-
HNRNPA2B1 Affects the Prognosis of Esophageal Cancer by Regulating the miR-17-92 Cluster.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 30;9:658642. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.658642. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34277606 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of MicroRNA92, MicroRNA638 in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia of Egyptian Children.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 May 1;22(5):1567-1572. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.5.1567. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 34048187 Free PMC article.
-
The miRNA-mRNA interactome of murine induced pluripotent stem cell-derived chondrocytes in response to inflammatory cytokines.FASEB J. 2020 Sep;34(9):11546-11561. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000889R. Epub 2020 Aug 7. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32767602 Free PMC article.
-
The microRNA-17 ~ 92 Family as a Key Regulator of Neurogenesis and Potential Regenerative Therapeutics of Neurological Disorders.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Feb;18(2):401-411. doi: 10.1007/s12015-020-10050-5. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 33030674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

