Elucidation of the enigma of glycosphingolipids in the regulation of inflammation and degeneration - Great progress over the last 70 years
- PMID: 30853699
- PMCID: PMC6541724
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.95.011
Elucidation of the enigma of glycosphingolipids in the regulation of inflammation and degeneration - Great progress over the last 70 years
Abstract
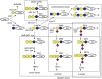
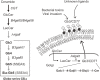
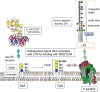
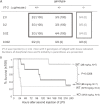
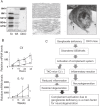
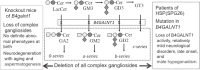
Since globotetraosylceramide was defined as a major glycosphingolipid in human erythrocytes, various glycolipids have been found in normal cells and diseased organs. However, the implications of their polymorphic structures in the function of individual cells and tissues have not been clarified. Genetic manipulation of glycosphingolipids in cultured cells and experimental animals has enabled us to substantially elucidate their roles. In fact, great progress has been achieved in the last 70 years in revealing that glycolipids are essential in the maintenance of integrity of nervous tissues and other organs. Furthermore, the correct composition of glycosphingolipids has been shown to be critical for the protection against inflammation and degeneration. Here, we summarized historic information and current knowledge about glycosphingolipids, with a focus on their involvement in inflammation and degeneration. This topic is significant for understanding the biological responses to various stresses, because glycosphingolipids play roles in the interaction with various intrinsic and extrinsic factors. These findings are also important for the application of therapeutic interventions of various diseases.
Keywords: carbohydrate; degeneration; glycosphingolipids; glycosyltransferase; inflammation; knockout.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulatory function of glycosphingolipids in the inflammation and degeneration.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Apr 1;571:58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.02.007. Epub 2015 Feb 14. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 25688919 Review.
-
Multi-system disorders of glycosphingolipid and ganglioside metabolism.J Lipid Res. 2010 Jul;51(7):1643-75. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R003996. Epub 2010 Mar 8. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 20211931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New era of research on cancer-associated glycosphingolipids.Cancer Sci. 2019 May;110(5):1544-1551. doi: 10.1111/cas.14005. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30895683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new turning point in glycosphingolipid research.Hum Cell. 2005 Sep;18(3):117-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-0774.2005.tb00002.x. Hum Cell. 2005. PMID: 17022144 Review.
-
Characterization of novel nonacid glycosphingolipids as biomarkers of human gastric adenocarcinoma.J Biol Chem. 2022 Apr;298(4):101732. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101732. Epub 2022 Feb 15. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35176282 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Contribution of Glucosylceramide Synthase to the Proliferation of Mouse Osteoblasts.In Vivo. 2021 Nov-Dec;35(6):3111-3123. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12606. In Vivo. 2021. PMID: 34697142 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidomic Profiling of Kidney Cortical Tubule Segments Identifies Lipotypes with Physiological Implications.Function (Oxf). 2024 Jul 11;5(4):zqae016. doi: 10.1093/function/zqae016. Function (Oxf). 2024. PMID: 38985001 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Gb3 Synthase in Mice Resulted in the Attenuation of Bone Formation via Decrease in Osteoblasts.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 18;20(18):4619. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184619. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31540393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamakawa T. (1996) A reflection on the early history of glycosphingolipids. Glycoconj. J. 13, 123–126. - PubMed
-
- Nagai Y. (1995) Functional roles of gangliosides in bio-signaling. Behav. Brain Res. 66, 99–104. - PubMed
-
- Yu R.K. (1994) Development regulation of ganglioside metabolism. Prog. Brain Res. 101, 31–44. - PubMed
-
- Schengrund C.L. (1990) The role(s) of gangliosides in neural differentiation and repair: A perspective. Brain Res. Bull. 24, 131–141. - PubMed
-
- Furukawa K., Ohmi Y., Ohkawa Y., Tajima O., Furukawa K. (2014) Glycosphingolipids in the regulation of the nervous system. Adv. Neurobiol. 9, 307–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

