Enhanced water solubility, antioxidant activity, and oral absorption of hesperetin by D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate and phosphatidylcholine
- PMID: 30829014
- PMCID: PMC6421126
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1800346
Enhanced water solubility, antioxidant activity, and oral absorption of hesperetin by D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate and phosphatidylcholine
Abstract
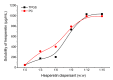
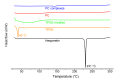
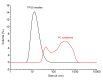
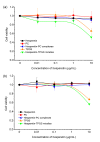
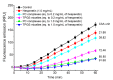
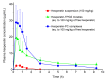
Hesperetin, an abundant bioactive component of citrus fruits, is poorly water-soluble, resulting in low oral bioavailability. We developed new formulations to improve the water solubility, antioxidant activity, and oral absorption of hesperetin. Two nano-based formulations were developed, namely hesperetin-TPGS (D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate) micelles and hesperetin-phosphatidylcholine (PC) complexes. These two formulations were prepared by a simple technique called solvent dispersion, using US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved excipients for drugs. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) were used to characterize the formulations' physical properties. Cytotoxicity analysis, cellular antioxidant activity assay, and a pharmacokinetic study were performed to evaluate the biological properties of these two formulations. The final weight ratios of both hesperetin to TPGS and hesperetin to PC were 1:12 based on their water solubility, which increased to 21.5- and 20.7-fold, respectively. The hesperetin-TPGS micelles had a small particle size of 26.19 nm, whereas the hesperetin-PC complexes exhibited a larger particle size of 219.15 nm. In addition, the cellular antioxidant activity assay indicated that both hesperetin-TPGS micelles and hesperetin-PC complexes increased the antioxidant activity of hesperetin to 4.2- and 3.9-fold, respectively. Importantly, the in vivo oral absorption study on rats indicated that the micelles and complexes significantly increased the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) from 2.64 μg/mL to 20.67 and 33.09 μg/mL and also increased the area under the concentration-time curve of hesperetin after oral administration to 16.2- and 18.0-fold, respectively. The micelles and complexes increased the solubility and remarkably improved the in vitro antioxidant activity and in vivo oral absorption of hesperetin, indicating these formulations' potential applications in drugs and healthcare products.
Keywords: Hesperetin; D-α-Tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS); Phosphatidylcholine; Antioxidant activity; Oral absorption.
Conflict of interest statement
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced solubility and oral absorption of sirolimus using D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate micelles.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2013 Apr;41(2):85-91. doi: 10.3109/21691401.2012.742100. Epub 2013 Jan 10. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23305536
-
Development and evaluation of a novel drug delivery: Soluplus®/TPGS mixed micelles loaded with piperine in vitro and in vivo.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018 Sep;44(9):1409-1416. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2018.1472277. Epub 2018 May 27. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29718714
-
Evaluation in vitro and in vivo of curcumin-loaded mPEG-PLA/TPGS mixed micelles for oral administration.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016 May 1;141:345-354. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.01.017. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016. PMID: 26874910
-
The applications of Vitamin E TPGS in drug delivery.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013 May 13;49(2):175-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2013.02.006. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013. PMID: 23485439 Review.
-
Current trends in the use of vitamin E-based micellar nanocarriers for anticancer drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2017 Jun;14(6):715-726. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2016.1229300. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2017. PMID: 27560621 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms of action of hesperidin in cancer: Recent trends and advancements.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020 Mar;245(5):486-497. doi: 10.1177/1535370220903671. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020. PMID: 32050794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and Characterization of Phosphatidylcholine-Based Solid Dispersions of Aprepitant for Enhanced Solubility and Dissolution.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Apr 29;12(5):407. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12050407. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32365589 Free PMC article.
-
Amorphous Inclusion Complexes: Molecular Interactions of Hesperidin and Hesperetin with HP-Β-CD and Their Biological Effects.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 4;23(7):4000. doi: 10.3390/ijms23074000. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409360 Free PMC article.
-
Amorphous System of Hesperetin and Piperine-Improvement of Apparent Solubility, Permeability, and Biological Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 2;24(5):4859. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054859. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902286 Free PMC article.
-
Finding inhibitors for PCSK9 using computational methods.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 5;16(8):e0255523. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255523. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34351937 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

