A nomogram to predict prognosis in Ewing sarcoma of bone
- PMID: 30815343
- PMCID: PMC6378909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbo.2019.100223
A nomogram to predict prognosis in Ewing sarcoma of bone
Abstract
Objective: This study was designed to develop a nomogram for assessing the survival of patients with Ewing sarcoma (ES).
Methods: Data from patients diagnosed with ES between 2004 and 2013 were collected from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database. Based on patient registration, the primary cohort was divided into a training set (n = 479, data from 17 cancer registries) and a validation set (n = 137, data from 1 cancer registry). Then, the prognostic effects of variables were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazard model. Moreover, nomograms were established for estimating 3- and 5-year overall survival (OS) and cancer-special survival (CSS) based on Cox regression model. Last, nomogram was validated by training set and validation set.
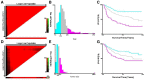
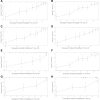
Results: According to the multivariate analysis of training set, nomogram which combined age, race, stage, tumor site, tumor size and chemotherapy was identified. The internal bootstrap resampling approach suggested the nomogram had sufficient discriminatory power with the C-index of OS: 0.754 (95% CI, 0.705-0.802) and CSS: 0.759 (95% CI, 0.700-0.800). The calibration plots also demonstrated good consistence between the prediction and the observation.
Conclusion: Our nomogram is a reliable and powerful tool for distinguishing and predicting the survival of ES patients, thus helping to better select medical examinations and optimize treatment options in collaboration with medical oncologists and surgeons.
Keywords: Ewing sarcoma; Nomogram; SEER.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Establishing a novel prognostic tool for Ewing sarcoma patients: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 13;99(46):e23050. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023050. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33181669 Free PMC article.
-
A SEER-based nomogram accurately predicts prognosis in Ewing's sarcoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 22;11(1):22723. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02134-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34811459 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram to predict the prognosis of patients with gastric cardia cancer.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 24;10(1):14143. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71146-z. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32839498 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for metastasis and poor prognosis of Ewing sarcoma: a population based study.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Mar 4;15(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01607-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 32131863 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram for determining the disease-specific survival in Ewing sarcoma: a population study.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jul 5;19(1):667. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5893-9. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31277591 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Overall survival comparison between pediatric and adult Ewing sarcoma of bone and adult nomogram construction: a large population-based analysis.Front Pediatr. 2023 May 23;11:1103565. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1103565. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37287626 Free PMC article.
-
TrkC, a novel prognostic marker, induces and maintains cell survival and metastatic dissemination of Ewing sarcoma by inhibiting EWSR1-FLI1 degradation.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Sep 28;13(9):836. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05275-w. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36171207 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Novel Clinical Prediction Model to Predict the Risk of Lung Metastasis from Ewing Sarcoma for Medical Human-Computer Interface.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Mar 29;2022:1888586. doi: 10.1155/2022/1888586. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35392046 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a prognostic score at baseline diagnosis for Ewing sarcoma family of tumors: a retrospective single institution analysis of 860 patients.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Feb 15;14(2):927-941. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35273696 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Prognostic Nomogram for Extremity Soft Tissue Leiomyosarcoma.Front Oncol. 2019 May 1;9:346. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00346. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31119101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ewing J. Diffuse endothelioma of bone. CA: Cancer J. Clin. 1972;22(2):95–98. - PubMed
-
- Bacci G., Ferrari S., Bertoni F., Rimondini S., Longhi A., Bacchini P. Prognostic factors in nonmetastatic Ewing's sarcoma of bone treated with adjuvant chemotherapy: analysis of 359 patients at the Istituto Ortopedico Rizzoli. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000;18(1):4. - PubMed
-
- Cotterill S., Ahrens S., Paulussen M., Jurgens H., Voute P., Gadner H. Prognostic factors in Ewing's tumor of bone: analysis of 975 patients from the European Intergroup Cooperative Ewing's Sarcoma Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000;18(17):3108–3114. - PubMed
-
- Bacci G., Longhi A., Ferrari S., Mercuri M., Versari M., Bertoni F. Prognostic factors in non-metastatic Ewing's sarcoma tumor of bone: an analysis of 579 patients treated at a single institution with adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy between 1972 and 1998. Acta Oncol. 2006;45(4):469–475. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

