Caspase-4 mediates cytoplasmic accumulation of TDP-43 in the primate brains
- PMID: 30810811
- PMCID: PMC6531422
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-019-01979-0
Caspase-4 mediates cytoplasmic accumulation of TDP-43 in the primate brains
Abstract
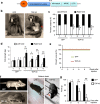
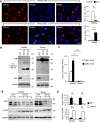
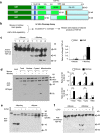
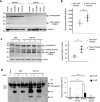
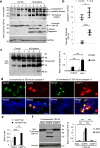
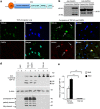
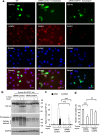
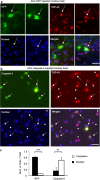
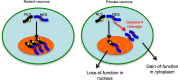
The cytoplasmic accumulation of the nuclear TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) is a pathologic hallmark in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, frontotemporal lobar degeneration, and other neurological disorders. However, most transgenic TDP-43 rodent models show predominant nuclear distribution of TDP-43 in the brain. By expressing mutant TDP-43 (M337V) in the brains of rhesus monkeys and mice, we verified that mutant TDP-43 is distributed in the cytoplasm of the monkey brain and that the majority of mutant TDP-43 remains in the nuclei of the mouse brain. The primate-specific caspase-4, but not mouse homologue caspase-11, could remove the NLS-containing N-terminal domain and generate fragmented TDP-43 that accumulates in the cytoplasm. Moreover, increased expression of caspase-4 in the monkey brain promotes the cytoplasmic accumulation of endogenous TDP-43, and suppressing caspase-4 reduces the cytoplasmic distribution of endogenous TDP-43 in cultured human neural cells. Our findings suggest that primate-specific caspase-4-mediated cleavage of TDP-43 accounts for its cytoplasmic mislocalization in the primate brains and may serve as a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: Aggregation; Caspase-4; Neurodegeneration; Non-human primate; TDP-43.
Figures
Comment in
-
Naturally occurring antibodies target Parkinson disease pathology.Nat Rev Neurol. 2019 Apr;15(4):186-187. doi: 10.1038/s41582-019-0167-3. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30872812 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cytoplasmic mislocalization of RNA splicing factors and aberrant neuronal gene splicing in TDP-43 transgenic pig brain.Mol Neurodegener. 2015 Sep 3;10:42. doi: 10.1186/s13024-015-0036-5. Mol Neurodegener. 2015. PMID: 26334913 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic TDP-43 impairs the activity of the ubiquitin-proteasome system.Exp Neurol. 2021 Nov;345:113833. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113833. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Exp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34363810
-
Both cytoplasmic and nuclear accumulations of the protein are neurotoxic in Drosophila models of TDP-43 proteinopathies.Neurobiol Dis. 2011 Feb;41(2):398-406. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2010.10.007. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Neurobiol Dis. 2011. PMID: 20951205
-
Physiological functions and pathobiology of TDP-43 and FUS/TLS proteins.J Neurochem. 2016 Aug;138 Suppl 1:95-111. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13625. Epub 2016 Jun 15. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27015757 Review.
-
TDP-43 functions and pathogenic mechanisms implicated in TDP-43 proteinopathies.Trends Mol Med. 2011 Nov;17(11):659-67. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2011.06.004. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Trends Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21783422 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A booming field of large animal model research.Zool Res. 2024 Mar 18;45(2):311-313. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.018. Zool Res. 2024. PMID: 38485501 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cytoplasmic Expression of the ALS/FTD-Related Protein TDP-43 Decreases Global Translation Both in vitro and in vivo.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Dec 8;14:594561. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.594561. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33363456 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically modified large animal models for investigating neurodegenerative diseases.Cell Biosci. 2021 Dec 21;11(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00729-8. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34933675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant protein aggregation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.J Neurol. 2024 Aug;271(8):4826-4851. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12485-z. Epub 2024 Jun 13. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38869826 Review.
-
Loss of TDP-43 mediates severe neurotoxicity by suppressing PJA1 gene transcription in the monkey brain.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jan 9;81(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05066-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38194085 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

