A Mouse Model of Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Demonstrates Potentially Reversible Effects on Hippocampal Neurons and Postoperative Cognitive Function
- PMID: 30808858
- PMCID: PMC6404631
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.912658
A Mouse Model of Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Demonstrates Potentially Reversible Effects on Hippocampal Neurons and Postoperative Cognitive Function
Abstract
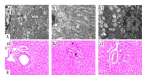
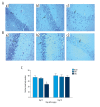
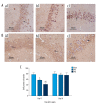
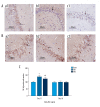
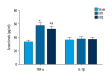
BACKGROUND This study aimed to investigate cognitive function, hippocampal neuronal changes, and the expression of inflammatory cytokines in a mouse model of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. MATERIAL AND METHODS Sixty mice were divided into the sham group, which underwent surgery without vascular occlusion; the I/R1 group, with occlusion of the left hepatic artery and portal vein for 20 min, and reperfusion for 30 min; and the I/R2 group, with occlusion of the left hepatic artery and portal vein for 40 min, and reperfusion for 30 min. At postoperative day 4 and 11, ten mice from each group underwent the Morris water maze (MWM) task. Hippocampal tissues were stained for Nissl bodies. Expression of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) were quantified by immunohistochemistry. Serum tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). RESULTS Groups I/R1 and I/R2 showed a significantly increased latency in the MWM test between days 5-9, compared with the sham group (P<0.05), with no difference by day 11; the I/R2 group had an initial lower crossing frequency (P<0.05), with no difference by day 18. The I/R2 group showed reduced numbers of Nissl bodies in hippocampal neurons. The I/R1 and I/R2 groups had increased expression of NF-κB, TNF-α, and IL-1β and decreased ChAT. No differences between the groups were found in levels of NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-1β, or ChAT by day 18. CONCLUSIONS A mouse model of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury showed transient and reversible cognitive dysfunction, changes in hippocampal neurons, and expression of inflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
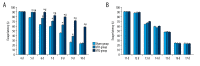
Similar articles
-
Endogenous danger signals trigger hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury through toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa B pathway.Chin Med J (Engl). 2007 Mar 20;120(6):509-14. Chin Med J (Engl). 2007. PMID: 17439747
-
Ribonuclease attenuates hepatic ischemia reperfusion induced cognitive impairment through the inhibition of inflammatory cytokines in aged mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jun;90:62-68. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.094. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28343072
-
[Effect of propofol on the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and expression of inflammatory cytokines in cerebral cortex during transient focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion: experiment with rats].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004 Dec 17;84(24):2110-4. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15730629 Chinese.
-
Effects of dexmedetomidine on postoperative cognitive function of sleep deprivation rats based on changes in inflammatory response.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):7920-7928. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1981757. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34622713 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol preconditioning protects hepatocytes against hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury via Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Jun;35:201-209. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.03.032. Epub 2016 Apr 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27064547
Cited by
-
Exosomes Mediate Hippocampal and Cortical Neuronal Injury Induced by Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury through Activating Pyroptosis in Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 13;2019:3753485. doi: 10.1155/2019/3753485. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31814872 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Protective Effects of Petunidin-3-O-(trans-p-coumaroylrutinoside)-5-O-glucoside on D-Gal-Induced Aging Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 13;25(20):11014. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011014. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456797 Free PMC article.
-
Communication Regarding the Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion and Cognitive Impairment: A Narrative Literature Review.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;97(4):1545-1570. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230886. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38277294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astaxanthin Attenuates Neuroinflammation in Status Epilepticus Rats by Regulating the ATP-P2X7R Signal.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Apr 30;14:1651-1662. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S249162. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32431490 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Exosomes Mediate Neurodegeneration Following Hepatic Ischemia-reperfusion Through Inducing Microglial Pyroptosis in the Developing Hippocampus.Transplantation. 2023 Nov 1;107(11):2364-2376. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000004664. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Transplantation. 2023. PMID: 37291725 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

