Interplay between miRNAs and host genes and their role in cancer
- PMID: 30785618
- PMCID: PMC6609535
- DOI: 10.1093/bfgp/elz002
Interplay between miRNAs and host genes and their role in cancer
Abstract
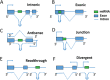
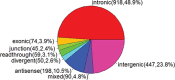
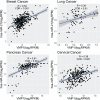
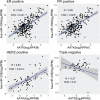
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small endogenous non-coding functional RNAs that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression. They play essential roles in nearly all biological processes including cell development and differentiation, DNA damage repair, cell death as well as intercellular communication. They are highly involved in cancer, acting as tumor suppressors and/or promoters to modulate cell proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor invasion and metastasis. Recent studies have shown that more than half of miRNAs are located within protein-coding or non-coding genes. Intragenic miRNAs and their host genes either share the promoter or have independent transcription. Meanwhile, miRNAs work as partners or antagonists of their host genes by fine-tuning their target genes functionally associated with host genes. This review outlined the complicated relationship between intragenic miRNAs and host genes. Focusing on miRNAs known as oncogenes or tumor suppressors in specific cancer types, it studied co-expression relationships between these miRNAs and host genes in the cancer types using TCGA data sets, which validated previous findings and revealed common, tumor-specific and even subtype-specific patterns. These observations will help understand the function of intragenic miRNAs and further develop miRNA therapeutics in cancer.
Keywords: cancer; host genes; interplay; intragenic miRNA biogenesis; miRNA.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Comment in
-
Challenges and promise of targeting miRNA in rheumatic diseases: a computational approach to identify miRNA association with cell types, cytokines, and disease mechanisms.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 9;14:1322806. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1322806. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38264662 Free PMC article. Review.
Similar articles
-
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors.Dev Biol. 2007 Feb 1;302(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.08.028. Epub 2006 Aug 16. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 16989803 Review.
-
Human microRNA oncogenes and tumor suppressors show significantly different biological patterns: from functions to targets.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 30;5(9):e13067. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013067. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20927335 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: master regulators of drug resistance, stemness, and metastasis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2014 Apr;92(4):321-36. doi: 10.1007/s00109-014-1129-2. Epub 2014 Feb 9. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24509937 Review.
-
A potential role for intragenic miRNAs on their hosts' interactome.BMC Genomics. 2010 Oct 1;11:533. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-533. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20920310 Free PMC article.
-
A step-by-step microRNA guide to cancer development and metastasis.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017 Aug;40(4):303-339. doi: 10.1007/s13402-017-0341-9. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017. PMID: 28748501 Review.
Cited by
-
Isochorismatase domain-containing protein 1 (ISOC1) participates in DNA damage repair and inflammation-related pathways to promote lung cancer development.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Mar;10(3):1444-1456. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-21-219. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33889521 Free PMC article.
-
Enriched atlas of lncRNA and protein-coding genes for the GRCg7b chicken assembly and its functional annotation across 47 tissues.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 19;14(1):6588. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56705-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38504112 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple information carried by RNAs: total eclipse or a light at the end of the tunnel?RNA Biol. 2020 Dec;17(12):1707-1720. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1783868. Epub 2020 Jun 26. RNA Biol. 2020. PMID: 32559119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary microRNAs and Their Significance in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: A 5-Year Update.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 28;14(13):3157. doi: 10.3390/cancers14133157. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35804929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNA BS-DRL1 modulates the DNA damage response and genome stability by interacting with HMGB1 in neurons.Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 1;12(1):4075. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24236-z. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34210972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004;116(2):281–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

