A two-circular RNA signature as a noninvasive diagnostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 30777071
- PMCID: PMC6380039
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-019-1800-z
A two-circular RNA signature as a noninvasive diagnostic biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Recently, circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been reported to be microRNA sponges and play essential roles in cancer development. This study aimed to evaluate whether circulating circRNAs could be used as diagnostic biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
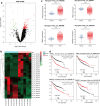
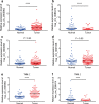
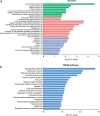
Methods: The Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) dataset was used to investigate differentially expressed circRNAs (DEcircRNAs) in paired LUAD tissues and adjacent nontumor tissues. The expression levels of the host genes were analyzed in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)-LUAD dataset, and the prognostic value was assessed using the Kaplan-Meier plotter. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed to validate the expression of candidate circRNAs in the LUAD plasma and cells. The CCK8 assay was used to measure the function of circRNAs in cell proliferation. Competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network, gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses were performed to predict the possible mechanisms and functions of circRNAs in LUAD.
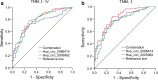
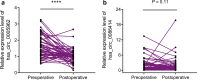
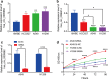
Results: Two upregulated and two downregulated circRNAs were identified as candidate circRNAs using bioinformatics analysis. qRT-PCR demonstrated that hsa_circ_0005962 was upregulated in LUAD plasma and cells, whereas hsa_circ_0086414 was downregulated. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis confirmed that a signature comprising the two circRNAs had good diagnostic potential, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.81 (P < 0.0001). In addition, we observed that overexpression of plasma hsa_circ_0086414 was related to EGFR mutations (P = 0.001). Plasma hsa_circ_0005962 displayed significantly different expression before and after surgery in patients with LUAD (P < 0.0001). In vitro experiments suggested that hsa_circ_0005962 promoted LUAD cell proliferation. For future studies, we predicted the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network for hsa_circ_0005962. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that hsa_circ_0005962 might be involved in LUAD development.
Conclusion: A circRNA signature was identified as a potential noninvasive biomarker for LUAD diagnosis.
Keywords: Biomarker; CircRNA; Diagnosis; Hsa_circ_0005962; Hsa_circ_0086414; LUAD; Plasma.
Figures
Comment in
-
New promising circulating RNA biomarkers for early diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Jul;7(Suppl 3):S130. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.05.70. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31576337 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
hsa_circ_0000729, a potential prognostic biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Aug;9(8):924-930. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12761. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29932500 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and comprehensive analysis of a ceRNA network to reveal potential prognostic biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jul 23;21(1):849. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08462-8. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34301211 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Plasma Exosomal lncRNA- and circRNA-Based ceRNA Regulatory Network in Patients With Lung Adenocarcinoma.Clin Respir J. 2024 Oct;18(10):e70026. doi: 10.1111/crj.70026. Clin Respir J. 2024. PMID: 39428538 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the association between circRNA expression and pediatric obesity based on a case-control study and related bioinformatics analysis.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Nov 13;23(1):561. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04261-1. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37957626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of circular RNAs and their potential applications in gastric cancer.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Feb;14(2):85-92. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2020.1715211. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31922886 Review.
Cited by
-
The diagnostic significance of blood-derived circRNAs in NSCLC: Systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 24;12:987704. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.987704. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36353543 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Implications of Circulating Circular RNAs in Lung Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 8;10(4):871. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040871. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insight into circRNAs: characterization, strategies, and biomedical applications.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023 Oct 12;12(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s40164-023-00451-w. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37828589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs in Lung Cancer: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 6;11:664290. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.664290. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34295810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of using blood circular RNA as liquid biopsy biomarker for human diseases.Protein Cell. 2021 Dec;12(12):911-946. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00799-3. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Protein Cell. 2021. PMID: 33131025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2018CXGC1212/Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Shandong Province/International
- 2014GSF118084/Science and Technology Foundation of Shandong Province/International
- 2016GSF121043/Science and Technology Foundation of Shandong Province/International
- 201805002/Medical and Health Technology Innovation Plan of Ji'nan City/International
- 81372333/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

