Soluble Fc-Disabled Herpes Virus Entry Mediator Augments Activation and Cytotoxicity of NK Cells by Promoting Cross-Talk between NK Cells and Monocytes
- PMID: 30770415
- PMCID: PMC6424646
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801449
Soluble Fc-Disabled Herpes Virus Entry Mediator Augments Activation and Cytotoxicity of NK Cells by Promoting Cross-Talk between NK Cells and Monocytes
Abstract
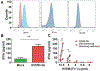
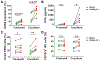
CD160 is highly expressed by NK cells and is associated with cytolytic effector activity. Herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM) activates NK cells for cytokine production and cytolytic function via CD160. Fc-fusions are a well-established class of therapeutics, where the Fc domain provides additional biological and pharmacological properties to the fusion protein including enhanced serum t 1/2 and interaction with Fc receptor-expressing immune cells. We evaluated the specific function of HVEM in regulating CD160-mediated NK cell effector function by generating a fusion of the HVEM extracellular domain with human IgG1 Fc bearing CD16-binding mutations (Fc*) resulting in HVEM-(Fc*). HVEM-(Fc*) displayed reduced binding to the Fc receptor CD16 (i.e., Fc-disabled HVEM), which limited Fc receptor-induced responses. HVEM-(Fc*) functional activity was compared with HVEM-Fc containing the wild type human IgG1 Fc. HVEM-(Fc*) treatment of NK cells and PBMCs caused greater IFN-γ production, enhanced cytotoxicity, reduced NK fratricide, and no change in CD16 expression on human NK cells compared with HVEM-Fc. HVEM-(Fc*) treatment of monocytes or PBMCs enhanced the expression level of CD80, CD83, and CD40 expression on monocytes. HVEM-(Fc*)-enhanced NK cell activation and cytotoxicity were promoted via cross-talk between NK cells and monocytes that was driven by cell-cell contact. In this study, we have shown that soluble Fc-disabled HVEM-(Fc*) augments NK cell activation, IFN-γ production, and cytotoxicity of NK cells without inducing NK cell fratricide by promoting cross-talk between NK cells and monocytes without Fc receptor-induced effects. Soluble Fc-disabled HVEM-(Fc*) may be considered as a research and potentially therapeutic reagent for modulating immune responses via sole activation of HVEM receptors.
Copyright © 2019 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures

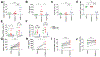
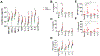
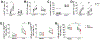
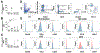
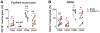
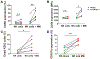
Similar articles
-
CD160 activation by herpesvirus entry mediator augments inflammatory cytokine production and cytolytic function by NK cells.J Immunol. 2013 Jul 15;191(2):828-36. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300894. Epub 2013 Jun 12. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23761635 Free PMC article.
-
Unconventional ligand activation of herpesvirus entry mediator signals cell survival.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Apr 14;106(15):6244-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902115106. Epub 2009 Mar 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19332782 Free PMC article.
-
CD160 isoforms and regulation of CD4 and CD8 T-cell responses.J Transl Med. 2014 Sep 2;12:217. doi: 10.1186/s12967-014-0217-y. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 25179432 Free PMC article.
-
The CD160, BTLA, LIGHT/HVEM pathway: a bidirectional switch regulating T-cell activation.Immunol Rev. 2009 May;229(1):244-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00783.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19426226 Review.
-
The signaling networks of the herpesvirus entry mediator (TNFRSF14) in immune regulation.Immunol Rev. 2011 Nov;244(1):169-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01064.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22017438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fauci AS, Mavilio D, and Kottilil S. 2005. NK cells in HIV infection: paradigm for protection or targets for ambush. Nat Rev Immunol 5: 835–843. - PubMed
-
- Pahl J, and Cerwenka A. 2017. Tricking the balance: NK cells in anti-cancer immunity. Immunobiology 222: 11–20. - PubMed
-
- Fang F, Xiao W, and Tian Z. 2017. NK cell-based immunotherapy for cancer. Semin Immunol 31: 37–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

