Targeting the BIR Domains of Inhibitor of Apoptosis (IAP) Proteins in Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 30766663
- PMCID: PMC6360406
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.01.009
Targeting the BIR Domains of Inhibitor of Apoptosis (IAP) Proteins in Cancer Treatment
Abstract
Inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) proteins are characterized by the presence of the conserved baculoviral IAP repeat (BIR) domain that is involved in protein-protein interactions. IAPs were initially thought to be mainly responsible for caspase inhibition, acting as negative regulators of apoptosis, but later works have shown that IAPs also control a plethora of other different cellular pathways. As X-linked IAP (XIAP), and other IAP, levels are often deregulated in cancer cells and have been shown to correlate with patients' prognosis, several approaches have been pursued to inhibit their activity in order to restore apoptosis. Many small molecules have been designed to target the BIR domains, the vast majority being inspired by the N-terminal tetrapeptide of Second Mitochondria-derived Activator of Caspases/Direct IAp Binding with Low pI (Smac/Diablo), which is the natural XIAP antagonist. These compounds are therefore usually referred to as Smac mimetics (SMs). Despite the fact that SMs were intended to specifically target XIAP, it has been shown that they also interact with cellular IAP-1 (cIAP1) and cIAP2, promoting their proteasome-dependent degradation. SMs have been tested in combination with several cytotoxic compounds and are now considered promising immune modulators which can be exploited in cancer therapy, especially in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors. In this review, we give an overview of the structural hot-spots of BIRs, focusing on their fold and on the peculiar structural patches which characterize the diverse BIRs. These structures are exploited/exploitable for the development of specific and active IAP inhibitors.
Figures
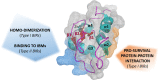

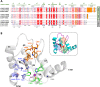
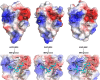

Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and biological activity of a potent Smac mimetic that sensitizes cancer cells to apoptosis by antagonizing IAPs.ACS Chem Biol. 2006 Sep 19;1(8):525-33. doi: 10.1021/cb600276q. ACS Chem Biol. 2006. PMID: 17168540
-
Structure-based design and molecular profiling of Smac-mimetics selective for cellular IAPs.FEBS J. 2018 Sep;285(17):3286-3298. doi: 10.1111/febs.14616. Epub 2018 Aug 16. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 30055105
-
Targeting the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein through 4-substituted azabicyclo[5.3.0]alkane smac mimetics. Structure, activity, and recognition principles.J Mol Biol. 2008 Dec 19;384(3):673-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.064. Epub 2008 Oct 7. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18851976
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein - a critical death resistance regulator and therapeutic target for personalized cancer therapy.Front Oncol. 2014 Jul 28;4:197. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00197. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25120954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) as potential molecular targets for therapy of hematological malignancies.Curr Mol Med. 2011 Nov;11(8):633-49. doi: 10.2174/156652411797536723. Curr Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21902653 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in Anticancer Drug Development Targeting Ubiquitination-Related Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 1;23(23):15104. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315104. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol as a modulatory of apoptosis and autophagy in cancer therapy.Clin Transl Oncol. 2022 Jul;24(7):1219-1230. doi: 10.1007/s12094-021-02770-y. Epub 2022 Jan 17. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35038152 Review.
-
SMAC mimetic birinapant inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth by activating the cIAP1/TRAF3 signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Mar;21(3):1251-1257. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.10908. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 31922244 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitination and deubiquitination in cancer: from mechanisms to novel therapeutic approaches.Mol Cancer. 2024 Jul 25;23(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02046-3. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39048965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SMAC Mimetics for the Treatment of Lung Carcinoma: Present Development and Future Prospects.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(14):1334-1352. doi: 10.2174/0113895575269644231120104501. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38275029 Review.
References
-
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Rothe M., Pan M.G., Henzel W.J., Ayres T.M., Goeddel D.V. The TNFR2-TRAF signaling complex contains two novel proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. Cell. 1995;83:1243–1252. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
