Connexin and Pannexin-Based Channels in Oligodendrocytes: Implications in Brain Health and Disease
- PMID: 30760982
- PMCID: PMC6361860
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00003
Connexin and Pannexin-Based Channels in Oligodendrocytes: Implications in Brain Health and Disease
Abstract
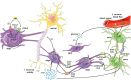
Oligodendrocytes are the myelin forming cells in the central nervous system (CNS). In addition to this main physiological function, these cells play key roles by providing energy substrates to neurons as well as information required to sustain proper synaptic transmission and plasticity at the CNS. The latter requires a fine coordinated intercellular communication with neurons and other glial cell types, including astrocytes. In mammals, tissue synchronization is mainly mediated by connexins and pannexins, two protein families that underpin the communication among neighboring cells through the formation of different plasma membrane channels. At one end, gap junction channels (GJCs; which are exclusively formed by connexins in vertebrates) connect the cytoplasm of contacting cells allowing electrical and metabolic coupling. At the other end, hemichannels and pannexons (which are formed by connexins and pannexins, respectively) communicate the intra- and extracellular compartments, serving as diffusion pathways of ions and small molecules. Here, we briefly review the current knowledge about the expression and function of hemichannels, pannexons and GJCs in oligodendrocytes, as well as the evidence regarding the possible role of these channels in metabolic and synaptic functions at the CNS. In particular, we focus on oligodendrocyte-astrocyte coupling during axon metabolic support and its implications in brain health and disease.
Keywords: connexons; demyelinating neuropathy; gap junctions; hemichannels; oligodendrocytes; pannexons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Connexins and Pannexins: New Insights into Microglial Functions and Dysfunctions.Front Mol Neurosci. 2016 Sep 22;9:86. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00086. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27713688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gap junction channels and hemichannels in the CNS: regulation by signaling molecules.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Dec;75:567-82. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.02.020. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23499663 Review.
-
Role of connexins and pannexins in ischemic stroke.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(19):2165-82. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666131228191714. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24372216 Review.
-
Connexons and pannexons: newcomers in neurophysiology.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Nov 4;8:348. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00348. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25408635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hemichannels in the neurovascular unit and white matter under normal and inflamed conditions.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011 May;10(3):404-14. doi: 10.2174/187152711794653869. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21288190 Review.
Cited by
-
Connexins-Based Hemichannels/Channels and Their Relationship with Inflammation, Seizures and Epilepsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 27;20(23):5976. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235976. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31783599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular Environment Remodels the Genomic Fabrics of Functional Pathways in Astrocytes.Genes (Basel). 2020 May 7;11(5):520. doi: 10.3390/genes11050520. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32392822 Free PMC article.
-
Tau Isoform-Driven CBD Pathology Transmission in Oligodendrocytes in Humanized Tau Mice.Front Neurol. 2021 Jan 15;11:589471. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.589471. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33519674 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Disorders and Chemical Pollutants: A Gap Junction Link?Biomolecules. 2020 Dec 31;11(1):51. doi: 10.3390/biom11010051. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33396565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple sclerosis iPS-derived oligodendroglia conserve their properties to functionally interact with axons and glia in vivo.Sci Adv. 2020 Dec 4;6(49):eabc6983. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc6983. Print 2020 Dec. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 33277253 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

