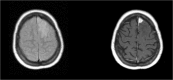
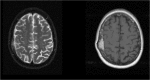
The association between preoperative edema and postoperative cognitive functioning and health-related quality of life in WHO grade I meningioma patients
- PMID: 30756243
- PMCID: PMC6407739
- DOI: 10.1007/s00701-019-03819-2
The association between preoperative edema and postoperative cognitive functioning and health-related quality of life in WHO grade I meningioma patients
Abstract
Background: Studies on the associations between preoperative cerebral edema, cognitive functioning, and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in WHO grade I meningioma patients are virtually lacking. We studied the association between preoperative cerebral edema on postoperative cognitive functioning and HRQOL 6 months postoperatively in WHO grade I meningioma patients.
Methods: Twenty-one consecutive WHO grade I meningioma patients, who underwent surgery, were matched individually for age, gender, and educational level to healthy controls. Tumor and edema volume were assessed on preoperative T1- and T2-weighted MRI images, respectively. At least 5 months postoperatively, functional status, cognitive functioning, and HRQOL, using a cognitive test battery and the Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36), were determined. The correlation between preoperative tumor and cerebral edema volume with postoperative cognitive functioning and HRQOL was investigated using Kendall's tau coefficients.
Results: Compared to healthy controls, patients had lower verbal memory capacity (p = .012), whereas HRQOL was similar to matched healthy controls. In all cognitive domains, postoperative functioning was much lower in patients with preoperative cerebral edema than in those without. There were significant correlations between preoperative cerebral edema and tumor volume and postoperative cognitive functioning. Preoperative cerebral edema and/or tumor volume were not associated with HRQOL.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that WHO grade I meningioma patients with larger volumes of preoperative cerebral edema are more at risk of experiencing limitations in longer-term cognitive functioning than patients with no or less edema preoperatively. This is an important knowledge for neurologists and neurosurgeons treating patients with a meningioma. More studies regarding the effect of peritumoral edema on cognitive functioning in meningioma patients are necessary.
Keywords: Brain edema; Cognition; Counseling; Meningioma; Quality of life; Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain invasion and the risk of seizures in patients with meningioma.J Neurosurg. 2019 Mar 1;130(3):789-796. doi: 10.3171/2017.11.JNS172265. Epub 2018 Apr 27. J Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 29701550
-
Differential effect of surgery and radiotherapy on neurocognitive functioning and health-related quality of life in WHO grade I meningioma patients.J Neurooncol. 2007 Sep;84(3):271-8. doi: 10.1007/s11060-007-9366-7. Epub 2007 Apr 13. J Neurooncol. 2007. PMID: 17431545
-
Neurocognitive Function Surrounding the Resection of Frontal WHO Grade I Meningiomas: A Prospective Matched-Control Study.World Neurosurg. 2017 Feb;98:203-210. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.10.095. Epub 2016 Oct 27. World Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 27989970
-
Cognitive functioning in meningioma patients: a systematic review.J Neurooncol. 2016 Jun;128(2):195-205. doi: 10.1007/s11060-016-2115-z. Epub 2016 Apr 5. J Neurooncol. 2016. PMID: 27048208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seizures in meningioma.Handb Clin Neurol. 2020;170:187-200. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-822198-3.00053-7. Handb Clin Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32586490 Review.
Cited by
-
Peritumoral edema correlates with mutational burden in meningiomas.Neuroradiology. 2021 Jan;63(1):73-80. doi: 10.1007/s00234-020-02515-8. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Neuroradiology. 2021. PMID: 32789536
-
Efficacy of Bevacizumab in High-Grade Meningiomas: A Retrospective Clinical Study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022 Aug 6;18:1619-1627. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S368740. eCollection 2022. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022. PMID: 35968510 Free PMC article.
-
The APOE ε4 allele in relation to pre- and postsurgical cognitive functioning of patients with primary brain tumors.Eur J Neurol. 2021 May;28(5):1665-1676. doi: 10.1111/ene.14693. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Eur J Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33342004 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple meningiomas: Epidemiology, management, and outcomes.Neurooncol Adv. 2023 Jun 3;5(Suppl 1):i35-i48. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdac108. eCollection 2023 May. Neurooncol Adv. 2023. PMID: 37287575 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological Burden in Meningioma Patients under a Wait-and-Watch Strategy and after Complete Resection Is High-Results of a Prospective Single Center Study.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 25;12(12):3503. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123503. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33255551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aaronson NK, Muller M, Cohen PD, Essink-Bot ML, Fekkes M, Sanderman R, Sprangers MA, te Velde A, Verrips E. Translation, validation, and norming of the Dutch language version of the SF-36 Health Survey in community and chronic disease populations. J Clin Epidemiol. 1998;51:1055–1068. doi: 10.1016/S0895-4356(98)00097-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Bie S. Standard questions 1987: proposal for uniformization of questions regarding background variables and interviews [Standaardvragen 1987: Voorstellen voor uniformering van vraagstellingen naar achtergrondkenmerken en interviews] 2. Leiden: Leiden University Press; 1987.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical