MicroRNA-24 promotes pancreatic beta cells toward dedifferentiation to avoid endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 30753517
- PMCID: PMC6821228
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz004
MicroRNA-24 promotes pancreatic beta cells toward dedifferentiation to avoid endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis
Abstract
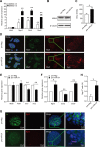
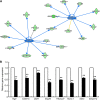
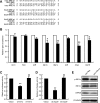
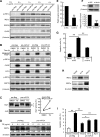
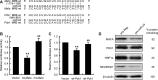
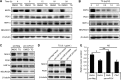
Current research indicates that beta cell loss in type 2 diabetes may be attributed to beta cell dedifferentiation rather than apoptosis; however, the mechanisms by which this occurs remain poorly understood. Our previous study demonstrated that elevation of microRNA-24 (miR-24) in a diabetic setting caused beta cell dysfunction and replicative deficiency. In this study, we focused on the role of miR-24 in beta cell apoptosis and dedifferentiation under endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress conditions. We found that miR-24 overabundance protected beta cells from thapsigargin-induced apoptosis at the cost of accelerating the impairment of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) and enhancing the presence of dedifferentiation markers. Ingenuity® Pathway Analysis (IPA) revealed that elevation of miR-24 had an inhibitory effect on XBP1 and ATF4, which are downstream effectors of two key branches of ER stress, by inhibiting its direct target, Ire1α. Notably, elevated miR-24 initiated another pathway that targeted Mafa and decreased GSIS function in surviving beta cells, thus guiding their dedifferentiation under ER stress conditions. Our results demonstrated that the elevated miR-24, to the utmost extent, preserves beta cell mass by inhibiting apoptosis and inducing dedifferentiation. This study not only provides a novel mechanism by which miR-24 dominates beta cell turnover under persistent metabolic stress but also offers a therapeutic consideration for treating diabetes by inducing dedifferentiated beta cells to re-differentiation.
Keywords: ER stress; apoptosis; dedifferentiation; microRNA-24; pancreatic beta cells; type 2 diabetes.
© The Author(s) (2019). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, IBCB, SIBS, CAS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The miR-200-Zeb1 axis regulates key aspects of β-cell function and survival in vivo.Mol Metab. 2021 Nov;53:101267. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101267. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34116231 Free PMC article.
-
A novel secretagogin/ATF4 pathway is involved in oxidized LDL-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and islet β-cell apoptosis.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Jan 12;53(1):54-62. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmaa142. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 33289795
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to NMDA-induced pancreatic β-cell dysfunction in a CHOP-dependent manner.Life Sci. 2019 Sep 1;232:116612. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116612. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31260687
-
A Brief Review of the Mechanisms of β-Cell Dedifferentiation in Type 2 Diabetes.Nutrients. 2021 May 10;13(5):1593. doi: 10.3390/nu13051593. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34068827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of β-cell dedifferentiation in diabetes: recent findings and future research directions.J Endocrinol. 2018 Feb;236(2):R109-R143. doi: 10.1530/JOE-17-0516. Epub 2017 Dec 4. J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29203573 Review.
Cited by
-
The Plasticity of Pancreatic β-Cells.Metabolites. 2021 Apr 2;11(4):218. doi: 10.3390/metabo11040218. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 33918379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MafA Regulation in β-Cells: From Transcriptional to Post-Translational Mechanisms.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 31;12(4):535. doi: 10.3390/biom12040535. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35454124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs Signature for Predicting Response to GLP1-RA Therapy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Pilot Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 31;22(17):9454. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179454. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502360 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-24 therapeutic potentials in infarction, stroke, and diabetic complications.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Nov 9;51(1):1137. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10089-4. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39520600 Review.
-
Targeting β-cell dedifferentiation and transdifferentiation: opportunities and challenges.Endocr Connect. 2021 Aug 13;10(8):R213-R228. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0260. Endocr Connect. 2021. PMID: 34289444 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allagnat F., Christulia F., Ortis F., et al. . (2010). Sustained production of spliced X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) induces pancreatic β cell dysfunction and apoptosis. Diabetologia 53, 1120–1130. - PubMed
-
- Biden T.J., Boslem E., Chu K.Y., et al. . (2014). Lipotoxic endoplasmic reticulum stress, β cell failure, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 25, 389–398. - PubMed
-
- Brown J.R., and Sanseau P. (2005). A computational view of microRNAs and their targets. Drug Discov. Today 10, 595–601. - PubMed

