[Theranostics of osteosarcoma and lung metastasis with new integrin α vβ 3 receptor targeted radiotracers]
- PMID: 30739410
- PMCID: PMC8337618
- DOI: 10.7507/1002-1892.201808014
[Theranostics of osteosarcoma and lung metastasis with new integrin α vβ 3 receptor targeted radiotracers]
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the value of integrin α vβ 3 targeted microPET/CT imaging with 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 as radiotracer for the detection of osteosarcoma and theranostics of osteosarcoma lung metastasis.
Methods: The 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 and 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2 were prepared via one-step method and their stability and integrin α vβ 3 binding specificity were investigated in vitro. Forty-one nude mice were injected with human MG63 osteosarcoma to established the animal model bearing subcutaneous osteosarcoma ( n=21), osteosarcoma in tibia ( n=5), and osteosarcoma pulmonary metastatic ( n=15). The microPET-CT imaging was carried out in 3 animal models at 1 hour after tail vein injection of 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2. Biodistribution study of 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 was performed in animal model bearing subcutaneous osteosarcoma at 10, 60, and 120 minutes. The animal model bearing pulmonary metastatic osteosarcoma was injected with 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2 at 7 weeks after model establishment to observe the therapeutic effect of pulmonary metastatic osteosarcoma. Histological and immunohistochemistry examinations were also done to confirm the establishment of animal model and integrin β 3 expression in animal models bearing subcutaneous osteosarcoma and bearing pulmonary metastatic osteosarcoma.
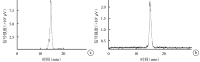
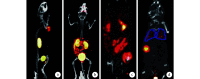
Results: 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 and 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2 had good stability in vitro with the 50% inhibitory concentration value of (5.0±1.1) and (6.5±0.8) nmol/L, respectively. The radiochemical purity of 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 at 1, 4, and 8 hours was 98.5%±0.3%, 98.3%±0.5%, and 97.9%±0.4%; while the radiochemical purity of 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2 at 1, 7, and 14 days was 99.3%±0.7%, 98.7%±1.2%, and 96.0%±2.8%. 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 microPET-CT showed that the accumulation of 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 in animal models bearing subcutaneous osteosarcoma and osteosarcoma in tibia and in lung metastasis as small as 1-2 mm in diameter of animal model bearing pulmonary metastatic osteosarcoma. Biodistribution study of 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 in animal model bearing subcutaneous osteosarcoma revealed rapid clearance from blood with tumor peak uptake of (3.85±0.84) %ID/g at 120 minutes. The distribution of 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2 in lung metastasis was similar with 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2. The number and size of osteosarcoma metastasis decreased at 2 weeks after 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2 administration and integrin targeting specificity was confirmed by pathology examination.
Conclusion: 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 was potential for positive imaging and early detection of osteosarcoma and metastasis. Targeted radiotherapy with 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2 was one potential alternative for osteosarcoma lung metastasis.
目的: 初步探讨整合素 α vβ 3 受体靶向显像诊断骨肉瘤及肺转移病灶及其靶向内放射性治疗肺转移病灶的价值。.
方法: 一步法制备 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 和 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2,体外检测其放射性比活度、放射性化学纯度(Radio-HPLC 法)和整合素 α vβ 3 受体靶向特异性。取 41 只裸鼠经皮下、胫骨髓腔及尾静脉注射 MG63 人骨肉瘤细胞,分别构建皮下骨肉瘤( n=21)、原位骨肉瘤( n=5)以及骨肉瘤肺转移( n=15)模型。3 种骨肉瘤动物模型于尾静脉注射 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2,1 h 后行 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 microPET/CT 显像;皮下骨肉瘤模型注射后 10、60、120 min,取重要脏器及肿瘤组织,行 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 生物学分布研究。骨肉瘤肺转移灶模型于细胞注射后 7 周经尾静脉注射 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2,观察其靶向治疗骨肉瘤肺转移效果。同时,取原位骨肉瘤模型胫骨骨肉瘤组织以及骨肉瘤肺转移模型的荷瘤肺组织行组织学及免疫组织化学染色观察。.
结果: 体外稳定性实验显示, 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 体外合成后 1、4、8 h,放射性化学纯度分别为 98.5%±0.3%、98.3%±0.5%、97.9%±0.4%。 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2 体外合成后 1、7、14 d,放射性化学纯度分别为 99.3%±0.7%、98.7%±1.2%、96.0%±2.8%。 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 及 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2 整合素 α vβ 3 受体结合实验半抑制浓度率值分别为(5.0±1.1)、(6.5±0.8)nmol/L。microPET-CT 显像,皮下骨肉瘤模型及原位骨肉瘤模型均可见明显 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 浓聚;骨肉瘤肺转移模型在转移灶 1~2 mm 时即可见 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 浓聚。生物学分布实验显示,皮下骨肉瘤模型中 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 血液中清除迅速,肌肉、正常骨骼摄取极少,注入 120 min 时达峰值,为(3.85±0.84)%ID/g。骨肉瘤肺转移灶模型注射 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2 后显示其在肺转移灶浓聚,第 2 周病灶数量和大小明显降低。组织学及免疫组织化学染色结果显示肿瘤形成及其整合素受体靶向性。.
结论: 68Ga-NODAGA-RGD 2 显像可有效探测骨肉瘤及其肺转移灶,为 177Lu-NODAGA-RGD 2 用于骨肉瘤肺转移的靶向治疗提供实验依据。.
Keywords: Integrin αvβ3; Osteosarcoma; lung metastasis; targeted endotheranostics.
Figures
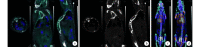


Similar articles
-
[68Ga]NODAGA-RGD for imaging αvβ3 integrin expression.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011 Jul;38(7):1303-12. doi: 10.1007/s00259-011-1778-0. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011. PMID: 21487838
-
Pegylated Arg-Gly-Asp peptide: 64Cu labeling and PET imaging of brain tumor alphavbeta3-integrin expression.J Nucl Med. 2004 Oct;45(10):1776-83. J Nucl Med. 2004. PMID: 15471848
-
Evaluation of an Integrin αvβ3 and Aminopeptidase N Dual-Receptor Targeting Tracer for Breast Cancer Imaging.Mol Pharm. 2020 Jan 6;17(1):349-358. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b01134. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31829615 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of two new angiogenesis PET tracers 68Ga-NODAGA-E[c(RGDyK)]2 and (64)Cu-NODAGA-E[c(RGDyK)]2; in vivo imaging studies in human xenograft tumors.Nucl Med Biol. 2014 Mar;41(3):259-67. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Nucl Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 24417983
-
64Cu-1,4,7-Triazacyclononane,1-glutaric acid-4,7-acetic acid-cyclo(Arg-Gly-Asp-d-Tyr-Lys).2013 Mar 28 [updated 2013 Jun 6]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2013 Mar 28 [updated 2013 Jun 6]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 23741768 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Imaging of pediatric bone tumors: A COG Diagnostic Imaging Committee/SPR Oncology Committee White Paper.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2023 Jun;70 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):e30000. doi: 10.1002/pbc.30000. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36250990 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Bielack SS, Hecker-Nolting S, Blattmann C, et al. Advances in the management of osteosarcoma.(2016-11-25).[2018-01-04] https://f1000research.com/articles/5-2767/v1
-
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
