The Legionella effector RavD binds phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate and helps suppress endolysosomal maturation of the Legionella-containing vacuole
- PMID: 30733336
- PMCID: PMC6484141
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.007086
The Legionella effector RavD binds phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate and helps suppress endolysosomal maturation of the Legionella-containing vacuole
Abstract
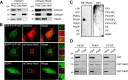
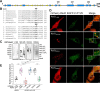
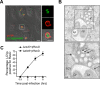
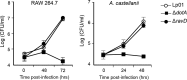
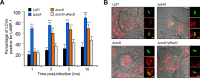
Upon phagocytosis into macrophages, the intracellular bacterial pathogen Legionella pneumophila secretes effector proteins that manipulate host cell components, enabling it to evade lysosomal degradation. However, the bacterial proteins involved in this evasion are incompletely characterized. Here we show that the L. pneumophila effector protein RavD targets host membrane compartments and contributes to the molecular mechanism the pathogen uses to prevent encounters with lysosomes. Protein-lipid binding assays revealed that RavD selectively binds phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI(3)P) in vitro We further determined that a C-terminal RavD region mediates the interaction with PI(3)P and that this interaction requires Arg-292. In transiently transfected mammalian cells, mCherry-RavD colocalized with the early endosome marker EGFP-Rab5 as well as the PI(3)P biosensor EGFP-2×FYVE. However, treatment with the phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor wortmannin did not disrupt localization of mCherry-RavD to endosomal compartments, suggesting that RavD's interaction with PI(3)P is not necessary to anchor RavD to endosomal membranes. Using superresolution and immunogold transmission EM, we observed that, upon translocation into macrophages, RavD was retained onto the Legionella-containing vacuole and was also present on small vesicles adjacent to the vacuole. We also report that despite no detectable effects on intracellular growth of L. pneumophila within macrophages or amebae, the lack of RavD significantly increased the number of vacuoles that accumulate the late endosome/lysosome marker LAMP-1 during macrophage infection. Together, our findings suggest that, although not required for intracellular replication of L. pneumophila, RavD is a part of the molecular mechanism that steers the Legionella-containing vacuole away from endolysosomal maturation pathways.
Keywords: Legionella pneumophila; Legionnaires' disease; bacterial effectors; bacterial pathogenesis; cellular localization; host–pathogen interaction; immune evasion; infection; phosphoinositide; virulence factor.
© 2019 Pike et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health
Figures
Similar articles
-
Legionella Effector AnkX Disrupts Host Cell Endocytic Recycling in a Phosphocholination-Dependent Manner.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Sep 8;7:397. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00397. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28944216 Free PMC article.
-
Legionella eukaryotic-like type IV substrates interfere with organelle trafficking.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Aug 1;4(8):e1000117. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000117. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18670632 Free PMC article.
-
Rab1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor SidM is a major phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate-binding effector protein of Legionella pneumophila.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 20;284(8):4846-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807505200. Epub 2008 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19095644 Free PMC article.
-
The road less traveled: transport of Legionella to the endoplasmic reticulum.J Cell Biol. 2002 Aug 5;158(3):415-9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200205011. Epub 2002 Jul 29. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12147677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoinositides and the Fate of Legionella in Phagocytes.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 30;11:25. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00025. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32117224 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural insight into the membrane targeting domain of the Legionella deAMPylase SidD.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Aug 27;16(8):e1008734. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008734. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32853279 Free PMC article.
-
Study of Legionella Effector Domains Revealed Novel and Prevalent Phosphatidylinositol 3-Phosphate Binding Domains.Infect Immun. 2019 May 21;87(6):e00153-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00153-19. Print 2019 Jun. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 30962397 Free PMC article.
-
Divergence of Legionella Effectors Reversing Conventional and Unconventional Ubiquitination.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Aug 21;10:448. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00448. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32974222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploitation of the Host Ubiquitin System: Means by Legionella pneumophila.Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 22;12:790442. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.790442. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 35003021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Indispensable Role for the MavE Effector of Legionella pneumophila in Lysosomal Evasion.mBio. 2021 Feb 9;12(1):e03458-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03458-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33563829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Copenhaver A. M., Casson C. N., Nguyen H. T., Fung T. C., Duda M. M., Roy C. R., and Shin S. (2014) Alveolar macrophages and neutrophils are the primary reservoirs for Legionella pneumophila and mediate cytosolic surveillance of type IV secretion. Infect. Immun. 82, 4325–4336 10.1128/IAI.01891-14 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clemens D. L., Lee B. Y., and Horwitz M. A. (2000) Deviant expression of Rab5 on phagosomes containing the intracellular pathogens Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Legionella pneumophila is associated with altered phagosomal fate. Infect. Immun. 68, 2671–2684 10.1128/IAI.68.5.2671-2684.2000 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

