Yangyin Yiqi Mixture Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats through Inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad Pathway and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition
- PMID: 30719057
- PMCID: PMC6335662
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/2710509
Yangyin Yiqi Mixture Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats through Inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad Pathway and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the current study was to investigate the protective effect of Yangyin Yiqi Mixture (YYYQ) on Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats based on TGF-β1/Smad signal pathway and epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT).
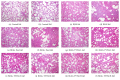
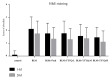
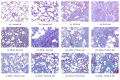
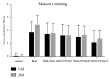
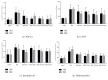
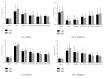
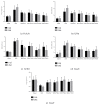
Methods: 120 Wistar rats were randomly divided into six groups: control group, BLM group, BLM + Pred group, BLM+YYYQ-L group, BLM+YYYQ-M group, and BLM+YYYQ-H group. Rats were given an intratracheal instillation of 3 mg/kg BLM to establish the pulmonary fibrosis model and followed by different dosages of YYYQ (11, 22, 44g/kg, via intragastric gavage) or prednisone soluble (4.2mg/kg, via intragastric gavage) or water. After 14 days and 28 days, tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin-eosin and Masson's trichrome to observe histopathological changes. Protein levels of TGF-β1, CTGF, Interleukin 18, and hydroxyproline were detected by ELISA method, and mRNA expressions of TGF-β1, TβRI, TβRII, Smad3, Smad7, α-SMA, E-cadherin, laminin, and collagen I were detected by RT-PCR.
Results: TGF-β1, CTGF, Interleukin 18, and hydroxyproline levels and mRNA expression of TGF-β1, TβRI, TβRII, Smad3, α-SMA, laminin, and collagen I were significantly increased (p <0.01), while Smad7 and E-cadherin levels were significantly decreased in BLM group (p <0.01). YYYQ-M and YYYQ-H group had downregulated the TGF-β1, CTGF, hydroxyproline contents, and mRNA expression of TGF-β1, TβRI, TβRII, Smad3, α-SMA, laminin, and collagen I and upregulated mRNA levels of Smad7 and E-cadherin significantly (p <0.01 or p <0.05). The result from the present study, which was also supported by histological evidence, suggested that YYYQ-M group and YYYQ-H group exhibited better treatment effect on Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrotic rats when compared to that of BLM + Pred group (p <0.01). Meanwhile, the effect of YYYQ, in three different dosages, on the level of interleukin 18 was not significant.
Conclusion: These results showed that YYYQ has the potential of ameliorating the progression of pulmonary fibrosis, and the mechanism may be related to suppressing TGF-β1/Smad signal pathway and EMT in BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis of rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydrogen inhalation attenuated bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting transforming growth factor-β1 and relevant oxidative stress and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Exp Physiol. 2019 Dec;104(12):1942-1951. doi: 10.1113/EP088028. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Exp Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31535412
-
GHK Peptide Inhibits Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice by Suppressing TGFβ1/Smad-Mediated Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Dec 12;8:904. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00904. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29311918 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane attenuates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Apr 2;19(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40360-018-0204-7. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29609658 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of andrographolide on the concentration of cytokines in BALF and the expressions of type I and III collagen mRNA in lung tissue in bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Jul;27(7):725-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21722520 Chinese.
-
[Anti-fibrotic effects of angiotensin1-7 on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013 May 28;93(20):1585-9. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24028731 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Role of nuclear factor-kappa B in bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis and the probable alleviating role of ginsenoside: histological, immunohistochemical, and biochemical study.Anat Cell Biol. 2021 Dec 31;54(4):448-464. doi: 10.5115/acb.21.068. Anat Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34936986 Free PMC article.
-
Scorpion Venom Polypeptide Inhibits Pulmonary Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Systemic Sclerosis-Interstitial Lung Disease Model Mice by Intervening TGF-β1/Smad Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Apr 13;2022:6557486. doi: 10.1155/2022/6557486. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35463079 Free PMC article.
-
From Basic Research to Clinical Practice: Considerations for Treatment Drugs for Silicosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 5;24(9):8333. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098333. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-200a inversely correlates with Hedgehog and TGF-β canonical/non-canonical trajectories to orchestrate the anti-fibrotic effect of Tadalafil in a bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis model.Inflammopharmacology. 2021 Feb;29(1):167-182. doi: 10.1007/s10787-020-00748-w. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Inflammopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 32914382
-
Natural Product-Based Potential Therapeutic Interventions of Pulmonary Fibrosis.Molecules. 2022 Feb 22;27(5):1481. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051481. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35268581 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

