Mesenchymal Stem Cells-derived Exosomes: A New Possible Therapeutic Strategy for Parkinson's Disease?
- PMID: 30717429
- PMCID: PMC6406999
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8020118
Mesenchymal Stem Cells-derived Exosomes: A New Possible Therapeutic Strategy for Parkinson's Disease?
Abstract
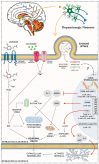
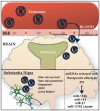
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder worldwide. Clinically, it is characterized by severe motor complications caused by a progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons (DAn) and dopamine loss. Current treatment is focused on mitigating the symptoms through administration of levodopa, rather than on preventing DAn damage. Therefore, the use and development of neuroprotective/disease-modifying strategies is an absolute need, which can lead to promising gains on PD translational research. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)⁻derived exosomes have been proposed as a promising therapeutic tool, since it has been demonstrated that they can act as biological nanoparticles with beneficial effects in different pathological conditions, including PD. Thus, considering their potential protective action in lesioned sites, MSCs-derived exosomes might also be active modulators of the neuroregeneration processes, opening a door for their future use as therapeutical strategies in human clinical trials. Therefore, in this review, we analyze the current understanding of MSCs-derived exosomes as a new possible therapeutic strategy for PD, by providing an overview about the potential role of miRNAs in the cellular and molecular basis of PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; exosomes; mesenchymal stem cells; microRNAs; secretome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of exosomes in pathogenesis and the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes against Parkinson's disease.Neurol Sci. 2023 Jul;44(7):2277-2289. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06706-y. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36949298 Review.
-
The potential use of mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes in Parkinson's disease treatment.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jul 28;13(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03050-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35902981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Comparison of Stem Cells Secretome and Levodopa Application in a 6-Hydroxydopamine Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease.Cells. 2020 Jan 28;9(2):315. doi: 10.3390/cells9020315. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32012897 Free PMC article.
-
miR-100a-5p-enriched exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance the anti-oxidant effect in a Parkinson's disease model via regulation of Nox4/ROS/Nrf2 signaling.J Transl Med. 2023 Oct 24;21(1):747. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04638-x. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37875930 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome in Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 23;21(15):5241. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155241. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32718092 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of exosomes in pathogenesis and the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes against Parkinson's disease.Neurol Sci. 2023 Jul;44(7):2277-2289. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06706-y. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36949298 Review.
-
Potential Roles of Exosomes in Parkinson's Disease: From Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment to Prognosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Feb 21;8:86. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00086. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32154247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate Parkinson's disease and neuronal damage through inhibition of microglia.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Oct;18(10):2291-2300. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.368300. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 37056150 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Towards Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2917. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032917. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conditioned Medium of Human Menstrual Blood-Derived Endometrial Stem Cells Protects Against MPP+-Induced Cytotoxicity in vitro.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Apr 5;12:80. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00080. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31024252 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

