Identification of genes functionally involved in the detrimental effects of mutant histone H3.3-K27M in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 30715493
- PMCID: PMC6502498
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noz021
Identification of genes functionally involved in the detrimental effects of mutant histone H3.3-K27M in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
Background: Recurrent specific mutations in evolutionarily conserved histone 3 (H3) variants drive pediatric high-grade gliomas (HGGs), but little is known about their downstream effects. The aim of this study was to identify genes involved in the detrimental effects of mutant H3.3-K27M, the main genetic driver in lethal midline HGG, in a transgenic Drosophila model.
Methods: Mutant and wild-type histone H3.3-expressing flies were generated using a φC31-based integration system. Genetic modifier screens were performed by crossing H3.3-K27M expressing driver strains and 194 fly lines expressing short hairpin RNA targeting genes selected based on their potential role in the detrimental effects of mutant H3. Expression of the human orthologues of genes with functional relevance in the fly model was validated in H3-K27M mutant HGG.
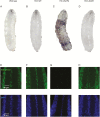
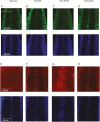
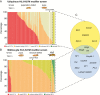
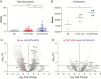
Results: Ubiquitous and midline glia-specific expression of H3.3-K27M but not wild-type H3.3 caused pupal lethality, morphological alterations, and decreased H3K27me3. Knockdown of 17 candidate genes shifted the lethal phenotype to later stages of development. These included histone modifying and chromatin remodeling genes as well as genes regulating cell differentiation and proliferation. Notably, several of these genes were overexpressed in mutant H3-K27M mutated HGG.
Conclusions: Rapid screening, identification, and validation of relevant targets in "oncohistone" mediated pathogenesis have proven a challenge and a barrier to providing novel therapies. Our results provide further evidence on the role of chromatin modifiers in the genesis of H3.3-K27M. Notably, they validate Drosophila as a model system for rapid identification of relevant genes functionally involved in the detrimental effects of H3.3-K27M mutagenesis.
Keywords: PRC2; chromatin remodeling; diffuse midline glioma; histone H3-K27M.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic and epigenetic profiling of 'diffuse midline gliomas, H3 K27M-mutant' discriminate two subgroups based on the type of histone H3 mutated and not supratentorial or infratentorial location.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018 Nov 5;6(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s40478-018-0614-1. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018. PMID: 30396367 Free PMC article.
-
Diffuse high-grade gliomas with H3 K27M mutations carry a dismal prognosis independent of tumor location.Neuro Oncol. 2018 Jan 10;20(1):123-131. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox149. Neuro Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29016894 Free PMC article.
-
H3F3A mutant allele specific imbalance in an aggressive subtype of diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27M-mutant.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020 Feb 5;8(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s40478-020-0882-4. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020. PMID: 32019606 Free PMC article.
-
Oncohistones and disrupted development in pediatric-type diffuse high-grade glioma.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023 Jun;42(2):367-388. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10105-2. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023. PMID: 37119408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone H3 mutations--a special role for H3.3 in tumorigenesis?Chromosoma. 2015 Jun;124(2):177-89. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0510-4. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Chromosoma. 2015. PMID: 25773741 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drosophila melanogaster: a fruitful model for oncohistones.Fly (Austin). 2021 Dec;15(1):28-37. doi: 10.1080/19336934.2020.1863124. Fly (Austin). 2021. PMID: 33423597 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenome Programming by H3.3K27M Mutation Creates a Dependence of Pediatric Glioma on SMARCA4.Cancer Discov. 2022 Dec 2;12(12):2906-2929. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1492. Cancer Discov. 2022. PMID: 36305747 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Efficacy of ONC201 in H3K27M-Mutant Diffuse Midline Gliomas Is Driven by Disruption of Integrated Metabolic and Epigenetic Pathways.Cancer Discov. 2023 Nov 1;13(11):2370-2393. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-23-0131. Cancer Discov. 2023. PMID: 37584601 Free PMC article.
-
The Leukemic Fly: Promises and Challenges.Cells. 2020 Jul 21;9(7):1737. doi: 10.3390/cells9071737. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32708107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutant H3 histones drive human pre-leukemic hematopoietic stem cell expansion and promote leukemic aggressiveness.Nat Commun. 2019 Jun 28;10(1):2891. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10705-z. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31253791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwartzentruber J, Korshunov A, Liu XY, et al. . Driver mutations in histone H3.3 and chromatin remodelling genes in paediatric glioblastoma. Nature. 2012;482(7384):226–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

