Talaromyces marneffei Mp1 Protein, a Novel Virulence Factor, Carries Two Arachidonic Acid-Binding Domains To Suppress Inflammatory Responses in Hosts
- PMID: 30670555
- PMCID: PMC6434130
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00679-18
Talaromyces marneffei Mp1 Protein, a Novel Virulence Factor, Carries Two Arachidonic Acid-Binding Domains To Suppress Inflammatory Responses in Hosts
Abstract
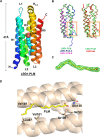
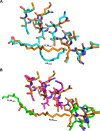
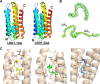
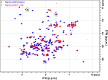
Talaromyces marneffei infection causes talaromycosis (previously known as penicilliosis), a very important opportunistic systematic mycosis in immunocompromised patients. Different virulence mechanisms in T. marneffei have been proposed and investigated. In the sera of patients with talaromycosis, Mp1 protein (Mp1p), a secretory galactomannoprotein antigen with two tandem ligand-binding domains (Mp1p-LBD1 and Mp1p-LBD2), was found to be abundant. Mp1p-LBD2 was reported to possess a hydrophobic cavity to bind copurified palmitic acid (PLM). It was hypothesized that capturing of lipids from human hosts by expressing a large quantity of Mp1p is a virulence mechanism of T. marneffei It was shown that expression of Mp1p enhanced the intracellular survival of T. marneffei by suppressing proinflammatory responses. Mechanistic study of Mp1p-LBD2 suggested that arachidonic acid (AA), a precursor of paracrine signaling molecules for regulation of inflammatory responses, is the major physiological target of Mp1p-LBD2. In this study, we use crystallographic and biochemical techniques to further demonstrate that Mp1p-LBD1, the previously unsolved first lipid binding domain of Mp1p, is also a strong AA-binding domain in Mp1p. These studies on Mp1p-LBD1 support the idea that the highly expressed Mp1p is an effective AA-capturing protein. Each Mp1p can bind up to 4 AA molecules. The crystal structure of Mp1p-LBD1-LBD2 has also been solved, showing that both LBDs are likely to function independently with a flexible linker between them. T. marneffei and potentially other pathogens highly expressing and secreting proteins similar to Mp1p can severely disturb host signaling cascades during proinflammatory responses by reducing the availabilities of important paracrine signaling molecules.
Keywords: X-ray crystallography; arachidonic acid (AA); lipid-protein interaction; nuclear magnetic resonance; virulence factors.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Talaromyces marneffei Mp1p Is a Virulence Factor that Binds and Sequesters a Key Proinflammatory Lipid to Dampen Host Innate Immune Response.Cell Chem Biol. 2017 Feb 16;24(2):182-194. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.12.014. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Cell Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28111099
-
Evolution of the ability to evade host innate immune defense by Talaromyces marneffei.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Dec 31;253(Pt 8):127597. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127597. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37884245
-
Mp1p Is a Virulence Factor in Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016 Aug 25;10(8):e0004907. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004907. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016. PMID: 27560160 Free PMC article.
-
Talaromyces marneffei Genomic, Transcriptomic, Proteomic and Metabolomic Studies Reveal Mechanisms for Environmental Adaptations and Virulence.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Jun 13;9(6):192. doi: 10.3390/toxins9060192. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28608842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Talaromycosis (Penicilliosis) Due to Talaromyces (Penicillium) marneffei: Insights into the Clinical Trends of a Major Fungal Disease 60 Years After the Discovery of the Pathogen.Mycopathologia. 2019 Dec;184(6):709-720. doi: 10.1007/s11046-019-00410-2. Mycopathologia. 2019. PMID: 31811603 Review.
Cited by
-
An Overlooked and Underrated Endemic Mycosis-Talaromycosis and the Pathogenic Fungus Talaromyces marneffei.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2023 Mar 23;36(1):e0005122. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00051-22. Epub 2023 Jan 17. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36648228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary Talaromycosis: A Window into the Immunopathogenesis of an Endemic Mycosis.Mycopathologia. 2021 Oct;186(5):707-715. doi: 10.1007/s11046-021-00570-0. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Mycopathologia. 2021. PMID: 34228343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Talaromyces marneffei Infection: Virulence, Intracellular Lifestyle and Host Defense Mechanisms.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Feb 19;8(2):200. doi: 10.3390/jof8020200. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical features of patients with talaromycosis marneffei and microbiological characteristics of the causative strains.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Nov;36(11):e24737. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24737. Epub 2022 Oct 21. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 36268985 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of pathogen genetics on clinical phenotypes in a population of Talaromyces marneffei from Vietnam.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 1:2023.03.30.534926. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.30.534926. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Genetics. 2023 Aug 9;224(4):iyad100. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad100 PMID: 37034632 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

