Basic transcription factor 3 expression silencing attenuates colon cancer cell proliferation and migration in vitro
- PMID: 30655745
- PMCID: PMC6313191
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.9613
Basic transcription factor 3 expression silencing attenuates colon cancer cell proliferation and migration in vitro
Abstract
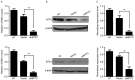
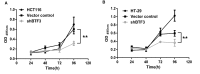
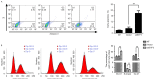
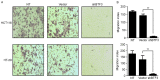
Basic transcription factor 3 (BTF3) is an RNA polymerase II transcription factor that also regulates apoptosis. Numerous studies have identified that BTF3 is aberrantly expressed in several types of tumor. However, the function of BTF3 in colorectal cancer remains unknown. The aim of the present study was to assess the function of BTF3 during colon cancer tumorigenesis. Applying a lentivirus-transfected short hairpin RNA approach, expression of BTF3 was dysregulated in the colon cancer HCT116 and HT-29 cell lines; knockdown efficiency was verified using the quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. To determine the function of BTF3 in colon cancer, cell proliferation was assessed using an MTT assay, cell apoptosis and the cell cycle were assessed using flow cytometry, and cell migration was assessed using a Transwell assay. Knockdown of BTF3 inhibited cell proliferation, possibly because BTF3 knockdown induced cell early apoptosis and arrested cells in G0-G1 phase. BTF3 knockdown also inhibited cell migration. The results of the present study identified that BTF3 expression is associated with colon cancer progress, and BTF3 may therefore be a molecular marker for diagnosis and treatment outcomes of human colon cancer.
Keywords: apoptosis; basic transcription factor 3; cell cycle; colon cancer; migration; proliferation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Basic transcription factor 3 is involved in gastric cancer development and progression.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jul 28;19(28):4495-503. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4495. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23901224 Free PMC article.
-
BTF3 Silencing Inhibits the Proliferation of Osteosarcoma Cells.J Cancer. 2019 Apr 21;10(8):1855-1861. doi: 10.7150/jca.28476. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31205542 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and clinical significance of basic transcription factor 3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jan;17(1):789-796. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9699. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30655831 Free PMC article.
-
Basic transcription factor 3 (BTF3) regulates transcription of tumor-associated genes in pancreatic cancer cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2007 Mar;6(3):367-76. doi: 10.4161/cbt.6.3.3704. Epub 2007 Mar 13. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17312387
-
Knockdown of Immature Colon Carcinoma Transcript 1 Inhibits Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Oct;16(5):559-569. doi: 10.1177/1533034616657977. Epub 2016 Jul 13. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 27413166 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulators of G-protein signaling, RGS2 and RGS4, inhibit protease-activated receptor 4-mediated signaling by forming a complex with the receptor and Gα in live cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Jun 9;18(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00552-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32517689 Free PMC article.
-
Interception of Signaling Circuits of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Cells by Resveratrol Reveals Molecular and Immunomodulatory Signatures.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 19;13(22):5811. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225811. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830970 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of the Oncogene BTF3 and Its Targets in Colorectal Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 11;8:601502. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.601502. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33644029 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Y, Zhang X, Lu S, Wang M, Wang L, Wang W, Cao F, Chen H, Wang J, Zhang J, Tu J. Inhibition of a basal transcription factor 3-like gene Osj10gBTF3 in rice results in significant plant miniaturization and typical pollen abortion. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012;53:2073–2089. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcs146. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
