N-acetylcysteine addition after vitrification improves oocyte mitochondrial polarization status and the quality of embryos derived from vitrified murine oocytes
- PMID: 30654800
- PMCID: PMC6337864
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-018-1743-2
N-acetylcysteine addition after vitrification improves oocyte mitochondrial polarization status and the quality of embryos derived from vitrified murine oocytes
Abstract
Background: Vitrification is the safest method to cryopreserve oocytes, however the process alters mitochondrial function resulting from increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Our aim was to alleviate ROS stress in vitrified mice oocytes using N-acetylcysteine (NAC at 1 mM), to improve the oocyte's developmental competence.
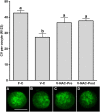
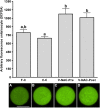
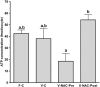
Results: Hence, four experimental groups were compared: fresh oocytes (F-C), vitrified oocytes (V-C), NAC addition prior to oocyte vitrification (V-NAC-Pre) and NAC addition after vitrification (V-NAC-Post). V-NAC-Pre and V-NAC-Post exhibited higher levels of mitochondrial polarization compared to vitrified oocytes (36.5 ± 3.1, 37.7 ± 1.3 and 27.2 ± 2.4 measured as the spatial coefficient of variation/oocyte respectively, mean ± SEM; p < 0.05). However, ROS production increased in vitrified oocytes added with NAC compared to the vitrified control (1124.7 ± 102.1 [V-NAC-Pre] and 1063.2 ± 82.1 [V-NAC-Post] vs. 794.6 ± 164.9 [V-C]; arbitrary fluorescence units/oocyte, mean ± SEM; p < 0.05). ATP significantly decreased in V-NAC-Pre compared to V-NAC-Post oocytes (18.5 ± 6.9 vs. 54.2 ± 4.6 fmol/oocyte respectively, mean ± SEM; p < 0.05), and no differences were observed between V-NAC-Post, F-C and V-C groups. Blastocyst rates derived from F-C oocytes was higher than those derived from V-NAC-Pre (90.7 ± 1.8 vs. 79.1 ± 1.8, respectively, mean % ± SEM,; p < 0.05) but similar to those derived from V-NAC-Post (90.7 ± 1.8, mean % ± SEM, p > 0.05). Total blastomere count of blastocysts derived from V-NAC-Post after in vitro fertilization (IVF) was higher than embryos produced from V-C.
Conclusions: The addition of NAC after vitrification improves the quality of vitrified mature murine oocytes while its addition prior to vitrification is advised against.
Keywords: Mouse; N-acetylcysteine; Oocyte; Vitrification.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All the experimental procedures were reviewed and approved by the Ethical Committee of the Junta de Extremadura Spain (Spain, Ref. SBC/mbr).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Financial competing interests
In the past five years the authors have not received reimbursements, fees, funding, or salary from an organization that may in any way gain or lose financially from the publication of this manuscript, either now or in the future.
The authors do not hold any stocks or shares in an organization that may in any way gain or lose financially from the publication of this manuscript, either now or in the future.
The authors are not currently applying for any patents relating to the content of the manuscript and have not received reimbursements, fees, funding, or salary from an organization that holds or has applied for patents relating to the content of the manuscript.
The authors declare no other financial competing interests.
- b)
Non-financial competing interests
The authors declare that there are no other non-financial competing interests including political, personal, religious, ideological, academic, intellectual, commercial or any other.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EFFECT OF NAC ON MOUSE GV OOCYTE SURVIVAL AND SUBSEQUENT EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT FOLLOWING VITRFICATION.Cryo Letters. 2016 Jul/Aug;37(4):295-302. Cryo Letters. 2016. PMID: 27925012
-
The presence of 1 mM glycine in vitrification solutions protects oocyte mitochondrial homeostasis and improves blastocyst development.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013 Jan;30(1):107-16. doi: 10.1007/s10815-012-9898-4. Epub 2012 Dec 18. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013. PMID: 23248076 Free PMC article.
-
Rutin enhances mitochondrial function and improves the developmental potential of vitrified ovine GV-stage oocyte.Theriogenology. 2024 Nov;229:214-224. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2024.08.029. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Theriogenology. 2024. PMID: 39217650
-
Epigenetics modification among vitrified oocytes and early embryos derived from them: a narrative review.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2024 Jul 28;70(7):22-28. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2024.70.7.4. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2024. PMID: 39097899 Review.
-
Vitrification of Mammalian Oocytes: Recent Studies on Mitochondrial Dysfunction.Biopreserv Biobank. 2024 Oct;22(5):428-440. doi: 10.1089/bio.2023.0062. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Biopreserv Biobank. 2024. PMID: 38227396 Review.
Cited by
-
N-acetyl cysteine restores the fertility of vitrified-warmed mouse oocytes derived through ultrasuperovulation.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 22;14(10):e0224087. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224087. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31639156 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol enhanced mitochondrial recovery from cryopreservation-induced damages in oocytes and embryos.Reprod Med Biol. 2021 Jun 27;20(4):419-426. doi: 10.1002/rmb2.12401. eCollection 2021 Oct. Reprod Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34646069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of N-acetylcysteine treatment in women with advanced age undergoing IVF/ICSI cycles: A prospective study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 4;9:917146. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.917146. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36267623 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress and Oocyte Cryopreservation: Recent Advances in Mitigation Strategies Involving Antioxidants.Cells. 2022 Nov 11;11(22):3573. doi: 10.3390/cells11223573. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36429002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of N-acetylcysteine on Growth, Viability, and Ultrastructure of In Vitro Cultured Bovine Secondary Follicles.Animals (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;12(22):3190. doi: 10.3390/ani12223190. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Toescu EC, Verkhratsky A: assessment of mitochondrial polarization status in living cells based on analysis of the spatial heterogeneity of rhodamine 123 fluorescence staining. Pflugers Arch 2000, 440(6):941–947. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

