Nuclear positioning and pairing of X-chromosome inactivation centers are not primary determinants during initiation of random X-inactivation
- PMID: 30643252
- PMCID: PMC7617203
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0305-7
Nuclear positioning and pairing of X-chromosome inactivation centers are not primary determinants during initiation of random X-inactivation
Abstract
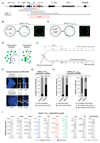
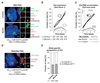
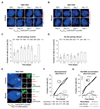
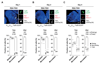
During X-chromosome inactivation (XCI), one of the two X-inactivation centers (Xics) upregulates the noncoding RNA Xist to initiate chromosomal silencing in cis. How one Xic is chosen to upregulate Xist remains unclear. Models proposed include localization of one Xic at the nuclear envelope or transient homologous Xic pairing followed by asymmetric transcription factor distribution at Xist's antisense Xite/Tsix locus. Here, we use a TetO/TetR system that can inducibly relocate one or both Xics to the nuclear lamina in differentiating mouse embryonic stem cells. We find that neither nuclear lamina localization nor reduction of Xic homologous pairing influences monoallelic Xist upregulation or choice-making. We also show that transient pairing is associated with biallelic expression, not only at Xist/Tsix but also at other X-linked loci that can escape XCI. Finally, we show that Xic pairing occurs in wavelike patterns, coinciding with genome dynamics and the onset of global regulatory programs during early differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kinetics of Xist-induced gene silencing can be predicted from combinations of epigenetic and genomic features.Genome Res. 2019 Jul;29(7):1087-1099. doi: 10.1101/gr.245027.118. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Genome Res. 2019. PMID: 31175153 Free PMC article.
-
Xist RNA is confined to the nuclear territory of the silenced X chromosome throughout the cell cycle.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;28(18):5583-94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02269-07. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18625719 Free PMC article.
-
Varying levels of X chromosome coalescence in female somatic cells alters the balance of X-linked dosage compensation and is implicated in female-dominant systemic lupus erythematosus.Sci Rep. 2019 May 29;9(1):8011. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44229-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31142749 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The effectiveness of abstinence-based and harm reduction-based interventions in reducing problematic substance use in adults who are experiencing homelessness in high income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Apr 21;20(2):e1396. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1396. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38645303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic reversal of random X-Chromosome inactivation during iPSC reprogramming.Genome Res. 2019 Oct;29(10):1659-1672. doi: 10.1101/gr.249706.119. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Genome Res. 2019. PMID: 31515287 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory principles and mechanisms governing the onset of random X-chromosome inactivation.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2023 Aug;81:102063. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2023.102063. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2023. PMID: 37356341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Molecular and Nuclear Dynamics of X-Chromosome Inactivation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022 May 17;14(4):a040196. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a040196. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022. PMID: 34312245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomics and the future of psychopharmacology: MicroRNAs offer novel therapeutics .Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2019;21(2):131-148. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2019.21.2/dgurwitz. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31636487 Free PMC article.
-
Gene regulation in time and space during X-chromosome inactivation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Apr;23(4):231-249. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00438-7. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35013589 Review.
References
-
- Rastan S, Robertson EJ. X-chromosome deletions in embryo-derived (EK) cell lines associated with lack of X-chromosome inactivation. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985;90:379–388. - PubMed
-
- Augui S, Nora EP, Heard E. Regulation of X-chromosome inactivation by the X-inactivation centre. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:429–442. - PubMed
-
- Galupa R, Heard E. X-chromosome inactivation: new insights into cis and trans regulation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2015;31:57–66. - PubMed
-
- Pollex T, Heard E. Recent advances in X-chromosome inactivation research. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012;24:825–832. - PubMed
-
- Borsani G, et al. Characterization of a murine gene expressed from the inactive X chromosome. Nature. 1991;351:325–329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

