EBNA3C facilitates RASSF1A downregulation through ubiquitin-mediated degradation and promoter hypermethylation to drive B-cell proliferation
- PMID: 30615685
- PMCID: PMC6336319
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007514
EBNA3C facilitates RASSF1A downregulation through ubiquitin-mediated degradation and promoter hypermethylation to drive B-cell proliferation
Abstract
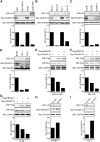
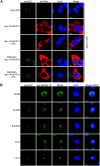
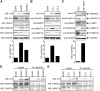
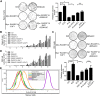
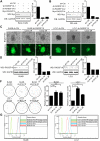
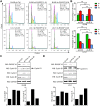
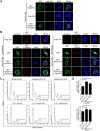
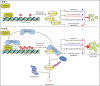
EBV latent antigen 3C (EBNA3C) is essential for EBV-induced primary B-cell transformation. Infection by EBV induces hypermethylation of a number of tumor suppressor genes, which contributes to the development of human cancers. The Ras association domain family isoform 1A (RASSF1A) is a cellular tumor suppressor, which regulates a broad range of cellular functions, including apoptosis, cell-cycle arrest, mitotic arrest, and migration. However, the expression of RASSF1A is lost in many human cancers by epigenetic silencing. In the present study, we showed that EBNA3C promoted B-cell transformation by specifically suppressing the expression of RASSF1A. EBNA3C directly interacted with RASSF1A and induced RASSF1A degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent pathway. SCFSkp2, an E3-ubiquitin ligase, was recruited by EBNA3C to enhance RASSF1A degradation. Moreover, EBNA3C decreased the transcriptional activity of RASSF1A promoter by enhancing its methylation through EBNA3C-mediated modulation of DNMTs expression. EBNA3C also inhibited RASSF1A-mediated cell apoptosis, disrupted RASSF1A-mediated microtubule and chromosomal stability, and promoted cell proliferation by upregulating Cyclin D1 and Cyclin E expression. Our data provides new details, which sheds light on additional mechanisms by which EBNA3C can induce B-cell transformation. This will also facilitate the development of novel therapeutic approaches through targeting of the RASSF1A pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 3C Facilitates Cell Proliferation by Regulating Cyclin D2.J Virol. 2018 Aug 29;92(18):e00663-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00663-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29997218 Free PMC article.
-
The EBV Latent Antigen 3C Inhibits Apoptosis through Targeted Regulation of Interferon Regulatory Factors 4 and 8.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(5):e1003314. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003314. Epub 2013 May 2. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23658517 Free PMC article.
-
The F-box E3 ligase protein FBXO11 regulates EBNA3C-associated degradation of BCL6.J Virol. 2024 Jul 23;98(7):e0054824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00548-24. Epub 2024 Jun 12. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38864622 Free PMC article.
-
The EBNA3 Family: Two Oncoproteins and a Tumour Suppressor that Are Central to the Biology of EBV in B Cells.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:61-117. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428372 Review.
-
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase/Nm23 and Epstein-Barr virus.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Sep;329(1-2):131-9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0123-4. Epub 2009 May 3. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19412732 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquitin-Mediated Effects on Oncogenesis during EBV and KSHV Infection.Viruses. 2024 Sep 26;16(10):1523. doi: 10.3390/v16101523. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39459858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of DNA methylation on the promotor of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) gene and the genome in patients with EBV-associated diseases.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jun;106(12):4413-4426. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12029-3. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35763069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic pan-cancer analysis identified RASSF1 as an immunological and prognostic biomarker and validated in lung cancer.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 21;10(12):e33304. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33304. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39022053 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Virus-Induced Host Cell Epigenetic Changes in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 3;22(15):8346. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158346. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34361112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RUVBL1-modulated chromatin remodeling alters the transcriptional activity of oncogenic CTNNB1 in uveal melanoma.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Apr 19;9(1):132. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01429-7. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37076452 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

