KCa1.1 and Kv1.3 channels regulate the interactions between fibroblast-like synoviocytes and T lymphocytes during rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 30612588
- PMCID: PMC6322314
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-018-1783-9
KCa1.1 and Kv1.3 channels regulate the interactions between fibroblast-like synoviocytes and T lymphocytes during rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) and CCR7- effector memory T (TEM) cells are two of the major cell types implicated in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In particular, FLS become highly invasive, whereas TEM cells proliferate and secrete proinflammatory cytokines, during RA. FLS and T cells may also interact and influence each other's phenotypes. Inhibition of the pathogenic phenotypes of both FLS and TEM cells can be accomplished by selectively blocking the predominant potassium channels that they upregulate during RA: KCa1.1 (BK, Slo1, MaxiK, KCNMA1) upregulated by FLS and Kv1.3 (KCNA3) upregulated by activated TEM cells. In this study, we investigated the roles of KCa1.1 and Kv1.3 in regulating the interactions between FLS and TEM cells and determined if combination therapies of KCa1.1- and Kv1.3-selective blockers are more efficacious than monotherapies in ameliorating disease in rat models of RA.
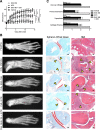
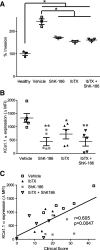
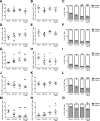
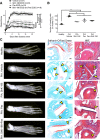
Methods: We used in vitro functional assays to assess the effects of selective KCa1.1 and Kv1.3 channel inhibitors on the interactions of FLS isolated from rats with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) with syngeneic TEM cells. We also used flow cytometric analyses to determine the effects of KCa1.1 blockers on the expression of proteins used for antigen presentation on CIA-FLS. Finally, we used the CIA and pristane-induced arthritis models to determine the efficacy of combinatorial therapies of KCa1.1 and Kv1.3 blockers in reducing disease severity compared with monotherapies.
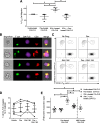
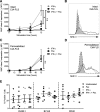
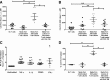
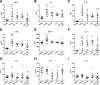
Results: We show that the interactions of FLS from rats with CIA and of rat TEM cells are regulated by KCa1.1 and Kv1.3. Inhibiting KCa1.1 on FLS reduces the ability of FLS to stimulate TEM cell proliferation and migration, and inhibiting Kv1.3 on TEM cells reduces TEM cells' ability to enhance FLS expression of KCa1.1 and major histocompatibility complex class II protein, as well as stimulates their invasion. Furthermore, we show that combination therapies of selective KCa1.1 and Kv1.3 blockers are more efficacious than monotherapies at reducing signs of disease in two rat models of RA.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate the importance of KCa1.1 and Kv1.3 in regulating FLS and TEM cells during RA, as well as the value of combined therapies targeting both of these cell types to treat RA.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Cell interactions; Dual therapy; Immunomodulation; Synovial fibroblast.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
The experiments involving the use of rats were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Baylor College of Medicine. De-identified human FLS were isolated by PSG’s group after patients provided written consent for their tissues to be studied, as approved by the Institutional Review Board at the Feinstein Institute for Medical Research. Baylor College of Medicine’s Institutional Review Board determined that the study of these cells did not constitute human research, because the samples were de-identified.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
CB and MWP are inventors on the patent for ShK-186/dalazatide. CB and MWP are cofounders of Airmid, Inc., and sit on its board of directors. CB and MWP are investors in Kineta, Inc. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KCa1.1 inhibition attenuates fibroblast-like synoviocyte invasiveness and ameliorates disease in rat models of rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Jan;67(1):96-106. doi: 10.1002/art.38883. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25252152 Free PMC article.
-
Different expression of β subunits of the KCa1.1 channel by invasive and non-invasive human fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 May 10;18(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1003-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27165430 Free PMC article.
-
KCa1.1 channels regulate β1-integrin function and cell adhesion in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.FASEB J. 2017 Aug;31(8):3309-3320. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601097R. Epub 2017 Apr 20. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28428266 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic changes in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: state of the art review.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 28;15:1250884. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1250884. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38482018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SFRP1 Negatively Modulates Pyroptosis of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 20;13:903475. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.903475. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35795672 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the therapeutic opportunities of potassium channels for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 9;15:1286069. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1286069. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38783950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ca2+-Activated K+ Channels in Progenitor Cells of Musculoskeletal Tissues: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 5;24(7):6796. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076796. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two Main Cellular Components in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Communication Between T Cells and Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in the Joint Synovium.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 1;13:922111. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.922111. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro-inflammatory Cytokines Drive Deregulation of Potassium Channel Expression in Primary Synovial Fibroblasts.Front Physiol. 2020 Mar 24;11:226. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00226. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32265733 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of carbonic anhydrases and membrane channels of synoviocytes in inflamed joints.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):1615-1622. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1659791. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31480869 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cope A, Schulze-Koops H, Aringer M. The central role of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007;25((5 Suppl 46)):S4–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

