The Network of Cancer Genes (NCG): a comprehensive catalogue of known and candidate cancer genes from cancer sequencing screens
- PMID: 30606230
- PMCID: PMC6317252
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-018-1612-0
The Network of Cancer Genes (NCG): a comprehensive catalogue of known and candidate cancer genes from cancer sequencing screens
Abstract
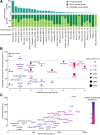
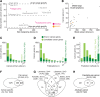
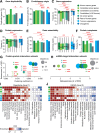
The Network of Cancer Genes (NCG) is a manually curated repository of 2372 genes whose somatic modifications have known or predicted cancer driver roles. These genes were collected from 275 publications, including two sources of known cancer genes and 273 cancer sequencing screens of more than 100 cancer types from 34,905 cancer donors and multiple primary sites. This represents a more than 1.5-fold content increase compared to the previous version. NCG also annotates properties of cancer genes, such as duplicability, evolutionary origin, RNA and protein expression, miRNA and protein interactions, and protein function and essentiality. NCG is accessible at http://ncg.kcl.ac.uk/ .
Keywords: Cancer genes; Cancer genomics screens; Cancer heterogeneity; Systems-level properties.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NCG 5.0: updates of a manually curated repository of cancer genes and associated properties from cancer mutational screenings.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D992-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1123. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26516186 Free PMC article.
-
Network of Cancer Genes: a web resource to analyze duplicability, orthology and network properties of cancer genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan;38(Database issue):D670-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp957. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19906700 Free PMC article.
-
Network of Cancer Genes (NCG 3.0): integration and analysis of genetic and network properties of cancer genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(Database issue):D978-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr952. Epub 2011 Nov 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22080562 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative assessment of genes driving cancer and somatic evolution in non-cancer tissues: an update of the Network of Cancer Genes (NCG) resource.Genome Biol. 2022 Jan 26;23(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13059-022-02607-z. Genome Biol. 2022. PMID: 35078504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low duplicability and network fragility of cancer genes.Trends Genet. 2008 Sep;24(9):427-30. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2008.06.003. Epub 2008 Jul 31. Trends Genet. 2008. PMID: 18675489 Review.
Cited by
-
Identify Biomarkers and Design Effective Multi-Target Drugs in Ovarian Cancer: Hit Network-Target Sets Model Optimizing.Biology (Basel). 2022 Dec 19;11(12):1851. doi: 10.3390/biology11121851. Biology (Basel). 2022. Retraction in: Biology (Basel). 2024 Jan 30;13(2):86. doi: 10.3390/biology13020086 PMID: 36552360 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Integrative Genome-Scale DNA Methylation Analysis of a Large and Unselected Cohort Reveals 5 Distinct Subtypes of Colorectal Adenocarcinomas.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;8(2):269-290. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30954552 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-specific cancer genes contribute to recurrently perturbed pathways and establish therapeutic vulnerabilities in esophageal adenocarcinoma.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 15;10(1):3101. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10898-3. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31308377 Free PMC article.
-
KCML: a machine-learning framework for inference of multi-scale gene functions from genetic perturbation screens.Mol Syst Biol. 2020 Mar;16(3):e9083. doi: 10.15252/msb.20199083. Mol Syst Biol. 2020. PMID: 32141232 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-cancer detection of driver genes at the single-patient resolution.Genome Med. 2021 Feb 1;13(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13073-021-00830-0. Genome Med. 2021. PMID: 33517897 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

