Identification of potential miRNA-mRNA regulatory network contributing to pathogenesis of HBV-related HCC
- PMID: 30602391
- PMCID: PMC6317219
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-018-1761-7
Identification of potential miRNA-mRNA regulatory network contributing to pathogenesis of HBV-related HCC
Abstract
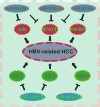
Background: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is one of the major risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Increasing evidence indicates that microRNA (miRNA)-mRNA axis is involved in HCC. However, a comprehensive miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in HBV-related HCC is still absent. This study aims to identify potential miRNA-mRNA regulatory pathways contributing to pathogenesis of HBV-related HCC.
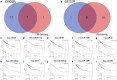
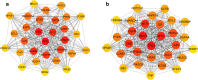
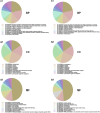
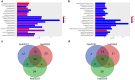
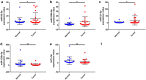
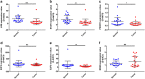
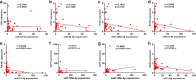
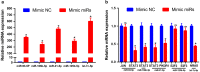
Methods: Microarray GSE69580 was downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. GEO2R and 'R-limma' were used to conduct differential expression analysis. The common miRNAs appeared in the two analytic sets were screened as potential differentially expressed miRNAs (DE-miRNAs). The prognostic roles of screened DE-miRNAs in HCC were further evaluated using Kaplan-Meier plotter database. Target genes of DE-miRNAs were predicted by miRNet. Then, protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks were established for these targets via the STRING database, after which hub genes in the networks were identified by Cytoscape. Functional annotation and pathway enrichment analyses for the target genes were performed through DAVID database. Three enriched pathways related to HBV-related HCC were selected for further analysis and potential target genes commonly appeared in all three pathways were screened. Cytoscape was employed to construct miRNA-hub gene network. The expression and correlation of potential miRNAs and targets were further detected in clinical HBV-related HCC samples by qRT-PCR.
Results: 7 upregulated and 9 downregulated DE-miRNAs were accessed. 5 of 7 upregulated DE-miRNAs and 5 of 7 downregulated DE-miRNAs indicated significant prognostic roles in HCC. 2312 and 1175 target genes were predicted for the upregulated and downregulated DE-miRNAs, respectively. TP53 was identified as the hub gene in the PPI networks. Pathway enrichment analysis suggested that these predicted targets were linked to hepatitis B, pathways in cancer, microRNAs in cancer and viral carcinogenesis. Further analysis of these pathways screened 20 and 16 target genes for upregulated and downregulated DE-miRNAs, respectively. By detecting the expression of 36 target genes, six candidate target genes were identified. Finally, a potential miRNA-mRNA regulatory network was established based on the results of qRT-PCR and expression correlation analysis.
Conclusions: In the study, potential miRNA-mRNA regulatory pathways were identified, exploring the underlying pathogenesis and effective therapy strategy of HBV-related HCC.
Keywords: Bioinformatic analysis; Hepatitis B virus (HBV); Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); Kaplan–Meier plotter (KM-plotter); MicroRNAs (miRNAs).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of invasion-metastasis-associated microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma based on bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation.J Transl Med. 2018 Sep 29;16(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1639-8. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30268144 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analyses of Potential miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Axis in HBV-related Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 1;18(2):335-346. doi: 10.7150/ijms.50126. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33390802 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and Functional Prediction of Key Candidate Genes in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Oct 9;2020:7653506. doi: 10.1155/2020/7653506. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33102593 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus and microRNAs: Complex interactions affecting hepatitis B virus replication and hepatitis B virus-associated diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 28;21(24):7375-99. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7375. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26139985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
Cited by
-
Identify miRNA-mRNA regulation pairs to explore potential pathogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Oct 19;14(20):8357-8373. doi: 10.18632/aging.204341. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 36260870 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Potential miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network Associated with Pig Growth Performance in the Pituitaries of Bama Minipigs and Landrace Pigs.Animals (Basel). 2022 Nov 7;12(21):3058. doi: 10.3390/ani12213058. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36359184 Free PMC article.
-
A novel miR-0308-3p revealed by miRNA-seq of HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma suppresses cell proliferation and promotes G1/S arrest by targeting double CDK6/Cyclin D1 genes.Cell Biosci. 2020 Feb 27;10:24. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00382-7. eCollection 2020. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32128112 Free PMC article.
-
Profibrotic Signaling and HCC Risk during Chronic Viral Hepatitis: Biomarker Development.J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 2;10(5):977. doi: 10.3390/jcm10050977. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33801181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miRNAs in maternal plasma as potential biomarkers of early pregnancy in sheep.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 17;13:929477. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.929477. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36061213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soriano V, Young B, Reau N. Report from the international conference on viral hepatitis-2017. AIDS Rev. 2018;20:58–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

