TNF-α is a potential therapeutic target to overcome sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 30594557
- PMCID: PMC6412090
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.047
TNF-α is a potential therapeutic target to overcome sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "TNF-α is a potential therapeutic target to overcome sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma" [EBioMedicine 40 (2019) 446-456].EBioMedicine. 2022 Jun;80:104074. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104074. Epub 2022 May 20. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35605430 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
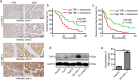
Background: The role of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) in targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains largely unknown. The current study aimed to clarify the mechanistic effects of targeting TNF-α to overcome sorafenib resistance in HCC.
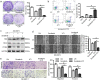
Methods: A correlation of TNF-α expression with the prognosis was analyzed in 62 HCC patients who underwent surgical resection and subsequent received adjuvant sorafenib treatment. The relation of TNF-α expression and sorafenib sensitivity was determined in different HCC cell lines. The combined therapeutic effects of sorafenib and ulinastatin, which could inhibit TNF-α expression, on HCC were examined in vitro and in vivo.
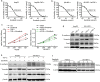
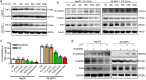
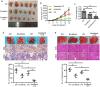
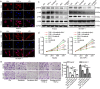
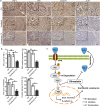
Findings: High TNF-α expression was correlated with poor outcomes in HCC patients who received adjuvant sorafenib after surgery. In vitro experiments showed that TNF-α promotes HCC cell resistant to sorafenib through inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Notably, the current study revealed that sorafenib has no significant influence on the expression and secretion of TNF-α, and sorafenib had limited effectiveness on reversing EMT in HCC cells with high TNF-α expression. Inhibiting the expression of TNF-α with ulinastatin significantly enhanced the anti-tumor effect of sorafenib on HCC cells with high expression of TNF-α in vitro and in vivo.
Interpretation: Our findings indicate that TNF-α may serve as a novel predictor of sorafenib sensitivity in HCC patients. Sorafenib combined with ulinastatin may improve the effectiveness of treatment of HCC in patients with high expression of TNF-α. FUND: This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no.81572398; no.81672419), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (no. 2017A010105003; no.2015A050502023; no.2016A020216010), and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (no.2014A030313061; no. 2013B021800101).
Keywords: Combination treatment; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Sorafenib resistance; TNF-α; Ulinastatin.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CRIPTO promotes an aggressive tumour phenotype and resistance to treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Pathol. 2018 Jul;245(3):297-310. doi: 10.1002/path.5083. Epub 2018 May 9. J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29604056
-
The synergistic effect of sorafenib and TNF-α inhibitor on hepatocellular carcinoma.EBioMedicine. 2019 Feb;40:11-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.01.007. Epub 2019 Jan 14. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30651221 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Increased expression of SLC46A3 to oppose the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and its effect on sorafenib therapy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jun;114:108864. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108864. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30981107
-
Upregulation of lncRNA NIFK-AS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma by m6A methylation promotes disease progression and sorafenib resistance.Hum Cell. 2021 Nov;34(6):1800-1811. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00587-z. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 34374933 Review.
-
Sorafenib resistance in hepatocarcinoma: role of hypoxia-inducible factors.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Oct 12;50(10):1-9. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0159-1. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30315182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: theoretical basis and therapeutic aspects.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jun 10;5(1):87. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0187-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32532960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ulinastatin modulates NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in PTZ-induced epileptic mice: A potential mechanistic insight.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 19;10(19):e38050. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38050. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39386862 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammasome-Mediated Cytokines: A Key Connection between Obesity-Associated NASH and Liver Cancer Progression.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 21;10(10):2344. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102344. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of Anti-Liver Cancer Activity of the Herbal Drug FDY003 Using Network Pharmacology.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Sep 9;2022:5765233. doi: 10.1155/2022/5765233. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36118098 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Inhibition of TGF-β1-Induced EMT and PD-L1 Silencing Re-Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Sorafenib Treatment.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 27;10(9):1889. doi: 10.3390/jcm10091889. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33925488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Qi X., Berzigotti A., Cardenas A., Sarin S. Emerging non-invasive approaches for diagnosis and monitoring of portal hypertension. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3(10):708–719. - PubMed
-
- Liu L., Cao Y., Chen C., Zhang X., McNabola A., Wilkie D. Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res. 2006;66(24):11851–11858. - PubMed
-
- Llovet J.M., Ricci S., Mazzaferro V., Hilgard P., Gane E., Blanc J.F. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378–390. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

