Achieving high uptake of human papillomavirus vaccination in Malaysia through school-based vaccination programme
- PMID: 30577816
- PMCID: PMC6303856
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-018-6316-6
Achieving high uptake of human papillomavirus vaccination in Malaysia through school-based vaccination programme
Abstract
Background: In 2006, 4 years of planning was started by the Ministry of Health, Malaysia (MOH), to implement the HPV (human papillomavirus) vaccination programme. An inter-agency and multi-sectoral collaborations were developed for Malaysia's HPV school-based immunisation programme. It was approved for nationwide school base implementation for 13-year-old girls or first year secondary students in 2010. This paper examines how the various strategies used in the implementation over the last 7 years (2010-2016) that unique to Malaysia were successful in achieving optimal coverage of the target population.
Methods: Free vaccination was offered to school girls in secondary school (year seven) in Malaysia, which is usually at the age of 13 in the index year. All recipients of the HPV vaccine were identified through school enrolments obtained from education departments from each district in Malaysia. A total of 242,638 girls aged between 12 to 13 years studying in year seven were approached during the launch of the program in 2010. Approximately 230,000 girls in secondary schools were offered HPV vaccine per year by 646 school health teams throughout the country from 2010 to 2016.
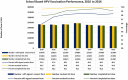
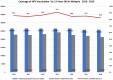
Results: Parental consent for their daughters to receive HPV vaccination at school was very high at 96-98% per year of the programme. Of those who provided consent, over 99% received the first dose each year and 98-99% completed the course per year. Estimated population coverage for the full vaccine course, considering also those not in school, is estimated at 83 to 91% per year. Rates of adverse events reports following HPV vaccination were low at around 2 per 100,000 and the majority was injection site reactions.
Conclusion: A multisectoral and integrated collaborative structure and process ensured that the Malaysia school-based HPV immunisation programme was successful and sustained through the programme design, planning, implementation and monitoring and evaluation. This is a critical factor contributing to the success and sustainability of the school-based HPV immunisation programme with very high coverage.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; HPV; Immunisation; Malaysia; School based.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
For developing this report, formal ethics approval was not required as the analysis was mainly a retrospective programme evaluation conducted at the policy and programme level. The report was based on existing data and documentation with any data aggregated at the population level. All data from key informant interviews and stakeholder meetings was analyzed in the aggregate and quotes anonymized, except where approval to quote was specifically provided. Written parental consent was obtained prior to vaccination. The consent forms were distributed to parents through school teachers prior to scheduled vaccination visits. The parents returned the consent form to the school team. Whenever the children were refused immunization by their parents, the school health teams would call the parents to determine reasons for refusal and made a remark on the student registration form.
Consent for publication
This manuscript has obtained the approval for publication from Director General of Health, Ministry of Health Malaysia. For the purpose of this reports, consent from the people portrayed in Fig. 1 was obtained prior to starting the programme.
Competing interests
All authors read and understood the policy on declaration of interest and declare that they have no competing interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Implementation of a human papillomavirus vaccination demonstration project in Malawi: successes and challenges.BMC Public Health. 2017 Jun 26;17(1):599. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4526-y. BMC Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28651574 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus vaccine uptake in boys and girls in a school-based vaccine delivery program in Prince Edward Island, Canada.Vaccine. 2015 Apr 8;33(15):1786-90. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.02.047. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 25731789
-
Potential process improvements to increase coverage of human papillomavirus vaccine in schools - A focus on schools with low vaccine uptake.Vaccine. 2020 Mar 23;38(14):2971-2977. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.02.047. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 32115296
-
Improved population coverage of the human papillomavirus vaccine after implementation of a school-based vaccination programme: the Singapore experience.Singapore Med J. 2023 May;64(5):294-301. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2022053. Singapore Med J. 2023. PMID: 35546141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Literature review of HPV vaccine delivery strategies: considerations for school- and non-school based immunization program.Vaccine. 2014 Jan 9;32(3):320-6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.11.070. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Vaccine. 2014. PMID: 24295804 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacists' experiences on adverse drug reaction: 10 years later.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 29;13:932942. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.932942. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36249772 Free PMC article.
-
Multidimensional social and cultural norms influencing HPV vaccine hesitancy in Asia.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Jul 2;16(7):1611-1622. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1756670. Epub 2020 May 19. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32429731 Free PMC article.
-
Priority-setting to integrate sexual and reproductive health into universal health coverage: the case of Malaysia.Sex Reprod Health Matters. 2020 Dec;28(2):1842153. doi: 10.1080/26410397.2020.1842153. Sex Reprod Health Matters. 2020. PMID: 33236973 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination intent and its associated factors: a study of ethnically diverse married women aged 27 to 45 in Malaysia, a Southeast Asian country.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Nov 30;18(5):2076525. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2076525. Epub 2022 Jun 17. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 35714272 Free PMC article.
-
Achieving cervical cancer elimination: The simulated impacts of HPV vaccination and transitioning from liquid-based cytology to HPV-based screening test.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 25;19(7):e0307880. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307880. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39052665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Genital HPV infection - fact sheet. 2016. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/std/hpv/stdfact-hpv.htm. Accessed on 13 Jan 2017.
-
- Lin Yang, ShuanghuaXie, Xiaoshuang Feng, Yuheng Chen, Tongzhang Zheng, Min Dai, Cindy Ke Zhou, Zhibin Hu, Ni Li, Dong Hang (2015); Worldwide Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus and Relative Risk of Prostate Cancer. Available at http://www.nature.com/articles/srep14667. Accessed 18 Jan 2017. - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO 2016; Immunization, Vaccines and biologicals. Available at http://www.who.int/immunization/diseases/hpv/en/. Accessed 18 Jan 2017
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

