The Club Cell Marker SCGB1A1 Downstream of FOXA2 is Reduced in Asthma
- PMID: 30576223
- PMCID: PMC6543749
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0199OC
The Club Cell Marker SCGB1A1 Downstream of FOXA2 is Reduced in Asthma
Abstract
Human SCGB1A1 protein has been shown to be significantly reduced in BAL, sputum, and serum from humans with asthma as compared with healthy individuals. However, the mechanism of this reduction and its functional impact have not been entirely elucidated. By mining online datasets, we found that the mRNA of SCGB1A1 was significantly repressed in brushed human airway epithelial cells from individuals with asthma, and this repression appeared to be associated with reduced expression of FOXA2. Consistently, both Scgb1A1 and FoxA2 were downregulated in an ovalbumin-induced mouse model of asthma. Furthermore, compared with wild-type mice, Scgb1a1 knockout mice had increased airway hyperreactivity and inflammation when they were exposed to ovalbumin, confirming the antiinflammatory role of Scgb1a1 in protection against asthma phenotypes. To search for potential asthma-related stimuli of SCGB1A1 repression, we tested T-helper cell type 2 cytokines. Both IL-4 and IL-13 repressed epithelial expression of SCGB1A1 and FOXA2. Importantly, infection of epithelial cells with human rhinovirus similarly reduced expression of these two genes, which suggests that FOXA2 may be the common regulator of SCGB1A1. To establish the causal role of reduced FOXA2 in SCGB1A1 repression, we demonstrated that FOXA2 was required for SCGB1A1 expression at baseline. FOXA2 overexpression was sufficient to drive promoter activity and expression of SCGB1A1 and was also able to restore the repressed SCGB1A1 expression in IL-13-treated or rhinovirus-infected cells. Taken together, these findings suggest that low levels of epithelial SCGB1A1 in asthma are caused by reduced FOXA2 expression.
Keywords: CC10; FOXA2; asthma; rhinovirus; secretoglobin.
Figures
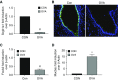
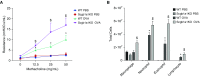
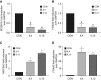
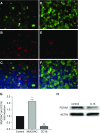
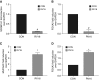
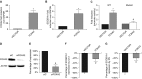
Comment in
-
An Elusive Fox that Suppresses Scgb1a1 in Asthma Has Been Found.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019 Jun;60(6):615-617. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2019-0019ED. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30726101 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Lung Secretoglobin Scgb1a1 Influences Alveolar Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation and Immunity.Front Immunol. 2020 Oct 1;11:584310. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584310. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33117399 Free PMC article.
-
Mediation of FOXA2/IL-6/IL-6R/STAT3 signaling pathway mediates benzo[a]pyrene-induced airway epithelial mesenchymal transformation in asthma.Environ Pollut. 2024 Sep 15;357:124384. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.124384. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Environ Pollut. 2024. PMID: 38901818
-
Molecular characterization of pulmonary defenses against bacterial invasion in allergic asthma: The role of Foxa2 in regulation of β-defensin 1.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 27;14(12):e0226517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226517. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31881038 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Involvement of CD44 in T Helper Type 2 Cell-Mediated Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Acute Asthma.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 7;12:811600. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.811600. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35069598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into the role of cytokines in asthma.J Clin Pathol. 2001 Aug;54(8):577-89. doi: 10.1136/jcp.54.8.577. J Clin Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11477111 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic developmental hypoxia alters rat lung immune cell transcriptomes during allergic airway inflammation.Physiol Rep. 2023 Feb;11(3):e15600. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15600. Physiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36750205 Free PMC article.
-
E-cigarette synthetic cooling agent WS-23 and nicotine aerosols differentially modulate airway epithelial cell responses.Toxicol Rep. 2022 Sep 20;9:1823-1830. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.09.010. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36518432 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchyme-derived vertebrate lonesome kinase controls lung organogenesis by altering the matrisome.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Mar 15;80(4):89. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04735-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36920550 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial barriers in allergy and asthma.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Jun;145(6):1499-1509. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.010. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32507228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Club cell protein (CC16) in serum as an effect marker for small airway epithelial damage caused by diesel exhaust and blasting fumes in potash mining.Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2024 Mar;97(2):121-132. doi: 10.1007/s00420-023-02035-x. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2024. PMID: 38110551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Broeckaert F, Bernard A. Clara cell secretory protein (CC16): characteristics and perspectives as lung peripheral biomarker. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000;30:469–475. - PubMed
-
- Mukherjee AB, Zhang Z, Chilton BS. Uteroglobin: a steroid-inducible immunomodulatory protein that founded the Secretoglobin superfamily. Endocr Rev. 2007;28:707–725. - PubMed
-
- Mansur AH. Secretoglobin 1A1 gene and asthma pre-disposition: what is the evidence? Clin Exp Allergy. 2009;39:8–11. - PubMed
-
- Singh G, Katyal SL. Clara cell proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;923:43–58. - PubMed
-
- Lakind JS, Holgate ST, Ownby DR, Mansur AH, Helms PJ, Pyatt D, et al. A critical review of the use of Clara cell secretory protein (CC16) as a biomarker of acute or chronic pulmonary effects. Biomarkers. 2007;12:445–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

