Conserved and variable natural killer cell receptors: diverse approaches to viral infections
- PMID: 30570753
- PMCID: PMC6418463
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.13039
Conserved and variable natural killer cell receptors: diverse approaches to viral infections
Abstract
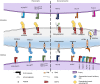
Natural killer (NK) cells are lymphocytes of the innate immune system with essential roles during viral infections. NK cell functions are mediated through a repertoire of non-rearranging inhibitory and activating receptors that interact with major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-peptide complexes on the surface of infected cells. Recent work studying the conserved CD94-NKG2A and variable killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor-MHC systems suggest that these two receptor families may have subtly different properties in terms of interactions with MHC class I bound peptides, and in recognition of down-regulation of MHC class I. In this review, we discuss how these properties generate diversity in the NK cell response to viruses.
Keywords: conserved; natural killer cells; polymorphic; receptor-ligand; viral infection.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Two to Tango: Co-evolution of Hominid Natural Killer Cell Receptors and MHC.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 19;10:177. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00177. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30837985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural killer cell specificity for viral infections.Nat Immunol. 2018 Aug;19(8):800-808. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0163-6. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Nat Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30026479 Review.
-
Effects of Peptide on NK cell-mediated MHC I recognition.Front Immunol. 2014 Mar 31;5:133. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00133. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24744756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HLA-E binds to natural killer cell receptors CD94/NKG2A, B and C.Nature. 1998 Feb 19;391(6669):795-9. doi: 10.1038/35869. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9486650
-
Reciprocal age related change in natural killer cell receptors for MHC class I.Mech Ageing Dev. 2005 Jun-Jul;126(6-7):722-31. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2005.01.004. Epub 2005 Feb 19. Mech Ageing Dev. 2005. PMID: 15888327 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The immune regulatory role of neutrophils.Immunology. 2019 Mar;156(3):215-216. doi: 10.1111/imm.13049. Immunology. 2019. PMID: 30767207 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Significance of HLA and KIR Diversity in Underrepresented Populations.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 15;12(6):1333. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061333. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the TRPML Mucolipin Channels in Viral Infections and Anti-viral Innate Immune Responses.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 29;11:739. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00739. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32425938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The combinatorial diversity of KIR and HLA class I allotypes in Peninsular Malaysia.Immunology. 2021 Apr;162(4):389-404. doi: 10.1111/imm.13289. Epub 2020 Dec 20. Immunology. 2021. PMID: 33283280 Free PMC article.
-
A New Look at Immunogenetics of Pregnancy: Maternal Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Educates Uterine Natural Killer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 15;25(16):8869. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168869. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201555 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Woolhouse ME, Webster JP, Domingo E, Charlesworth B, Levin BR. Biological and biomedical implications of the co‐evolution of pathogens and their hosts. Nat Genet 2002; 32:569–77. - PubMed
-
- Beltrame LM, Sell AM, Moliterno RA, Clementino SL, Cardozo DM, Dalalio MM et al Influence of KIR genes and their HLA ligands in susceptibility to dengue in a population from southern Brazil. Tissue Antigens 2013; 82:397–404. - PubMed
-
- Khakoo SI, Thio CL, Martin MP, Brooks CR, Gao X, Astemborski J et al HLA and NK cell inhibitory receptor genes in resolving hepatitis C virus infection. Science 2004; 305:872–4. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez‐Ramirez D, Esparza‐Perez MA, Ramirez‐Garcialuna JL, Arguello JR, Mandeville PB, Noyola DE et al Association of KIR3DL1/S1 and HLA‐Bw4 with CD4 T cell counts in HIV‐infected Mexican mestizos. Immunogenetics 2015; 67:413–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

