Low-dose rituximab is no less effective for nephrotic syndrome measured by 12-month outcome
- PMID: 30564878
- PMCID: PMC6424916
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-018-4172-3
Low-dose rituximab is no less effective for nephrotic syndrome measured by 12-month outcome
Abstract
Objective: Rituximab is an effective treatment for children with steroid dependent or frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome. The optimum dosing schedule for rituximab has not been established. We hypothesized that a single low dose of 375 mg/m2 would have comparable outcomes to higher doses in reducing the frequency of relapse and time to B cell reconstitution.
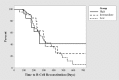
Methods: We conducted a multicenter retrospective observational cohort study of children with steroid-sensitive frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome. Data were extracted from clinical records including the dates of diagnosis, treatment, relapses, the use of concomitant immunosuppression, and lymphocyte subset profiling. Patients treated earlier received variable doses of rituximab, although typically two doses of 750 mg/m2. Later, patients received the current regimen of a single dose of 375 mg/m2. The primary outcome was an absence of clinically confirmed relapse 12 months following rituximab administration. Secondary outcomes were median time to relapse, probability of being relapse-free at 6 and 24 months and time to reconstitution of CD19+ B cells.
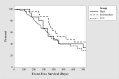
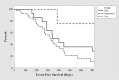
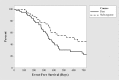
Results: Sixty patients received 143 courses of rituximab. Seven different dosing regimen strategies were used, ranging between 375 and 750 mg/m2 per dose, with administration of 1-4 doses. There was no significant difference in event-free survival at 12 months between dosing strategies. The median time to reconstitution of B cells was not significantly different between groups.
Conclusions: Use of a single low-dose regimen of rituximab in the management of frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome does not affect the probability of relapse at 12 months or time to B cell reconstitution compared to a conventional higher dose.
Keywords: Dosing; Nephrotic syndrome; Rituximab.
Conflict of interest statement
Ben Reynolds has previously had speaking fees from Alexion Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of different rituximab regimens on B cell depletion and time to relapse in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome.Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 Feb;34(2):253-259. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-4052-x. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30109447
-
Predictors of relapse and long-term outcome in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome after rituximab treatment.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017 Aug;21(4):671-676. doi: 10.1007/s10157-016-1328-y. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27558467
-
Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome and rituximab: may we predict circulating B lymphocytes recovery?Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 Mar;34(3):529-532. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-4139-4. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 30542932
-
Rituximab therapy for refractory steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in children.Pediatr Nephrol. 2020 Jan;35(1):17-24. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-4166-1. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Pediatr Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 30564879 Review.
-
Rituximab in children with steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome: in quest of the optimal regimen.Pediatr Nephrol. 2021 Jun;36(6):1397-1405. doi: 10.1007/s00467-020-04609-0. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 32577808 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment response to cyclophosphamide, rituximab, and bortezomib in chronic immune-mediated sensorimotor neuropathies: a retrospective cohort study.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2021 Mar 5;14:1756286421999631. doi: 10.1177/1756286421999631. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2021. PMID: 33747132 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric idiopathic steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome: diagnosis and therapy -short version of the updated German best practice guideline (S2e) - AWMF register no. 166-001, 6/2020.Pediatr Nephrol. 2021 Oct;36(10):2971-2985. doi: 10.1007/s00467-021-05135-3. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34091756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Response and Pattern of B cell Suppression with Single Low Dose Rituximab in Nephrology.Kidney360. 2020 Apr 2;1(5):359-367. doi: 10.34067/KID.0000072020. eCollection 2020 May 28. Kidney360. 2020. PMID: 35369364 Free PMC article.
-
Population Pharmacokinetics of Rituximab in Pediatric Patients With Frequent-Relapsing or Steroid-Dependent Nephrotic Syndrome.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 2;12:725665. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.725665. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34539407 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab treatment for difficult-to-treat nephrotic syndrome in children: a multicenter, retrospective study.Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Aug 30;51(4):1781-1790. doi: 10.3906/sag-2012-297. Turk J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33581711 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

