Baicalin Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis Through the Suppression of Janus Kinase 1 (JAK1)/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) Signaling in Mice
- PMID: 30562763
- PMCID: PMC6322370
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.910347
Baicalin Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis Through the Suppression of Janus Kinase 1 (JAK1)/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) Signaling in Mice
Abstract
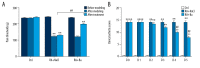
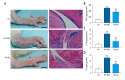
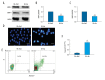
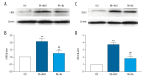
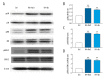
BACKGROUND Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic joint inflammation and there is no cure. Baicalin, as an ingredient in the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis, is supposed to possess an anti-inflammatory effect. However, the protective effect of baicalin on collagen-induced arthritis requires further investigation. MATERIAL AND METHODS A model of rheumatoid arthritis was established in 20 mice (8- to 10-weeks old). The mice were randomly divided into 2 groups after modeling and then injected with saline or baicalin, respectively. The synovial fluids and tissues were collected, and the pressure pain threshold and clinical arthritis score were measured. The levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interlukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-2, MMP-9, nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and their downstream inflammatory mediators Janus kinase 1 (JAK1)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2), p38, Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK) activation were detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and western blotting analyses. The mononuclear cells apoptosis ratio was calculated by flowcytometry analyses. RESULTS Baicalin significantly reduced disease activities in a rheumatoid arthritis mouse model, which were reflected by pressure pain thresholds and clinical arthritis scores. Relevant proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, gelatinases (MMP-2, MMP-9) and inducible enzymes (iNOS, COX-2) were generally suppressed. Moreover, baicalin treatment induced cells apoptosis in synovial fluid monocytes and markedly down regulated JAK1/STAT3 but not mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) expressions in synovium of arthritis. CONCLUSIONS These observations confirm the relief of rheumatoid arthritis by baicalin. Our results indicate the effect is related with the modulation of decreased proinflammatory cytokines and inflammatory markers. And the apoptosis promotion of monocytes in synovial fluid were also inhibited. Moreover, the molecular mechanism implies suppressed JAK1/STAT3 signaling with baicalin treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
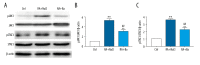
Similar articles
-
Metabolic effects of quercetin on inflammatory and autoimmune responses in rheumatoid arthritis are mediated through the inhibition of JAK1/STAT3/HIF-1α signaling.Mol Med. 2024 Oct 10;30(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00929-1. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39390367 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-3-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-1-(5-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-2H-chromen-6-yl)prop-2-en-1-one ameliorates the collagen-arthritis via blocking ERK/JNK and NF-κB signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Dec;17(4):1125-33. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24135236
-
Xuetongsu ameliorates synovial inflammatory hyperplasia in rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;337(Pt 1):118786. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118786. Epub 2024 Sep 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39244174
-
The JAK1/STAT3/SOCS3 axis in bone development, physiology, and pathology.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Aug;52(8):1185-1197. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0445-6. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32788655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal transduction in rheumatoid arthritis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2004 May;16(3):231-7. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200405000-00011. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2004. PMID: 15103250 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential therapeutic effects of baicalin and baicalein.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2024 Jan-Feb;14(1):23-49. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2023.22307. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2024. PMID: 38948180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scutellaria baicalensis georgi is a promising candidate for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 16;13:946030. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.946030. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural medicines of targeted rheumatoid arthritis and its action mechanism.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 1;13:945129. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.945129. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35979373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aqueous Extract of Kan-Lu-Hsiao-Tu-Tan Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses.Life (Basel). 2020 Nov 27;10(12):313. doi: 10.3390/life10120313. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33260891 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Plantain in the Treatment of Gout and Hyperuricemia Based on Network Pharmacology.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Oct 22;2020:3023127. doi: 10.1155/2020/3023127. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33149752 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2010;376(9746):1094–108. - PubMed
-
- Vogel WV, van Riel PL, Oyen WJ. FDG-PET/CT can visualise the extent of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis of the tarsus. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007;34(3):439. - PubMed
-
- Pitzalis C, Kelly S, Humby F. New learnings on the pathophysiology of RA from synovial biopsies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2013;25(3):334–44. - PubMed
-
- Amin AR, Attur M, Abramson SB. Nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenases: Distribution, regulation, and intervention in arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1999;11(3):202–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

