Gluconeogenesis is essential for trypanosome development in the tsetse fly vector
- PMID: 30557412
- PMCID: PMC6312356
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007502
Gluconeogenesis is essential for trypanosome development in the tsetse fly vector
Abstract
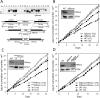
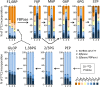
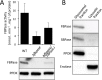
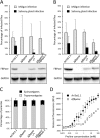
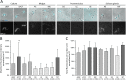
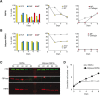
In the glucose-free environment that is the midgut of the tsetse fly vector, the procyclic form of Trypanosoma brucei primarily uses proline to feed its central carbon and energy metabolism. In these conditions, the parasite needs to produce glucose 6-phosphate (G6P) through gluconeogenesis from metabolism of non-glycolytic carbon source(s). We showed here that two phosphoenolpyruvate-producing enzymes, PEP carboxykinase (PEPCK) and pyruvate phosphate dikinase (PPDK) have a redundant function for the essential gluconeogenesis from proline. Indeed, incorporation of 13C-enriched proline into G6P was abolished in the PEPCK/PPDK null double mutant (Δppdk/Δpepck), but not in the single Δppdk and Δpepck mutant cell lines. The procyclic trypanosome also uses the glycerol conversion pathway to feed gluconeogenesis, since the death of the Δppdk/Δpepck double null mutant in glucose-free conditions is only observed after RNAi-mediated down-regulation of the expression of the glycerol kinase, the first enzyme of the glycerol conversion pathways. Deletion of the gene encoding fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Δfbpase), a key gluconeogenic enzyme irreversibly producing fructose 6-phosphate from fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, considerably reduced, but not abolished, incorporation of 13C-enriched proline into G6P. In addition, the Δfbpase cell line is viable in glucose-free conditions, suggesting that an alternative pathway can be used for G6P production in vitro. However, FBPase is essential in vivo, as shown by the incapacity of the Δfbpase null mutant to colonise the fly vector salivary glands, while the parental phenotype is restored in the Δfbpase rescued cell line re-expressing FBPase. The essential role of FBPase for the development of T. brucei in the tsetse was confirmed by taking advantage of an in vitro differentiation assay based on the RNA-binding protein 6 over-expression, in which the procyclic forms differentiate into epimastigote forms but not into mammalian-infective metacyclic parasites. In total, morphology, immunofluorescence and cytometry analyses showed that the differentiation of the epimastigote stages into the metacyclic forms is abolished in the Δfbpase mutant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
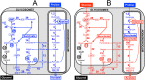
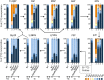
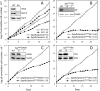
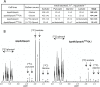
Similar articles
-
Cytosolic NADPH homeostasis in glucose-starved procyclic Trypanosoma brucei relies on malic enzyme and the pentose phosphate pathway fed by gluconeogenic flux.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 21;288(25):18494-505. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.462978. Epub 2013 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23665470 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of pyruvate phosphate dikinase in the maintenance of the glycosomal ATP/ADP balance in the Trypanosoma brucei procyclic form.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 20;289(25):17365-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.567230. Epub 2014 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24794874 Free PMC article.
-
Tsetse fly tolerance to T. brucei infection: transcriptome analysis of trypanosome-associated changes in the tsetse fly salivary gland.BMC Genomics. 2016 Nov 25;17(1):971. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3283-0. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27884110 Free PMC article.
-
Flying tryps: survival and maturation of trypanosomes in tsetse flies.Trends Parasitol. 2013 Apr;29(4):188-96. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Trends Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23507033 Review.
-
Antigenic variation during the developmental cycle of Trypanosoma brucei.J Protozool. 1984 Feb;31(1):41-7. J Protozool. 1984. PMID: 6204043 Review.
Cited by
-
Procyclic trypanosomes recycle glucose catabolites and TCA cycle intermediates to stimulate growth in the presence of physiological amounts of proline.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Mar 1;17(3):e1009204. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009204. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33647053 Free PMC article.
-
The Trypanosome UDP-Glucose Pyrophosphorylase Is Imported by Piggybacking into Glycosomes, Where Unconventional Sugar Nucleotide Synthesis Takes Place.mBio. 2021 Jun 29;12(3):e0037521. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00375-21. Epub 2021 May 28. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34044588 Free PMC article.
-
The bloodstream form of Trypanosoma brucei displays non-canonical gluconeogenesis.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Feb 23;18(2):e0012007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012007. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38394337 Free PMC article.
-
Positional Dynamics and Glycosomal Recruitment of Developmental Regulators during Trypanosome Differentiation.mBio. 2019 Jul 9;10(4):e00875-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00875-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31289175 Free PMC article.
-
Glycerol suppresses glucose consumption in trypanosomes through metabolic contest.PLoS Biol. 2021 Aug 13;19(8):e3001359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001359. eCollection 2021 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2021. PMID: 34388147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bringaud F, Barrett MP, Zilberstein D. Multiple roles of proline transport and metabolism in trypanosomatids. Frontiers in Bioscience 2012;17:349–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

