Risk Factors for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in Population-Based Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 30544688
- PMCID: PMC6313801
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph15122805
Risk Factors for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in Population-Based Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
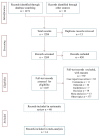
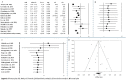
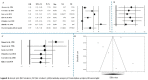
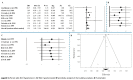
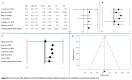
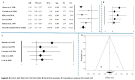
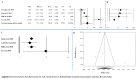
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) represents an important public health problem with a prevalence between 1.3% and 12.5%. Several population-based randomized trials have evaluated ultrasound screening for AAA providing evidence of a reduction in aneurysm-related mortality in the screened population. The aim of our study was to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of the risk factors for AAA. We conducted a systematic review of observational studies and we performed a meta-analysis that evaluated the following risk factors: gender, smoking habits, hypertension, coronary artery disease and family history of AAA. Respect to a previous a meta-analysis we added the funnel plot to examine the effect sizes estimated from individual studies as measure of their precision; sensitivity analysis to check the stability of study findings and estimate how the overall effect size would be modified by removal of one study; cumulative analysis to evaluate the trend between studies in relation to publication year. Abdominal aortic aneurysm prevalence is higher in smokers and in males. On the other hand, while diabetes is a risk factor for many cardiovascular diseases, it is not a risk factor for AAA. In addition, it is important to underline that all countries, where AAA screening was set up, had high income level and the majority belong to Western Europe (United Kingdom, Sweden, Italy, Poland, Spain and Belgium). Abdominal aortic aneurysm screening is fundamental for public health. It could avoid deaths, ruptures, and emergency surgical interventions if abdominal aortic aneurysm was diagnosed early in the population target for screening.
Keywords: abdominal aortic aneurysm; meta-analysis; observational studies; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Prevalence and risk factors of sub-renal abdominal aortic aneurysm in an Algerian population aged over 60].J Med Vasc. 2018 Dec;43(6):361-368. doi: 10.1016/j.jdmv.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 26. J Med Vasc. 2018. PMID: 30522708 French.
-
Meta-Analysis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease.Am J Cardiol. 2015 Nov 1;116(9):1451-6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.07.074. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Am J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26347003
-
Risk factors for asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysm: systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based screening studies.Eur J Public Health. 2004 Dec;14(4):343-9. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/14.4.343. Eur J Public Health. 2004. PMID: 15542867 Review.
-
High prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysm in patients with three-vessel coronary artery disease.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2014 Mar;47(3):273-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2013.12.011. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 24456737
-
A systematic review of short-term vs long-term effectiveness of one-time abdominal aortic aneurysm screening in men with ultrasound.J Vasc Surg. 2018 Aug;68(2):612-623. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.03.411. J Vasc Surg. 2018. PMID: 30037679 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of differentially expressed ferroptosis-related genes in abdominal aortic aneurysm: Bioinformatics analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 29;9:991613. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.991613. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36247434 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs to reduce bleeding and transfusion in major open vascular or endovascular surgery: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 17;2(2):CD013649. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013649.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36800489 Free PMC article.
-
The burden of aortic aneurysm in China from 1990 to 2019: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.BMC Public Health. 2022 Apr 18;22(1):782. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13221-w. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35436885 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of Life for Patients Receiving Elective Interventions for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms.J Pers Med. 2022 May 31;12(6):910. doi: 10.3390/jpm12060910. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35743698 Free PMC article.
-
AAA Revisited: A Comprehensive Review of Risk Factors, Management, and Hallmarks of Pathogenesis.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 2;10(1):94. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010094. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35052774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moll F.L., Powell J.T., Fraedrich G., Verzini F., Haulon S., Waltham M., van Herwaarden J.A., Holt P.J., van Keulen J.W., Rantner B., et al. European Society for Vascular Surgery. Management of abdominal aortic aneurysms clinical practice guidelines of the European society for vascular surgery. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011;41(Suppl. 1):S1–S58. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2010.09.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Krumholz H.M., Keenan P.S., Brush J.E., Jr., Bufalino V.J., Chernew M.E., Epstein A.J., Heidenreich P.A., Ho V., Masoudi F.A., Matchar D.B., et al. Standards for measures used for public reporting of efficiency in health care: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Interdisciplinary Council on Quality of Care and Outcomes research and the American College of Cardiology Foundation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008;52:1518–1526. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.09.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Makrygiannis G., Labalue P., Erpicum M., Schlitz M., Seidel L., El Hachemi M., Gangolf M., Albert A., Defraigne J.O., Lindholt J.S., et al. Extending abnominal aortic aneurysm detection to older age older age groups: Preliminary results from the Liege screening programme. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2016;36:55–63. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2016.02.034. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation Global Burden of Disease Study. [(accessed on 30 June 2018)]; Available online: http//www.healthmetricsandevaluation.org/gbd/visualizations/gbd-cause-pa....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

