SIRT3 a Major Player in Attenuation of Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Reducing ROS via Its Downstream Mediators: SOD2, CYP-D, and HIF-1 α
- PMID: 30538800
- PMCID: PMC6258096
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/2976957
SIRT3 a Major Player in Attenuation of Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Reducing ROS via Its Downstream Mediators: SOD2, CYP-D, and HIF-1 α
Abstract
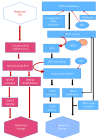
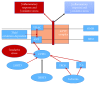
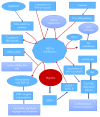
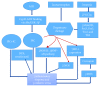
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a complex process where multiple cellular and molecular pathways are involved. Few of those molecular pathways are under the direct influence of SIRT3 and its downstream mediators. SIRT3 plays a major role in the mechanism of IRI, and its activation has been shown to attenuate the deleterious effect of ROS during IRI via SOD2-, CYP-D-, and HIF-1α-mediated pathways. The objective of this review is to analyze the current knowledge on SIRT3 and its downstream mediators: SOD2, CYP-D, and HIF-1α, and their role in IRI. For the references of this review article, we have searched the bibliographic databases of PubMed, Web of Science databases, MEDLINE, and EMBASE with the headings "SIRT3," "SOD2," "CYP-D," "HIF-1α," and "liver IRI." Priority was given to recent experimental articles that provide information on ROS modulation by these proteins. All the recent advancement demonstrates that activation of SIRT3 can suppress ROS production during IRI through various pathways and few of those are via SOD2, CYP-D, and HIF-1α. This effect can improve the quality of the remnant liver following resection as well as a transplanted liver. More research is warranted to disclose its role in IRI attenuation via this pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vosaroxin induces mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in cervical cancer HeLa cells: Involvement of AMPK/Sirt3/HIF-1 pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2018 Jun 25;290:57-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.05.011. Epub 2018 May 22. Chem Biol Interact. 2018. PMID: 29800573
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protects the liver against ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating the A2B adenosine receptor.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3737-3752. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1953217. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34288817 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin-mediated upregulation of Sirt3 attenuates sodium fluoride-induced hepatotoxicity by activating the MT1-PI3K/AKT-PGC-1α signaling pathway.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Nov;112:616-630. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.09.005. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28912098
-
Systematic review with meta-analysis: HIF-1α attenuates liver ischemia-reperfusion injury.Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2015 Jul;29(3):127-34. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 May 7. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2015. PMID: 26007634 Review.
-
The novel relationship between Sirt3 and autophagy in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.J Cell Physiol. 2019 May;234(5):5488-5495. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27329. Epub 2018 Nov 28. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30485429 Review.
Cited by
-
Focusing on Ischemic Reperfusion Injury in the New Era of Dynamic Machine Perfusion in Liver Transplantation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 17;25(2):1117. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021117. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maresin 1 Alleviates Diabetic Kidney Disease via LGR6-Mediated cAMP-SOD2-ROS Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 19;2022:7177889. doi: 10.1155/2022/7177889. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35498124 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acids profile and redox status in healthy infants.Pediatr Res. 2023 Jun;93(7):1856-1864. doi: 10.1038/s41390-022-02350-y. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 36272998
-
Anti-oxidative effect of zinc in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.Biophys Rep. 2021 Apr 30;7(2):142-151. doi: 10.52601/bpr.2021.200046. Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 37288149 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Polyphenols from Plum (Prunus salicina Lindl) on RAW264.7 Macrophages Induced by Monosodium Urate and Potential Mechanisms.Foods. 2023 Jan 5;12(2):254. doi: 10.3390/foods12020254. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36673346 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

