Mechanistic insights into the slow peptide bond formation with D-amino acids in the ribosomal active site
- PMID: 30520988
- PMCID: PMC6393236
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky1211
Mechanistic insights into the slow peptide bond formation with D-amino acids in the ribosomal active site
Abstract
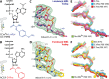
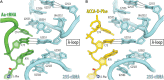
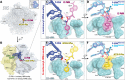
During protein synthesis, ribosomes discriminate chirality of amino acids and prevent incorporation of D-amino acids into nascent proteins by slowing down the rate of peptide bond formation. Despite this phenomenon being known for nearly forty years, no structures have ever been reported that would explain the poor reactivity of D-amino acids. Here we report a 3.7Å-resolution crystal structure of a bacterial ribosome in complex with a D-aminoacyl-tRNA analog bound to the A site. Although at this resolution we could not observe individual chemical groups, we could unambiguously define the positions of the D-amino acid side chain and the amino group based on chemical restraints. The structure reveals that similarly to L-amino acids, the D-amino acid binds the ribosome by inserting its side chain into the ribosomal A-site cleft. This binding mode does not allow optimal nucleophilic attack of the peptidyl-tRNA by the reactive α-amino group of a D-amino acid. Also, our structure suggests that the D-amino acid cannot participate in hydrogen-bonding with the P-site tRNA that is required for the efficient proton transfer during peptide bond formation. Overall, our work provides the first mechanistic insight into the ancient mechanism that helps living cells ensure the stereochemistry of protein synthesis.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The ribosome can discriminate the chirality of amino acids within its peptidyl-transferase center.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 12;112(19):6038-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424712112. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25918365 Free PMC article.
-
A proton wire to couple aminoacyl-tRNA accommodation and peptide-bond formation on the ribosome.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014 Sep;21(9):787-93. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2871. Epub 2014 Aug 17. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25132179 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of peptide bond synthesis on the ribosome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Aug 30;102(35):12395-400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504043102. Epub 2005 Aug 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16116099 Free PMC article.
-
The ribosome as a versatile catalyst: reactions at the peptidyl transferase center.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Aug;23(4):595-602. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.04.012. Epub 2013 May 24. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23711800 Review.
-
Ribosomal crystallography: peptide bond formation and its inhibition.Biopolymers. 2003 Sep;70(1):19-41. doi: 10.1002/bip.10412. Biopolymers. 2003. PMID: 12925991 Review.
Cited by
-
Chiral checkpoints during protein biosynthesis.J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 8;294(45):16535-16548. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV119.008166. Epub 2019 Oct 7. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31591268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fundamental Clock of Biological Aging: Convergence of Molecular, Neurodegenerative, Cognitive and Psychiatric Pathways: Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics Meet Psychology.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 28;23(1):285. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010285. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for in vitro engineering of the translation machinery.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Feb 20;48(3):1068-1083. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1011. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31777928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aminobenzoic Acid Derivatives Obstruct Induced Fit in the Catalytic Center of the Ribosome.ACS Cent Sci. 2023 May 30;9(6):1160-1169. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.3c00153. eCollection 2023 Jun 28. ACS Cent Sci. 2023. PMID: 37396857 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome-mediated biosynthesis of pyridazinone oligomers in vitro.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 24;13(1):6322. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33701-2. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36280685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Radkov A.D., Moe L.A.. Bacterial synthesis of D-amino acids. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014; 98:5363–5374. - PubMed
-
- Schieber A., Bruckner H., Ling J.R.. GC-MS analysis of diaminopimelic acid stereoisomers and amino acid enantiomers in rumen bacteria. Biomed. Chromatogr. 1999; 13:46–50. - PubMed
-
- Kirschner D.L., Green T.K.. Separation and sensitive detection of D-amino acids in biological matrices. J. Sep. Sci. 2009; 32:2305–2318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

