Traditional Chinese herbal medicine for vascular dementia
- PMID: 30520514
- PMCID: PMC6516869
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010284.pub2
Traditional Chinese herbal medicine for vascular dementia
Abstract
Background: Traditional Chinese herbal medicine (TCHM) is widely used for treating vascular dementia (VaD) in China. Recent studies of a number of TCHMs have demonstrated in vitro biological activity and therapeutic effects in animals, but the published clinical evidence has not been systematically appraised.
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of TCHMs listed in either the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (CP) or the Chinese National Essential Drug List (NEDL) that are used to treat VaD. A secondary aim was to identify promising TCHMs for further clinical research.
Search methods: We searched ALOIS, the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group's Specialised Register (on 14 March 2018) and also several Chinese biomedical databases: the Chinese Biological Medicine Database (January 1979 to May 2015), Wanfang database (January 1998 to May 2015), Chongqing VIP Information Co. Ltd or Weipu (January 1998 to May 2015) and the Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (January 1979 to May 2015).
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of TCHMs compared to placebo, to Western medicine (WM) or to routine therapy for VaD risk factors. Eligible participants were men and women aged 18 years and above, diagnosed with VaD by any of the following four criteria: (1) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) versions III, III-R, IV, IV-TR; (2) National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS-AIREN); (3) International Classification of Diseases 9 or 10; (4) the Hachinski or the Modified Hachinski Ischaemic Score. We required the use of an imaging technique to differentiate VaD from other dementias. We excluded (1) trials with participants diagnosed with mixed dementia or those that did not use an imaging technique to ascertain VaD; (2) trials of NEDL-listed Gingko biloba or Huperzine A as experimental interventions, to avoid duplication of existing Cochrane Reviews; (3) trials using acupuncture alone as the experimental intervention; (4) trials using another CP- or NEDL-listed TCHM (except for Huperzine A and Gingko which are popular in Western practice) as the control intervention; and (5) trials using purely non-pharmacological interventions as the control intervention unless explicitly described as 'routine therapy for VaD risk factors'.
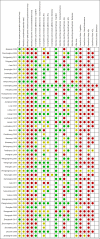
Data collection and analysis: We assessed the risks of bias using the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' tool and adapted the Outcome Reporting Bias in Trials (ORBIT) classification system for outcome reporting bias. We assessed TCHM effects on five clinically important outcomes: cognition, global performance, safety, activities of daily living and behaviour and summarised the effects using mean differences for continuous outcomes and risk ratios or risk differences for binary outcomes. We stratified the studies into those that estimated the TCHM versus 'no treatment' effect and those that estimated the TCHM versus the WM effect, with further stratification by the specific TCHM tested or by one of the four modes of action. We pooled using a random-effects model. Due to substantial clinical and design heterogeneity, we did not estimate an 'overall TCHM effect'.
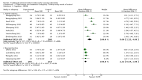
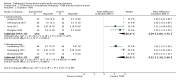
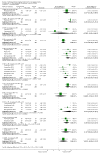
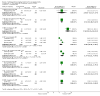
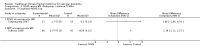
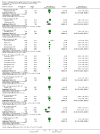
Main results: We only found studies (47 studies, 3581 participants) for 18 of the 29 eligible TCHMs as defined by our inclusion criteria. All were superiority trials conducted in China between 1997 and 2013, with most employing a two-arm parallel design with sample sizes ranging from 26 to 240 and a median treatment duration of 12 weeks (range: 2 to 24 weeks).We found that reporting and trial methodology were generally poor; in particular, there was a lack of information on randomisation, an absence of blinding of participants and outcome assessors and incomplete reporting of adverse events (AEs). None of the 30 trials published from 2007 onwards adopted the CONSORT recommendations for reporting RCTs of herbal interventions.We found seven TCHMs which each had potentially large benefits in studies estimating the TCHM versus 'no treatment' effect and in studies estimating the TCHM versus the WM effect. Two TCHMs (NaoXinTong and TongXinLuo) were common to both groups. Three of these TCHMs - Nao XinTong, NaoMaiTai and TongXinLuo - had the strongest evidence to justify further research. Two TCHMs (NaoMaiTai and TongXinLuo) had a 5% or more increased risk of AEs compared to the 'no Treatment' control, but the quality of this evidence was poor.
Authors' conclusions: We found moderate- to very low-quality evidence of benefit and harm of TCHMs for VaD. Methodological inadequacies need to be addressed by better conducted and reported trials. We identified NaoMaiTai, NaoXinTong and TongXinLuo as warranting special research priority.
Conflict of interest statement
Edwin SY Chan: None known Dianne T Bautista: None known Yanan Zhu: None known Yong You: None known Jian Ting Long: None known Wenyun Li: None known Christopher Chen: None known
Figures
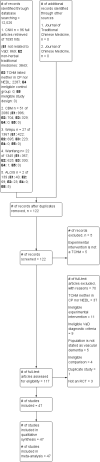

















Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010284
Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicines for unexplained recurrent miscarriage.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 14;2016(1):CD010568. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010568.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26760986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral traditional Chinese medication for adhesive small bowel obstruction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 May 16;(5):CD008836. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008836.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22592734 Review.
-
Acupuncture for depression.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 4;3(3):CD004046. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004046.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29502347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture for symptomatic gastroparesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 18;12(12):CD009676. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009676.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30560568 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological treatments for vascular dementia: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 22;15:1451032. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1451032. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39239652 Free PMC article.
-
General practitioners' role in safeguarding patients with dementia in their use of dietary supplements. A qualitative study.Scand J Prim Health Care. 2024 Mar;42(1):16-28. doi: 10.1080/02813432.2023.2283182. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2024. PMID: 37982720 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal Medicine for Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Limitations.Front Neurol. 2020 Sep 18;11:772. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00772. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33071922 Free PMC article.
-
Reporting Quality of Oral TCM Systematic Reviews Based on the PRISMA Harms Checklist from 2013 to 2020.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jan 24;2023:4612036. doi: 10.1155/2023/4612036. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 36733845 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Enriched Rehabilitation on Cognitive Function and Serum Glutamate Levels Post-stroke.Front Neurol. 2022 Mar 17;13:829090. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.829090. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35370905 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Baiweijie 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bai WJ, Tan JL, Liu YX. Clinical efficacy of DengZhanXiXin injection for 30 patients with vascular dementia [灯盏细辛注射液治疗血管性痴呆30例临床疗效观察]. Chinese Journal of Contemporary Neurology and Neurosurgery 2006;6(3):216‐7.
Chenhonghua 2008 {published data only}
-
- Chen HH, Wang JX, Guo MY. The efficacy of ShenFu injection in the treatment of elderly patients with vascular dementia on cognition function [参附注射液对老年血管性痴呆的治疗效果]. Medical Journal of Qilu 2008;23(5):413‐5.
Dengguiying 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Deng GY. A follow‐up study of patients with vascular dementia after treating with compound Salvia tablet for 24 weeks [复方丹参片治疗血管性痴呆后的随访研究]. Thesis for Master of Chinese Medicine from Beijing University of Chinese Medicine 2011.
Dingyang 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ding Y. Clinical observation on NaoMaiTai capsule for the treatment of vascular dementia [脑脉泰胶囊治疗老年血管性痴呆临床观察]. Chinese Journal of Information on TCM 2005;12(3):60.
Gaoli 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gao L. Clinical analysis on NaoXinTong combined with nimodipine for the treatment of 45 patients with vascular dementia [脑心通联合尼莫地平治疗血管性痴呆45 例临床分析]. China Modern Medicine 2012;19(25):92‐4.
Guoqingjun 2013 {published data only}
-
- Guo QJ, Shi Y. Therapeutic efficacy of NaoXinTong capsule on vascular dementia and effect of it on oxidative stress [脑心通胶囊治疗血管性痴呆的疗效及对患者氧化应激指标影响的临床观察]. China Pharmacy 2013;24(3):262‐4.
Guoweiling 2009 {published data only}
-
- Guo WL, Liu SJ, Lin WJ. Clinical efficacy observation on BuChang NaoXinTong capsule for the treatment of vascular dementia [步长脑心通胶囊治疗血管性痴呆疗效观察]. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine 2009;18(5):696,711.
Hanxingguo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Han XG, Sun KZ, Zhang RS, Wang Y. Clinical investigation of effect of NaoXinTong capsules on vascular dementia on 30 cases [脑心通胶囊治疗血管性痴呆30例临床观察]. Health Horizon · Medical Science Fascicule 2007;4:6‐7.
Hanzucheng 2010 {published data only}
-
- Han ZC, Wang C, Qiao SZ, Liu DL, Hui ZL, Tian LQ. Clinical study on NaoMaiTai capsule for the treatment of vascular dementia [脑脉泰胶囊治疗血管性痴呆的临床研究]. China Medicine 2010;5(8):715‐6.
-
- Han ZC, Wang C, Qiao SZ, Liu DL, Hui ZL, Tian LQ, Wang L. Therapeutic efficacy and safety profile of NaoMaiTai capsul on vascular dementia: results of a randomized,double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, multicenter clinical trial [[脑脉泰胶囊治疗血管性痴呆(气虚血瘀兼痰浊阻窍证)有效性、安全性的随机、双盲、平行对照、多中心临床研究分中心报告]]. World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies, International TCM Forum (Xi'an). 2010.
Haoweiping 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hao WP, Ye FH, Li LZ. Clinical observations of TongXinLuo capsule in the treatment of vascular dementia [通心络胶囊治疗血管性痴呆患者临床观察]. Journal of Clinical Psychosomatic Diseases 2006;12(6):424‐5.
Heyuping 2006 {published data only}
-
- He YP, Yang Y, Zhang WP, Lv HQ. Clinical efficacy observation on FuFangHaiShe capsule for the treatment of vascular dementia [复方海蛇胶囊治疗血管性痴呆的疗效观察]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2006;9(2):66‐7.
Huangchaoyun 2004 {published data only}
-
- Huang CY, Zhang JJ, Zhang XQ. Clinical study on NaoXinTong for the treatment of 50 cases of vascular dementia [脑心通治疗血管性痴呆50例临床研究]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio‐/Cerebrovascular Disease October 2014;2(10):610‐1.
Huanggenxian 2013 {published data only}
-
- Huang GX, Lu JB. NaoXinTong capsule combined with Donepezil in treatment of 32 cases of vascular dementia [脑心通胶囊联合多奈哌齐治疗血管性痴呆32例]. Zhejiang Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2013;48(10):775‐6.
Jiangyouyi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Jiang YY. BuChang NaoXinTong for the treatment of 30 cases of vascular dementia [步长脑心通治疗血管性痴呆30例]. Fujian Journal of TCM 2006;37(5):7,9.
Lican 2007 {published data only}
-
- Li C, Zhong BW, He MD. Clinical observation on XingNaoZaiZao capsule for the treatment of vascular dementia [醒脑再造胶囊治疗血管性痴呆临床观察]. Journal of TCM Univ. of Hunan 2007;27(5):61‐2.
Lifuhui 2011 {published data only}
-
- Li FH. Clinical research of fleabane injection combined with piracetam on vascular dementia [灯盏细辛注射液联合吡拉西坦治疗血管性痴呆临床研究]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2011;14(5):10‐3.
Lijingyi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Li JY, Huang JS, Zhang ZD, Lin J, Zhang WB, Zheng XM, et al. Clinical study on RuanMaiLing oral liquid in treatment of vascular dementia [软脉灵口服液治疗血管性痴呆的临床研究]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio‐/Cerebrovascular Disease 2009;7(9):1032‐4. - PubMed
-
- Zhang ZD. The clinical observation and the influence on SOD, VEGF, E2, T of RuanMaiLing koufuye on vascular dementia (Master's degree thesis) [软脉灵口服液治疗血管性痴呆的临床观察及其对SOD,VEGF,E2,T等的影响]. Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2007.
Liushujuan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Liu SJ, Liu JM. Clinical study of HuangQi with FuFangDanShen for 50 patients with vascular dementia [黄芪注射液加复方丹参注射液治疗早期血管性痴呆50 例临床研究]. Pharmacology & Clinic of TCM 2002;18(5):45‐6.
Liuyujin 1997 {published data only}
-
- Liu YJ, Tai XF, Huang FH, Xia X. Clinical observation of DengZhanHuaSu for 35 patients with vascular dementia [灯盏花素片治疗老年痴呆35 例临床观察]. Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 1997;24(6):362.
Luohaidong 2013 {published data only}
-
- Luo HD, Luo HL. The clinical effect observation of NaoMaiTai capsule combined with Donepezil Hydrochloride in treatment of vascular dementia [脑脉泰胶囊联合盐酸多奈哌齐治疗血管性痴呆的临床疗效观察]. Practical Journal of Cardiac Cerebral Pneumal and Vascular Disease 2013;21(4):72‐3.
Mayu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ma Y, Pan XQ, Ren YQ, Li YL, Zhang JW. Clinical effect of NaoMaiTai capsule on vascular dementia patients [脑脉泰胶囊治疗血管性痴呆41例]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae 2013;19(9):339‐41.
Piaozhiyong 2005 {published data only}
-
- Piao ZY, Piao MA. Clinical observation on ShenFu injection for the treatment of vascular dementia [参附注射液治疗血管性痴呆的临床观察]. Acta Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology 2005;33(6):47.
Qianrenyi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Qian RY, Song Q. Clinical observation on QingKaiLing injection for the treatment of 40 cases of vascular dementia [清开灵注射液治疗血管性痴呆40例临床观察]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Medical Science and Technology 1999;6(4):264‐5.
Shaopeng 2012 {published data only}
-
- Shao P, Zheng J, Shao P. Clinical efficacy observation on YinDanXinNaoTong capsule for the treatment of vascular dementia [银丹心脑通软胶囊治疗血管性痴呆的临床疗效观察]. For all Health 2012;6(11):21‐2.
Shiliangrong 2010 {published data only}
-
- Shi LR. Clinical observation on ChuanXiongQin combined with Piracetam for the treatment of vascular dementia [川芎嗪联合吡啦西坦治疗血管性痴呆的临床观察]. Practical Clinical Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine 2010;10(5):22‐3.
Tianjinzhou 2013 {published data only}
-
- Tian JZ, Shi J, Wei MQ, Qin RA, Chen YP, Wang YY. Efficacy and safety of FFDS tablets in people with mild‐to‐moderate vascular dementia: A 24‐week randomized, double‐blind, placebo, parallel‐controlled trial. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2013;4(9):P670‐1.
Wanghan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wang H. Clinical study of ShenFu injection for vascular dementia [参附注射液治疗血管性痴呆的疗效观察]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine 2004;13(21):2486‐7.
Wangjingming 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wang JM, Lv XY, Wang CH. Clinical study of Breviscapine treated the patients with vascular dementia [灯盏花素治疗血管性痴呆的临床研究]. Acta Academiae Medicinae Weifang 2007;29(6):428‐30.
Wanglinglin 2005 {published data only}
-
- Wang LL, Ying PZ, Wang XM. Clinical efficacy of TongXinLuo capsule in the treatment of vascular dementia [通心络胶囊治疗血管性痴呆患者的临床疗效观察]. Chinese Journal of Difficult and Complicated Cases 2005;4(5):260‐2.
Wangyihu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Wang YH. Donepezil combined with FuFangHaiShe for the treatment of 68 patients with vascular dementia [多奈哌齐联合复方海蛇胶囊治疗血管性痴呆68例]. Zhejiang Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine 2011;21(7):488‐9.
Wengyinghong 2011 {published data only}
-
- Weng YH. Clinical study of FuFangDanShen tablets on treatment of vascular dementia [复方丹参片治疗瘀血阻络型血管性痴呆的临床研究]. Thesis for Master of Internal Medicine in Chinese Medicine from Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine 2011.
Wuhongbin 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wu HB, Xu HN, He HG. Clinical observation of YangXueQingNao granula for 80 cases of vascular dementia [养血清脑颗粒治疗血管性痴呆病人临床观察]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio‐/Cerebrovascular Disease 2007;5(11):1069‐70.
Xujingqiang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Xu JQ, Lu X. The efficacy of TongXinLuo capsule for senile vascular dementia [通心络胶囊治疗老年血管性痴呆疗效观察]. World Health Digest Medical Periodical 2007;4(10):32‐3.
Xuke 2011 {published data only}
-
- Xu K, Wang KF. Impact of Donepezil Hydrochloride combined with YinDanXinNaoTong soft capsule on cognitive function in patients of vascular dementia [盐酸多奈哌齐联合银丹心脑通软胶囊对血管性痴呆患者认知功能的影响]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio‐/Cerebrovascular Disease 2011;9(10):1213‐5.
Yanyongxing 2007 {published data only}
-
- Yan YX, Liang LZ, Zhou ZL. Clinical study of combined treatment with compound Reinhartdt and sea cumber and Donepezil for vascular dementia [复方海蛇胶囊及盐酸多奈哌齐联合治疗血管性痴呆的临床研究]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine 2007;27(10):887‐90. - PubMed
Yaoxinsheng 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yao XS. Combined treatment of NaoXinTong with Nimodipine for vascular dementia [脑心通联合尼莫地平治疗血管性痴呆的临床研究]. Acta Medicinae Universitatis Scientiae et Technologiae Huazhong 2011;40(4):490‐2.
Yudecai 2008 {published data only}
-
- Yu DC, Zhang YY, Liu QL. Clinical study on NaoMaiTai capsule for the treatment of vascular dementia [脑脉泰胶囊治疗血管性痴呆的相关性研究]. China Clinical Practical Medicine 2008;2(7):58‐9.
Zhangjianping 2006 {published data only}
-
- Zhang JP, Hu YT, Zhang XY. The rehabilitation effect of NaoMaiTai capsule on cognitive dysfunction of vascular dementia patients [脑脉泰胶囊对血管性痴呆患者认知功能障碍的康复作用]. China Medical Herald 2006;3(29):141‐2.
Zhangjinsheng 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhang JS, Zheng LH. Clinical observation on ShenFu injection for the treatment of vascular dementia [参附注射液治疗血管性痴呆临床观察]. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine 2003;12(4):334‐5.
Zhangtao 2000 {published data only}
-
- Zhang T, Zhang XQ, Zhu RH. GeGenSu with Citicoline for 36 patients with vascular dementia [葛根素配合胞二磷胆碱治疗血管性痴呆36例]. Journal of Shandong University of TCM 2000;24(1):37‐8.
Zhangyoutai 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zhang YT. Effect of NaoXinTong capsule in treating vascular dementia [脑心通胶囊治疗血管性痴呆]. Journal of Liaoning University of TCM 2012;14(6):174‐5.
Zhangyujin 2002 {published data only}
-
- Zhang YJ, Zhang WZ. The efficacy of NaoAn capsule for vascular dementia [脑安胶囊治疗脑血管性痴呆疗效观察]. Journal of Practical TCM 2002;18(12):32.
Zhengtaolin 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zheng TL, Wang Z, Liu C, He W. Clinical study of BuChang NaoXinTong capsule for the treatment of 85 cases of vascular dementia [步长脑心通胶囊治疗血管性痴呆85例临床研究]. Shanxi Medical Journal 2014;43(2):205‐7.
Zhoulongshou 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zhou LS, Wang JX. The clinical observation of Donepezil Hydrochloride combined with NaoXinTong capsule in the treatment of vascular dementia after cerebral infarction [安理申联合脑心通胶囊治疗脑梗死后血管性痴呆临床观察]. Zhejiang Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine 2013;23(12):981‐2.
Zhouqiang 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhou Q, Zhuang YL. Clinical observations of 25 wei ZhenZhuWan in the treatment of vascular dementia [25味珍珠丸综合治疗血管性痴呆疗效观察]. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine 2003;10(10):55‐6.
Zhouwei 2009 {published data only}
-
- Zhou W, Wu YB, Xu XR. Clinical observation on NaoXinTong capsule for the treatment of vascular dementia [脑心通胶囊治疗血管性痴呆患者临床观察]. Shandong Medical Journal 2009;49(8):99‐100.
Zhufengmei 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhu FM, Sun GQ. The treatment of QingKaiLing injection for 46 patients with vascular dementia [清开灵注射液治疗血管性痴呆46例]. Clinical Focus 2003;18(23):1352‐3.
References to studies excluded from this review
Caijing 2003 {published data only}
-
- Cai J, Du J, Huang JS, Lin QC, Chen KY. Clinical observation of KangXin capsule on the influence of vascular dementia [康欣胶囊对血管性痴呆影响的临床观察]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology 2003;23(8):482‐4.
Caijing 2003‐2 {published data only}
-
- Cai J, Du J, Huang JS, Lin QC, Chen KY. Efficacy of Kangxin capsule on Homocysteine and β‐amyloid protein in vascular dementia patients [康欣胶囊对血管性痴呆患者血浆同型半胱氨酸及β‐淀粉样蛋白的影响]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine September 2003;23(9):664‐7. - PubMed
Caoxiongbin2015 {published data only}
-
- Cao XB, Gong L, Dai J, Kuang LH, Liu YF, Sun YP, et al. Clinical study of Oxiracetam combined with LeMai capsule for the dialectical treatment of vascular dementia [奥拉西坦联合乐脉颗粒辨证治疗血管性痴呆临床研究]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2015;18(3):60‐1.
Changdennis 2015 {unpublished data only}
-
- Chang D, Steiner G, Yeung A, Blasio F, Pipingas A, Scholey A, et al. Sailuotong (SLT), a standardised Chinese herbal medicine formula, enhances working memory in healthy adults: a pilot study. Conference: Integrative Medicine Research. 2015.
Chenrong 2006 {published data only}
-
- Chen R, Chen ZB, Wang T, Cai MH, Su QJ. Impact of GuHong injection on cognitive function in patients of vascular dementia [谷红注射液对血管性痴呆患者智能的影响]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Healthcare 2006;9(5):470‐1.
Dengpinrui 2011 {published data only}
-
- Deng PR, Su YJ. Clinical observation of ZhuYuTongMai capsule for the treatment of multi‐infarct dementia [逐瘀通脉胶囊治疗多梗死性痴呆的临床观察]. Guide of China Medicine 2011;9(7):131‐2.
Duguiyou 2003 {published data only}
-
- Du GY, Zhu XC, Zhao JJ, Wang J, Tian JZ, Liu XF, et al. Clinical observation of TianZhi granule for the treatment of senile vascular dementia [天智颗粒治疗老年血管性痴呆临床观察]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica 2003;28(1):73‐7. - PubMed
Fengjiong 2010 {published data only}
-
- Feng J, Zang M. Clinical study on LiuWeiDiHuangWan for the treatment of mild and moderate vascular cognitive impairment [六味地黄丸治疗轻中度血管性认知障碍的临床研究]. Clinical Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine April 2010;22(2):131‐2.
Gaoqi 2007 {published data only}
-
- Gao Q. Clinical study of ShuMaiYiNao capsule for the treatment of 58 cases of vascular dementia [疏脉益脑胶囊治疗血管性痴呆58例临床研究]. Journal of Gansu College of TCM 2007;24(5):14‐6.
Gongxuhai 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gong XH, Yang FM, He XH, Li XS, Zhang JH, Yu RL, et al. The efficacy of ShenQiFuZheng injection for vascular dementia [参芪扶正注射液治疗血管性痴呆的疗效观察]. Chinese Journal for Clinicians 2004;32(6):37‐8.
Guolei 2009 {published data only}
-
- Guo L, Feng HS. Efficacy of TianZhi Granule combined with Nunodipine in the treatment of vascular dementia [天智颗粒联合尼莫地平治疗老年血管性痴呆的临床疗效观察]. Medical Information August 2009;22(8):4‐6.
Guoqiang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Guo Q, Cao WZ, Zhao H, Zhu YX, Yang DD, Zhong S, et al. Effect of Sancaijiangtang on plasma nitric oxide and endothelin‐1 levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and vascular dementia: a single‐blind randomized controlled trial. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2015;35(4):375‐80. - PubMed
Guozhisheng 2009 {published data only}
-
- Guo ZS, Jin J, Jia JX. Clinical observation of DanHong injection for the treatment of 42 cases of vascular dementia [丹红注射液治疗气滞血瘀型血管性痴呆42例疗效观察]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2009;12(1):59‐61.
Hejinbo 2012 {published data only}
-
- He JB, Jin J. Clinical research of ShenXiong glucose injection treating vascular dementia and influence on AVP [参芎葡萄糖注射液治疗血管性痴呆的疗效及对AVP的影响]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae 2012;18(21):306‐10.
Hejun 2006 {published data only}
-
- He J, Cai YY, Wang HW, Zang DJ, Tan XM. Danshen injection with cerebrolysin for vascular dementia [丹参联合脑神经生长素对血管性痴呆病人智能状况的改善]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio‐/Cerebrovascular Disease February 2006;4(2):104‐5.
Hejun 2010 {published data only}
-
- He J, Zang DJ, Zhai J. DanHong injection and Vinpocetine injection improve intelligence of vascular dementia patients in clinic [丹红注射液联合长春西汀对于老年血管性痴呆患者智能康复的临床研究]. Journal of Chengdu University of TCM 2010;33(1):32‐4.
Houderen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hou DR, Chen K, Wang Y, Tian Y, Wan S, Tang JC, et al. Efficacy and mechanism of Butylphthalide for the treatment of vascular dementia [丁苯酞治疗血管性痴呆的疗效和作用机制]. Journal of Southern Medical University 2009;29(3):574‐5,8.
Huangliwu 2006 {published data only}
-
- Huang LW, Yuan JF, Wu Y, Mai LS, Pan HZ. Mongolian milkvetch root injection for improving the cognitive disorder of chronic cerebral ischaemic patients [黄芪注射液改善慢性脑缺血患者认知功能障碍的效应]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2006;10(43):34‐6.
Jiajianping 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Jia Jianping (study leader). Phase 2 clinical trial of SaiLuoTong capsule for vascular dementia:A 26‐week, multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial with a 26‐week open‐label extension. www.chictr.org/en/proj/show.aspx?proj=6441 (first received 7 May 2014). [Trial registration: ChiCTR‐TRC‐14004613]
Jiajianping 2016 {published data only}
-
- Jia JP, Wei CB, Liang JH, Zhou AH, Zuo XM, Song HQ, et al. The effects of DL‐3‐n‐butylphthalide in patients with vascular cognitive impairment without dementia caused by subcortical ischaemic small vessel disease: A multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Alzheimer's & Dementia 2016;12(2):89‐99. - PubMed
Jianghaipeng 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jiang HP, Kuang SX. Early efficacy observation of NaoTong capsule for the treatment of vascular dementia [脑通胶囊治疗血管性痴呆早期疗效观察]. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine 2010;19(10):1669‐70,78.
Liguolin2013 {published data only}
-
- Li GL. Clinical study on FuFangDanShen injection combined with HuangQi injection for the treatment of vascular dementia [复方丹参注射液与黄芪注射液联合治疗血管性痴呆临床研究]. Nei Mongol Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2013;32(19):33‐4.
Lihong2013 {published data only}
-
- Li H. Clinical study on FuFangDanShen injection combined with HuangQi injection for the treatment of vascular dementia [复方丹参注射液联合黄芪注射液治疗血管性痴呆临床研究]. China Health Industry 2013;10(5):67.
Lishilin 2011 {published data only}
-
- Li SL. Clinical observation of TianZhi granule for the treatment of 62 cases of vascular dementia [天智颗粒治疗血管性痴呆62例临床观察]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2011;14(13):35‐7.
Liuguirong 2009 {published data only}
-
- Liu GR. Efficacy observation on TianZhi granule for the treatment of mild and moderate vascular dementia [天智颗粒治疗轻度及中度血管性痴呆疗效观察]. Chinese Community Doctors 2009;19:119.
Liuq 2016 {published data only}
Liuwei 2009 {published data only}
-
- Liu W. Clinical observation of Butylphthalide for the treatment of vascular dementia [丁苯酞治疗血管性痴呆临床观察]. Clinical Focus 2009;24(17):1533‐4.
Liuxifei 2007 {published data only}
-
- Liu XF, Du J, Cai J, Liu XF, Wang LL, Xu GL, et al. Clinical observation of KangXin capsule for the treatment of vascular dementia [康欣胶囊治疗老年肾虚血瘀型血管性痴呆的临床观察]. Journal of Nanjing TCM University 2007;23(3):148‐51.
Liweiwei 2013 {published data only}
-
- Li WW, Wang MC, Yu PP, Wang Y. Observation on clinical effects of Oxiracetam capsule and SanQiTongShu capsule in treating vascular dementia [奥拉西坦联合三七通舒治疗血管性痴呆的临床疗效观察]. Western Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2013;26(2):81‐3.
Liying 2009 {published data only}
-
- Li Y, Du XH, Zhao XW. Clinical efficacy of ShuXueTong injection for vascular dementia [疏血通注射液治疗血管性痴呆的临床观察]. China Pharmacy 2009;20(33):2620‐1.
Liyuehua 2011 {published data only}
-
- Li YH. Clinical observation of PeiYuanTongNao capsule for the treatment of vascular dementia [培元通脑胶囊治疗老年血管性痴呆的临床观察]. Seek Medical And Ask The Medicine 2011;9(6):143,110.
Majingmei 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ma JM. The efficacy of ShenMai injection for patients with vascular dementia [参麦注射液治疗血管性痴呆的疗效观察]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2006;9(1):89.
NCT02641886 {unpublished data only}
-
- Zhang YL. The study of Jian Pi Yi Shen Hua Tan granules in cognitive impairment after acute cerebral infarction. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02641886 (first received 30 December 2015). [NCT02641886]
NCT02693795 {unpublished data only}
-
- Mao S. Baduanjin exercise prevents post‐myocardial infarction left ventricular remodeling (BE‐PREMIER Trial). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02693795 (first received 29 February 2016). [NCT02693795] - PubMed
NCT02728180 {unpublished data only}
-
- Gao Y. Xingnaojing for Moderate‐to‐severe Acute Ischaemic Stroke (XMAS). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02728180 (first received 5 April 2016). [NCT02728180]
NCT02802072 {unpublished data only}
-
- Meng Ji. Enterprise stent implantation in the treatment of carotid artery stenosis with ischaemic stroke. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02802072 (first received 16 June 2016). [NCT02802072]
Qinfusheng 2009 {published data only}
-
- Qin FS, Liu XM. Clinical observation on DanHong injection for the treatment of 68 cases of vascular dementia [丹红注射液治疗血管性痴呆68例临床观察]. Chinese Journal of Modern Drug Application 2009;3(11):141‐2.
Shidehai 2011 {published data only}
-
- Shi DH, Zhang HT, Zhao MY, He L, Sun Q, Tan JW, et al. Clinical research of DanHong injection combined with piracetam on vascular dementia [丹红注射液联合吡拉西坦治疗血管性痴呆临床研究]. Clinical Journal of Medical Officers 2011;39(1):43‐5.
Shiguangxia 2014 {published data only}
-
- Shi GX, Liu CZ, Guan W, Wang ZK, Wang L, Xiao C. Effects of acupuncture on Chinese medicine syndromes of vascular dementia. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 2014;20(9):661‐6. - PubMed
Shihaiting 2011 {published data only}
-
- Shi HT. Efficacy observation on TianZhi granule for the treatment of vascular dementia [天智颗粒治疗血管性痴呆疗效观察]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio‐/Cerebrovascular Disease 2011;9(8):955‐6.
Sunmeibo 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sun MB, Chen XZ. Effect of tetramethylpyrazine in improving cognitive function and content of arginine vasopressin in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with vascular dementia [川芎嗪对血管性痴呆患者认知功能及血浆和脑脊液中精氨酸加压素含量的提高效应]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2005;9(24):194‐6.
Taogenyu 2004 {published data only}
-
- Tao GY. Clinical research on treatment of vascular dementia with Brain‐refreshing Pill [醒脑丸治疗血管性痴呆临床研究]. Journal of Shaanxi College of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2004;27(1):5‐7.
Wangdongming 2003 {published data only}
-
- Wang DM, Li AM, Yuan YG, Wang L, Yi RB, Lin YJ, et al. Study of effect of treatment of vascular dementia on event related potential by Tzepao Sanpien pills [三鞭丸治疗血管性痴呆对事件相关电位影响的研究]. Journal of Chinese Clinical Medicine 2003;4(7):30‐1.
Wangguang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Wang G. Clinical study of YangXueQingNao granule and needing in treating vascular dementia [养血清脑颗粒配合针刺治疗血管性痴呆的临床研究]. Hebei Medicine 2006;12(2):131‐3.
Wanglixin 1999 {published data only}
-
- Wang LX, Liu GH, Yan RP, Zheng XL, Li LH. The treatment of XingNaoJing injection for 39 patients with vascular dementia [醒脑静治疗血管性痴呆39例临床分析]. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine 1999;6(5):54‐5.
Wanglixin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Wang LX, Li LH, Liu GH, Ma ZJ, Ma YQ. Effect of XingNaoJing injection and hyperbaric oxygen on intelligence and apolipoprotein in treating vascular dementia [醒脑静注射液联合高压氧对血管性痴呆患者智能和载脂蛋白的影响]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine in Intensive and Critical Care 2000;7(3):158‐60.
Wangsongzhen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wang SZ, Zhang YJ. XingNaoJing injection for 31 patients with dementia [醒脑静注射液治疗痴呆症31 例]. TCM Research 2002;15(6):32.
Wangyankuo 2010 {published data only}
-
- Wang YK, Sun LP, Zhang M. Butylphthalide soft capsules joint donepezil treatment of vascular dementia in clinical efficacy [丁苯酞软胶囊联合多奈哌齐治疗血管性痴呆临床疗效观察]. Journal of Brain and Nervous Diseases 2010;18(5):387‐90.
Wanjifeng 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wan JF, Lu Y, Xu YY, Liu CC, Chang SJ, Zhou WD. Clinical effect of LeMai granule combined with Oxiracetam on treatment of vascular dementia [乐脉颗粒联合奥拉西坦治疗血管性痴呆疗效观察]. Chinese Journal of General Practice 2012;10(1):31,82.
Weichunhua 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wei CH. Clinical observation on TianZhi granule for the treatment of vascular dementia [天智颗粒治疗血管性痴呆的临床观察]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2013;16(16):83‐4.
Wutianchen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wu TC, Xu RQ. Clinical observation on HuanShaoDan for the treatment of 32 patients with vascular dementia [还少丹加减治疗血管性痴呆32例临床观察]. Hunan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2012;28(5):43‐4.
Xieyongyong 1996 {published data only}
-
- Xie YY. FuFangDanShen injection for the treatment of 15 cases of vascular dementia [复方丹参注射液治疗血管性痴呆15例]. Zhejiang Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 1997;4:156.
Xudongmei 2009 {published data only}
-
- Xu DM, Zhang YL, Ma XQ. Clinical efficacy observation on YangXueQingNao granule for the treatment of 60 cases of vascular dementia [养血清脑颗粒治疗血管性痴呆60例疗效观察]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2009;12(19):64.
Xuhaibo 2007 {published data only}
-
- Xu HB, Chen H. Clinical observation of TongXinLuo capsule for vascular dementia [通心络胶囊联合氢麦角碱治疗血管性痴呆效果观察]. Medical Journal of Communications 2007;21(4):390‐1.
Yangxiaoli 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yang XL. Butylphthalide soft capsules and nimodipine treatment of vascular dementia after stroke effect assessment (Master Degree Thesis) [丁苯酞软胶囊与尼莫地平治疗卒中后血管性痴呆的疗效评价]. HeBei Medical University 2008.
Yinjunxiang 2000 {published data only}
-
- Yin JX, Tian JZ, Yang CZ, Liu H. A single‐blind controlled study of Jian Nao An( JNA) treatment of the syndrome of deficiency of the kidney and phlegm turbidness of vascular dementia [健脑安治疗血管性痴呆肾虚痰浊证的单盲对照研究]. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicine 2000;2(4):212‐5.
Yufangchen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Yu FC, Yu MQ, Song JC. The efficacy of HuaTuoZaiZao pill for age‐related dementia [华佗再造丸治疗老年期痴呆205例疗效观察]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials 1999;22(5):269‐70.
Zhangchunyan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Zhang CY, Li YP, Li MX, Wang RL. Efficacy observation on TianMaSu for the treatment of vascular dementia [天麻素治疗血管性痴呆疗效观察]. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine 2009;18(8):1220‐1.
Zhangdaodong 1999 {published data only}
-
- Zhang DD, Yang YQ. MaiLuoNing injection for 64 patients with vascular dementia [脉络宁注射液治疗脑血管性痴呆64例]. Journal of PLA Junior College of Medicine 1999;27(2):110‐2.
Zhangfeng 2011 {published data only}
-
- Zhang F, He L, Zhu C, Zhu QF. HuanShaoDan for the treatment of 60 cases of vascular dementia [还少丹加减治疗血管性痴呆60例]. GuangMing Chinese Medicine 2011;26(8):1591‐2.
Zhangxuehong 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zhang XH. Efficacy observation on Butylphthalide soft capsule combined with Donepezil for the treatment of vascular dementia [丁苯酞软胶囊联合多奈哌齐治疗血管性痴呆疗效观察]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2013;16(3):70‐1.
Zhangyunling 2016 {unpublished data only}
-
- Zhang YL. An fMRI Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Jianpi Yishen Huatan Granules for Cognitive Impairment After Acute Cerebral Infarction. clinicaltrials.gov 2016; Vol. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02752867.
Zhangzhipeng2014 {published data only}
-
- Zhang ZP, Gao JF, Dong SX, Zhang RK, Wang YL, Li HS. Clinical observation on YangXueQingNao granule for the treatment of vascular dementia [养血清脑颗粒治疗血管性痴呆临床观察]. Clinical Journal of Clinical Rational Drug Use 2014;7(11A):48‐9.
Zhaoyan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Zhao Y. Clinical observation of DanHong injection treatment of vascular dementia [丹红注射液治疗血管性痴呆的临床观察]. Journal of China Traditional Chinese Medicine Information 2010;2(10):113.
Zhaoyiming 1994 {published data only}
-
- Zhao YM, Wu XS. Observation of MaiLuoNing for 36 patients with vascular dementia [脉络宁治疗血管性痴呆36例疗效观察]. Journal of Zheijiang College of TCM 1994;18(6):19‐20.
Zhaoyun 2010 {published data only}
-
- Zhao Y, Li ZX. HuanShaoDan for the treatment of 80 cases of vascular dementia [还少丹治疗肝肾亏虚型血管性痴呆80例]. Henan Traditional Chinese Medicine 2010;30(4):380‐1.
Zhuaihua 2005 {published data only}
-
- Zhu AH, Tian JZ, Zhong J, Shi J. A clinical study on a randomized, double‐blind control of Tianzhi granules in treatment of the senile vascular dementia [天智颗粒治疗老年人血管性痴呆的随机双盲临床对照研究]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology 2005;12:1435‐8.
Zhuanghuikui 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zhuang HK, Chi YL, Gao HF. Clinical study of HuaZhuoQingNao decoction for vascular dementia [化浊清脑合剂治疗血管性痴呆临床研究]. Journal of Shandong University of TCM 2007;31(1):28‐30.
Zhuning 2011 {published data only}
-
- Zhu N, Zhu HS, Liu HY. Effect of Tianzhi granule combined oxiracetam on mild or moderate vascular dementia [天智颗粒联合奥拉西坦治疗轻中度血管性痴呆临床观察]. Chinese Journal of Practical Nervous Diseases 2011;14(17):29‐31.
References to ongoing studies
NCT01761227 {unpublished data only}
-
- Jinzhou Tian. Efficacy and safety of Fufangdanshen tablets in mild to moderate vascular dementia. ClinicalTrials.gov/show/ NCT01761227 (first received 4 January 2013). [NCT01761227 ]
Additional references
Alagiakrishnan 2018
-
- Alagiakrishnan K, Masaki K. Vascular Dementia Clinical Presentation. emedicine.medscape.com/article/292105‐clinical#a0216 (accessed 25 October 2018).
APA 1980
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐III). 3rd Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1980.
APA 1987
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐III). 3rd Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1987.
APA 1994
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM‐IV). 4th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1994.
Balshem 2011
-
- Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence.. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):401‐6. - PubMed
Bao 2005
-
- Bao HY, Zhang J, Yeo SJ, Myung CS, Kim HM, Kim JM, et al. Memory‐enhancing and neuroprotective effects of selected ginsenosides. Archives of Pharmacal Research 2005;28(3):335‐42. - PubMed
Birks 2009
Chen 2006
-
- Chen F, Eckman EA, Eckman CB. Reductions in levels of the Alzheimer's amyloid beta peptide after oral administration of ginsenosides. Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 2006;20(8):1269‐71. - PubMed
ChP 2005
-
- National Pharmacopeia Committee. Chinese Pharmacopeia. Pharmacopeia of the People's Republic of China. Chemical Industry Press, 2005.
ChP 2010
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China 2010. 9th Edition. Vol. I, II, III, Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, August 2011.
DeFeudis 1991
-
- DeFeudis FV. Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761): pharmacological activities and clinical applications. Editions Scientifiques. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. Paris: Elsevier, 1991:78‐84.
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177‐88. - PubMed
Dwan 2010
Erkinjuntti 2009
-
- Erkinjuntti T, Gauthier S. The concept of vascular cognitive impairment. Front Neurology and Neurosciences 2009;24:79‐85. - PubMed
Flower 2012
Frierman 2006
-
- Fierman D. Understanding and Applying Differential Diagnosis (ZhenDuan): The Heart of TCM Clinical Methodology. www.acupuncturetoday.com/mpacms/at/article.php?id=31280&no_paginate=true... (accessed 23 Apr 2018).
Gagnier 2006
-
- Gagnier J, Boon H, Rochon P, Moher D, Barnes J, Bombardier C, CONSORT group. Recommendations for the reporting of randomized controlled trials of herbal interventions: explanation and elaboration. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(11):1134‐49. - PubMed
Gong 2002
-
- Gong X, Sucher NJ. Stroke therapy in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM): prospects for drug discovery and development. Phytomedicine 2002;9(5):478‐84. - PubMed
GRADEproGDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- Evidence Prime. GRADEpro GDT: GRADEpro GUideline Development Tool [Software]. McMaster University, 2015.
Hachinski 1975
-
- Hachinski VC, Iliff LD, Zilhka E, Du Boulay GH, McAllister VL, Marshall J, et al. Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Archives of Neurology 1975;32(9):632‐7. - PubMed
Hao 2009
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Howard 2011
-
- Howard R, Phillips P, Johnson T. Determining the minimum clinically important differences for outcomes in the DOMINO trial. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2011;26(8):812‐7. - PubMed
Howes 2009
-
- Howes MJ, Houghton P. Traditional medicine for memory enhancement. In: Ramawat KG editor(s). Herbal Drugs: Ethnomedicine to Modern Medicine. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer‐Verlag, 2009:239‐91.
Huang 2004
-
- Huang WM. 中国老年病秘方全书. 1st Edition. Scientific and Technical Documentation Press, 2004.
Huang 2007
-
- Huang JL, Fu ST, Jiang YY, Cao YB, Guo ML, Wang Y, et al. Protective effects of Nicotiflorin on reducing memory of dysfunction, energy metabolism failure and oxidative stress in multi‐infarct dementia model rats. Pharmacology, Biochemestry and Behaviour 2007;86(4):741‐8. - PubMed
Jia 2001
-
- Jia W, Zhang LX. Challenges and opportunities in the Chinese herbal drug industry. In: Zhang L, Demain AL editor(s). Natural Products: Drug Discovery and Therapeutic Medicine. Totowa, New Jersey: Humana Press Inc, 2001:229‐50.
Kalaria 2008
Koltringer 1989
-
- Koltringer P, Eber O, Klima G, Rothlauer W, Wakonig P, Langsteger W, et al. Microcirculation in parenteral Ginkgo biloba extract therapy [Die mikrozirkulation unter parenteraler Ginkgo‐biloba‐extrakt‐therapie]. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 1989;101(6):198‐200. - PubMed
Lee 2003
-
- Lee B, Choi Y, Kim H, Kim SY, Hahm DH, Lee HJ, et al. Protective effects of methanol extract of Acori graminei rhizome and Uncariae Ramulus et Uncus on ischaemia‐induced neuronal death and cognitive impairments in the rat. Life Sciences 2003;74(4):435‐50. - PubMed
Lim 1997
-
- Lim JH, Wen TC, Matsuda S, Tanaka J, Maeda N, Peng H, et al. Protection of ischaemic hippocampal neurons by ginsenoside Rbl, a main ingredient of ginseng root. Neuroscience Research 1997;28(3):191‐200. - PubMed
Lu 2001
-
- Lu MC. Danggui shaoyao san improves colchicine‐induced learning acquisition impairment in rats. Acta Pharamcologica Sinica 2001;22(12):1149‐53. - PubMed
Man 2012
McVeigh 2006
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman DG. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;134(8):657‐62. [PUBMED: 11154618] - PubMed
NEDL 2009
-
- State Food, Drug Administration. National Essential Drug List of the People's Republic of China. app1.sfda.gov.cn/datasearch/face3/base.jsp (accessed 7 Nov 2012).
NICE‐SCIE 2006
-
- National Institute for Clinical Excellence, Social Care Institute for Excellence. Dementia ‐ Supporting people with dementia and their carers in health and social care. NICE Clinical Guidelines, No. 42 (www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG42) (accessed 29 Oct 2012).
Nomura 1997
-
- Nomura Y, Arima T, Namba T, Hattori M, Kadota S. Ameliorating effects of dan‐shen and its major ingredient calcium/magnesium lithospermate B on cognitive deficiencies in senescence‐accelerated mouse. Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi 1997;110:142‐7. - PubMed
O’Brien 2015
Pan 2010
Pincemail 1989
-
- Pincemail J, Dupuis M, Nasr C, Hans P, Haag‐Berrurier M, Anton R, et al. Superoxide anion scavenging effect and superoxide dismutase activity of Ginkgo biloba extract. Experientia 1989;45(8):708‐12. [PUBMED: 2547645] - PubMed
Prabhakar 2011
Qaseem 2008
-
- Qaseem A, Snow V, Cross JT Jr. Current pharmacologic treatment of dementia: a clinical practice guideline from the American Academy of Family Physicians. Annals of Internal Medicine 2008;148(5):370‐8. - PubMed
Qin 2013
Revman 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008.
Roman 1993
-
- Roman GC, Tatemichi TK, Erkinjuntti T, Cummings JL, Masdeu JC, Garcia JH, et al. Vascular dementia: diagnostic criteria for research studies: Report of the NINDS‐AIREN International Workshop. Neurology 1993;43(2):250‐60. - PubMed
Roman 2004
-
- Roman, GC. Facts, myths and controversies in vascular dementia. Journal of Neurological Sciences 2004;226(1‐2):49‐52. - PubMed
Rosen 1980
-
- Rosen WG, Terry RD, Fuld PA, Katzman R, Peck A. Pathological verification of Ischaemic Score in differentiation of dementias. Annals of Neurology 1980;7(5):486‐8. - PubMed
Wang 2006
-
- Wang R, Yan H, Tang XC. Progress in huperzine A, a natural cholinesterase inhibitor from Chinese herbal medicine. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2006;27(1):1‐26. - PubMed
Wang 2017
-
- Wang TF, Dong J. What is “zheng” in traditional Chinese medicine?. Journal of Traditional Medical Sciences 2017;4:14‐15.
WHO 1992
-
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Diseases (ICD‐10). Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders. www.who.int/classifications/icd/en/bluebook.pdf (accessed 29 Oct 2012).
WHO 2000
-
- World Health Organization. General Guidelines for Methodologies on Research and Evaluation of Traditional Medicine. apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/66783/WHO_EDM_TRM_2000.1.pdf;js... (accessed 25 October 2018).
Wu 2007
Wu 2009
Xu 2018
Zeng 2015
-
- Zeng LF, Zou YP, Kong LS, Wang NS, Wang Q, Wang L, et al. Can Chinese herbal medicine adjunctive therapy improve outcomes of senile vascular dementia? Systematic review with meta‐analysis of clinical trials. Phytotherapy Research 2015;29(12):1843‐57. - PubMed
Zhang 2006
-
- Zhang HY, Tang XC. Neuroprotective effects of huperzine A: new therapeutic targets for neurodegenerative disease. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 2006;27(12):619‐25. - PubMed
Zhang 2008a
Zhang 2008b
-
- Zhang H, Han T, Zhang L, Yu CH, Wan DG, Rahman K, et al. Effects of tenuifolin extracted from radix polygalae on learning and memory: a behavioral and biochemical study on aged and amnesic mice. Phytomedicine 2008;15(8):587‐94. - PubMed
Zhong‐zi 2010
-
- Zhong‐zhi Q, Dan Y, Yan‐ze L, Yong P. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2010 Edition): a milestone in development of China’s healthcare. Chinese Herbal Medicines 2010;2(2):157‐60.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

