The Chinese herbal formula Fuzheng Quxie Decoction attenuates cognitive impairment and protects cerebrovascular function in SAMP8 mice
- PMID: 30519025
- PMCID: PMC6233692
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S175484
The Chinese herbal formula Fuzheng Quxie Decoction attenuates cognitive impairment and protects cerebrovascular function in SAMP8 mice
Abstract
Purpose: This study was designed to explore the underlying mechanism of action for a Fuzheng Quxie Decoction (FQD) in Alzheimer's disease (AD), to validate its neuroprotective effects, and to provide experimental support for its predicted mechanism of action.
Methods: An integrative approach to network pharmacology was performed to predict the mechanism of action for treatment of AD with FQD. The predicted mechanism was validated in SAMP8 mice.
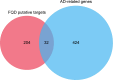
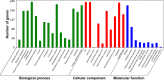
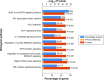
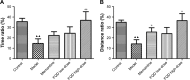
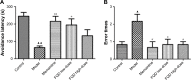
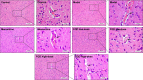
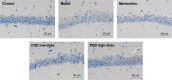
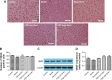
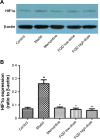
Results: With predicted putative FQD targets and a collection of AD-related genes, 245 possible regulatory targets of FQD were identified for the treatment of AD. Pathway-enrichment analysis for the possible regulatory targets indicated that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGF-receptor signaling were pivotal in the treatment of AD with FQD. In vivo experiments confirmed the neuroprotective effect and the predicted mechanism of action for treatment of AD with FQD.
Conclusion: This study contributes to an understanding of the neuroprotective effect of FQD and its potential mechanism of action for the treatment of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Fuzheng Quxie Decoction; hypoxia-induced factor 1α; microcerebrovascular; network pharmacology; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fuzheng Quxie Decoction Ameliorates Learning and Memory Impairment in SAMP8 Mice by Decreasing Tau Hyperphosphorylation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:5934254. doi: 10.1155/2017/5934254. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 29422936 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Study on the Treatment of Complex Anal Fistula by Phased Chinese Herbal Sitz Bath Based on "Fuzheng Quxie" Theory.Altern Ther Health Med. 2024 Feb;30(2):50-55. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024. PMID: 37856804 Clinical Trial.
-
[Mechanism of Danggui Sini Decoction in treatment of primary dysmenorrhea based on network pharmacology and molecular docking].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Feb;46(4):855-864. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20201104.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33645090 Chinese.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
-
LW-AFC, a new formula from the traditional Chinese medicine Liuwei Dihuang decoction, as a promising therapy for Alzheimer's disease: Pharmacological effects and mechanisms.Adv Pharmacol. 2020;87:159-177. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2019.10.005. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Adv Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32089232 Review.
Cited by
-
Medicine-Food Herbs against Alzheimer's Disease: A Review of Their Traditional Functional Features, Substance Basis, Clinical Practices and Mechanisms of Action.Molecules. 2022 Jan 28;27(3):901. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030901. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying the Mechanisms and Molecular Targets of Yizhiqingxin Formula on Alzheimer's Disease: Coupling Network Pharmacology with GEO Database.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2020 Oct 15;13:487-502. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S269726. eCollection 2020. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 33116763 Free PMC article.
-
Yizhiqingxin Formula Alleviates Cognitive Deficits and Enhances Autophagy via mTOR Signaling Pathway Modulation in Early Onset Alzheimer's Disease Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 17;10:1041. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01041. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31607908 Free PMC article.
-
Yizhi Qingxin Formula Extract Ameliorates Cognitive Decline in Aged Rats via the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor/Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase B Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 30;11:510. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00510. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. Retraction in: Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 09;15:1451575. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1451575 PMID: 32425777 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Network Pharmacology Analysis of Liquid-Cultured Armillaria ostoyae Mycelial Metabolites and Their Molecular Mechanism of Action against Gastric Cancer.Molecules. 2024 Apr 8;29(7):1668. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071668. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buckner RL. Memory and Executive Function in Aging and AD. Neuron. 2004;44(1):195–208. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2017;13(4):325–373.
-
- Savelieff MG, Nam G, Kang J, Lee HJ, Lee M, Lim MH. Development of Multifunctional Molecules as Potential Therapeutic Candidates for Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis in the Last Decade. Chem Rev. 2018 Aug 10; Epub. - PubMed
-
- Makin S. The amyloid hypothesis on trial. Nature. 2018;559(7715):S4–S7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

