Effects of B-cell directed therapy on the preclinical stage of rheumatoid arthritis: the PRAIRI study
- PMID: 30504445
- PMCID: PMC6352407
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212763
Effects of B-cell directed therapy on the preclinical stage of rheumatoid arthritis: the PRAIRI study
Abstract
Objectives: We explored the effects of B-cell directed therapy in subjects at risk of developing autoantibodypositive rheumatoid arthritis (RA), who never experienced inflammatory arthritis before, and explored biomarkers predictive of arthritis development.
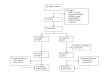
Methods: Individuals positive for both anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor but without arthritis were included in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to receive a single infusion of 1000 mg rituximab or placebo.
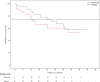
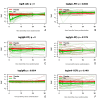
Results: Eighty-one individuals received treatment and were followed up for a mean of 29.0 (0-54) months, during which 30/81 (37%) individuals developed arthritis. The observed risk of developing arthritis in the placebo-treated group was 40%, which was decreased by 55% (HR 0.45, 95% CI 0.154 to 1.322) in the rituximab-treated group at 12 months. Rituximab treatment caused a delay in arthritis development of 12 months compared with placebo treatment at the point when 25% of the subjects had developed arthritis (p<0.0001). Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and the presence of anti-citrullinated α-enolase peptide 1 at baseline were significant predictors of arthritis development.
Conclusions: A single infusion of 1000 mg rituximab significantly delays the development of arthritis in subjects at risk of developing RA, providing evidence for the pathogenetic role of B cells in the earliest, prearthritis stage of autoantibody positive RA.
Keywords: cure; pre-rheumatoid arthritis; prevention; rheumatoid arthritis; rituximab.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: PPT is a former employee and DMG a current employee of GlaxoSmithKline, UK. GlaxoSmithKline was not involved in the design and/or execution of the study. NdV reports grants from AbbVie, Janssen Biologics, Ergomed Clinical Research, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Roche, as well as personal fees from MSD, UCB, Janssen, non-financial support from Roche, personal fees and non-financial support from Pfizer, all outside the submitted work. In addition, NdV has a patent method for determining the risk of developing arthritis pending. MS reports a research grant from AstraZeneca (received in August 2015). AstraZeneca was not involved in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibodies to citrullinated α-enolase peptide 1 and clinical and radiological outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Jun;70(6):1095-8. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.138909. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. PMID: 21367760
-
B cell depletion with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Multiplex bead array reveals the kinetics of IgG and IgA antibodies to citrullinated antigens.J Autoimmun. 2016 Jun;70:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.03.010. Epub 2016 Apr 4. J Autoimmun. 2016. PMID: 27055777
-
Inflammation and autoantibody markers identify rheumatoid arthritis patients with enhanced clinical benefit following rituximab treatment.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Dec;63(12):3681-91. doi: 10.1002/art.30596. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 22127691 Clinical Trial.
-
[B cell therapy of rheumatoid arthritis with rituximab. Practice-relevant aspects for the routine].Z Rheumatol. 2015 Apr;74(3):250-7. doi: 10.1007/s00393-014-1563-0. Z Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25854158 Review. German.
-
Preclinical rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis prevention.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2020 May;32(3):289-296. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000708. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32205569 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expansion of HLA-DR Positive Peripheral Helper T and Naive B Cells in Anticitrullinated Protein Antibody-Positive Individuals At Risk for Rheumatoid Arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024 Jul;76(7):1023-1035. doi: 10.1002/art.42839. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38412870
-
Can the General Public Be a Proxy for an "At-Risk" Group in a Patient Preference Study? A Disease Prevention Example in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Med Decis Making. 2024 Feb;44(2):189-202. doi: 10.1177/0272989X231218265. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Med Decis Making. 2024. PMID: 38240281 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Autoimmune Disease: a Comparison of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 30;13:899372. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.899372. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Population-based estimates of humoral autoimmunity from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 1960-2014.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 13;15(1):e0226516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226516. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31929535 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound subclinical synovitis in anti-CCP-positive at-risk individuals with musculoskeletal symptoms: an important and predictable stage in the rheumatoid arthritis continuum.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022 Aug 3;61(8):3192-3200. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab862. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022. PMID: 34849610 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
